Adaptive decoupling method for modal-aliasing problem in empirical mode decomposition
A technique for empirical mode decomposition and mode aliasing, applied in the field of signal processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
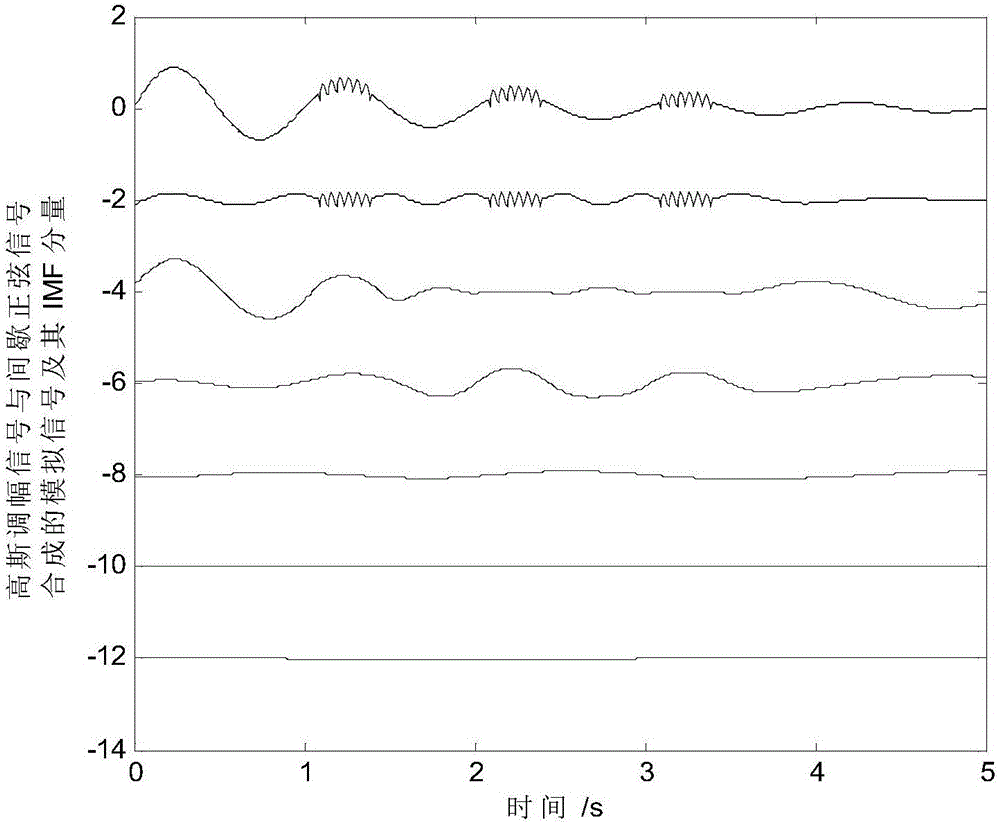
[0107] Taking the exponential amplitude modulation signal containing intermittent signals in formula (1) as an example, the local maximum and local minimum found by using the definition of local extremum are as follows: Figure 4a Indicated by '*' and 'o'. The window extreme points selected from the local extreme points are as follows Figure 4b Indicated by '*' and 'o'. From Figure 4a It can be seen that a high-frequency sinusoidal signal is superimposed near the second to fourth maximum points of the exponential amplitude modulation signal, and the mean signal calculated by using the upper and lower envelopes constructed by the local extreme point near it is an exponential amplitude modulation signal. Elsewhere the mean is zero. Therefore, some parts of the difference between the original signal and the envelope mean value are high-frequency sinusoidal signals, and some parts are exponential amplitude modulation signals, and present jumps and discontinuities, resulting i...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Taking the composite signal of chirplet signal and harmonic signal superimposed with intermittent noise as an example, by decomposing the synthetic analog signal with intermittent, and calculating the relative mean square error of the single analog signal and IMF, the empirical mode decomposition of the extreme value of the verification window (WE -EMD) method to deal with the effectiveness of the mode mixing problem. EMD is the most primitive method to deal with nonlinear and non-stationary signals, and EEMD is the most effective method among many dealing with modal mixing problems. Choose to compare with the decomposition results of these two methods to verify the validity and practicability of WE-EMD.
[0111] Such as Figure 6a As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the intermittent noise signal waveform in the second embodiment. Such as Figure 6b As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the superimposed signal waveform of the Chirplet signal and the harmonic sign...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com