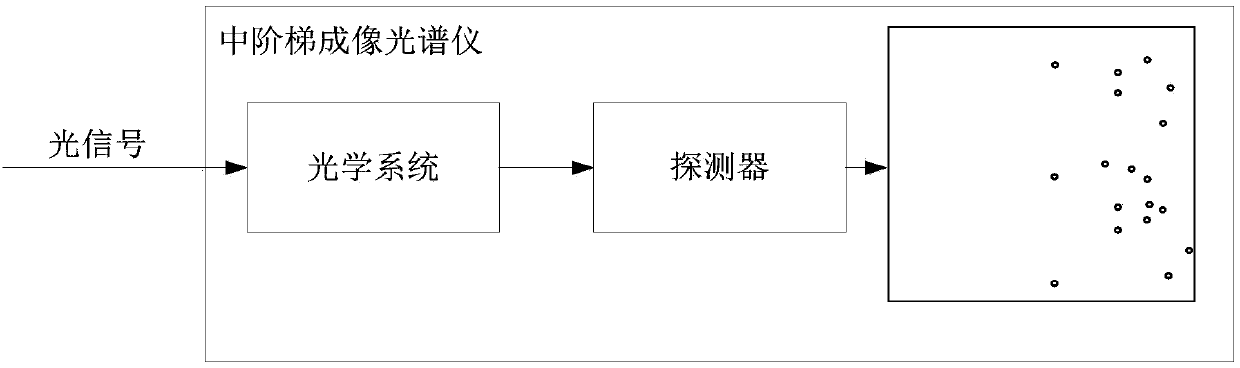
Method and apparatus to calculate target position using imaging spectrometer
An imaging spectrometer and imaging position technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, positioning, etc., can solve problems affecting the measurement accuracy of imaging spectrometers, measurement results errors, drift errors, etc., to improve system accuracy, improve measurement accuracy, and ensure calculation accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
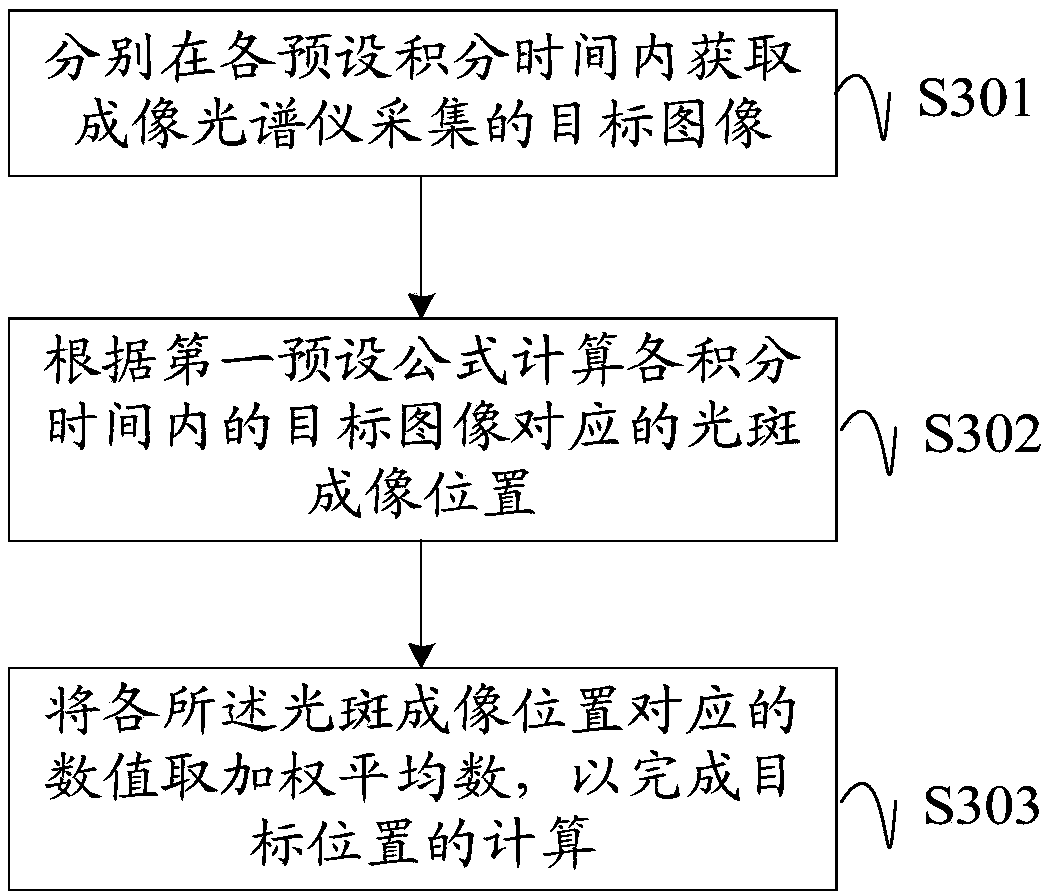
[0053] see first image 3 , image 3 A schematic flowchart of a method for calculating a target position by an imaging spectrometer provided in an embodiment of the present invention, the embodiment of the present invention may include the following contents:
[0054] S301: Acquire a target image collected by an imaging spectrometer within each preset integration time respectively.
[0055] The integration time may be preset, or may be set according to the needs of the technicians themselves during testing, which does not affect the implementation of the embodiments of the present invention.
[0056] The integration time is short, the spot energy will not be saturated, and the gray value of the spot has a linear relationship with the spot energy. Without considering the noise, the position of the center of gravity of the spot is close to the center of the spot; however, the spot energy in the image is low, and the electronic noise is relatively serious, and the noise has a s...
Embodiment 2
[0071] see Figure 4 , Figure 4 A schematic flowchart of another method for calculating a target position by an imaging spectrometer provided in an embodiment of the present invention may specifically include the following content:
[0072] S401: Acquire a target image collected by an imaging spectrometer within each preset integration time respectively.
[0073] The specifics are the same as those described in S301 of the first embodiment, and are not repeated here.
[0074] S402: Acquire a preset number of sub-images collected by the imaging spectrometer in each of the integration times respectively.
[0075] S403: Select a sub-image from the sub-images corresponding to each integration time according to a preset method as a target image of the corresponding integration time.
[0076] Specifically, it can be:
[0077] Calculate the spot imaging position of each sub-image corresponding to each integration time according to the second preset formula;
[0078] Select a su...
Embodiment 3
[0096] see Figure 5 , Figure 5 A structural diagram of an imaging spectrometer calculating target position device provided in an embodiment of the present invention in a specific implementation manner, the device may include:
[0097] An information acquisition module 501 is configured to acquire target images collected by the imaging spectrometer within each preset integration time respectively.
[0098] The calculation module 502 is configured to calculate the spot imaging position corresponding to the target image in each integration time according to the first preset formula; take a weighted average of the values corresponding to each of the spot imaging positions to complete the calculation of the target position.
[0099] Optionally, in some implementations of this embodiment, the information acquiring module 501 may further include, for example:
[0100] an acquiring sub-image unit 5011, configured to acquire sub-images of a preset number of frames collected by th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com