Single-phase brushless motor
A single-phase brushless motor and stator technology, applied in the direction of electric components, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor starting reliability, small positioning starting angle, vibration and noise, etc., to improve starting reliability and reduce Activate the dead center effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
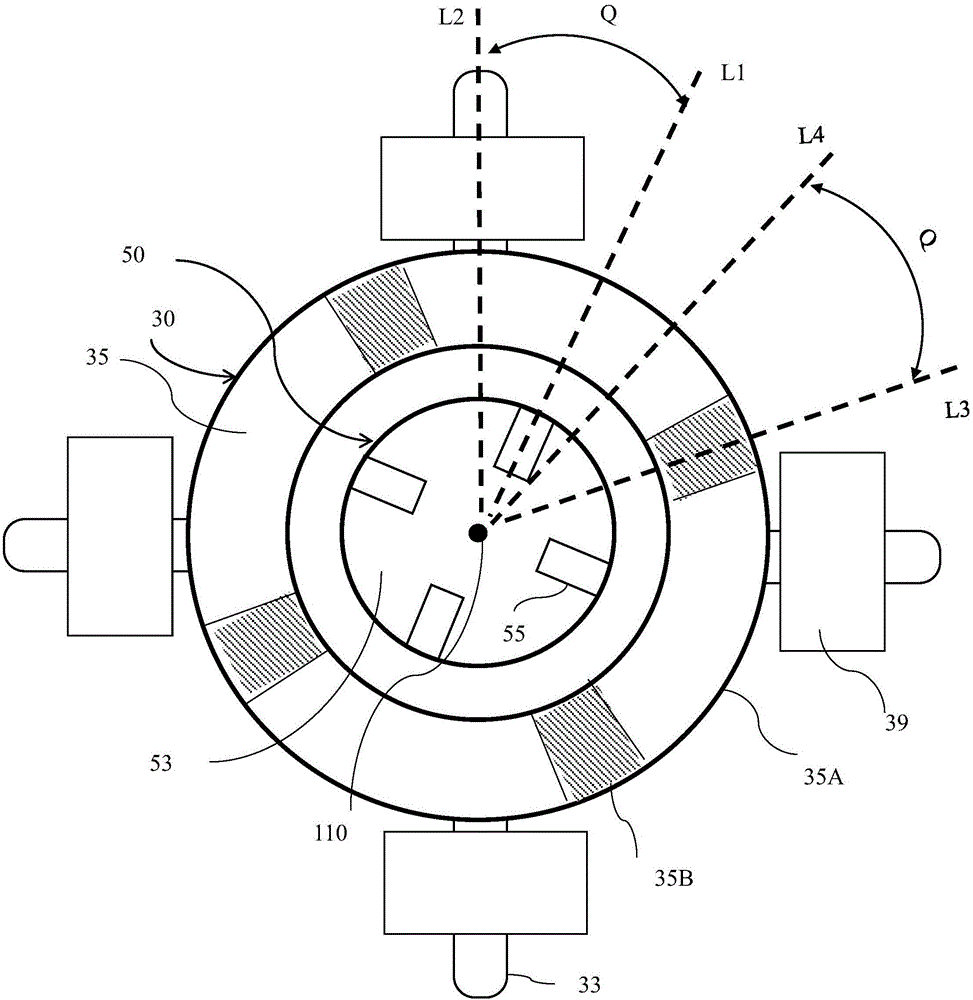
[0049] see Figure 2 to Figure 6 , The single-phase brushless motor 10 provided by the present invention includes a stator 20 and a rotor 50 that can rotate relative to the stator.
[0050] The stator includes a cylindrical shell 21 with an open end, an end cover 23 mounted to the open end of the shell 21, a stator core 30 mounted in the shell 21, an insulating wire frame 40 mounted to the stator core 30 and wound around the stator core. Winding 39 on and supported by insulating wire frame 40. The stator core 30 includes an outer yoke 31 , a plurality of teeth 33 protruding inward from the outer yoke 31 , and pole pieces 35 protruding from the radially inner ends of the teeth 33 to both sides in the circumferential direction. The winding 39 can preferably be wound on the corresponding tooth body 33 , of course, the winding can also be wound on other parts of the stator core 30 , and the winding 39 and the stator core 30 are isolated and insulated by the insulating wire frame ...
no. 2 example
[0062] Please refer to Figure 9 , and the difference from the previous embodiment is that in order to improve the winding efficiency of the winding 39, the stator core adopts a split structure. Specifically, the tooth body 33 and the outer yoke are integrally formed as a whole, and the tooth body 33 and a plurality of teeth The inner ring part formed by connecting the pole pieces of the body is a split structure, that is, the inner ring part and the tooth body 33 are formed separately and then assembled together. It can be understood that each tooth body 33 can be fixedly connected to the inner ring portion by welding or various mechanical connection methods (such as snap-fit method with dovetail groove). In an alternative solution, the tooth body 33 can also be formed separately from the outer yoke portion 31 and the inner ring portion, and the tooth body 33 is fixedly connected to the outer yoke portion 31 and the inner ring portion after the winding 50 is wound. The sta...
no. 3 example
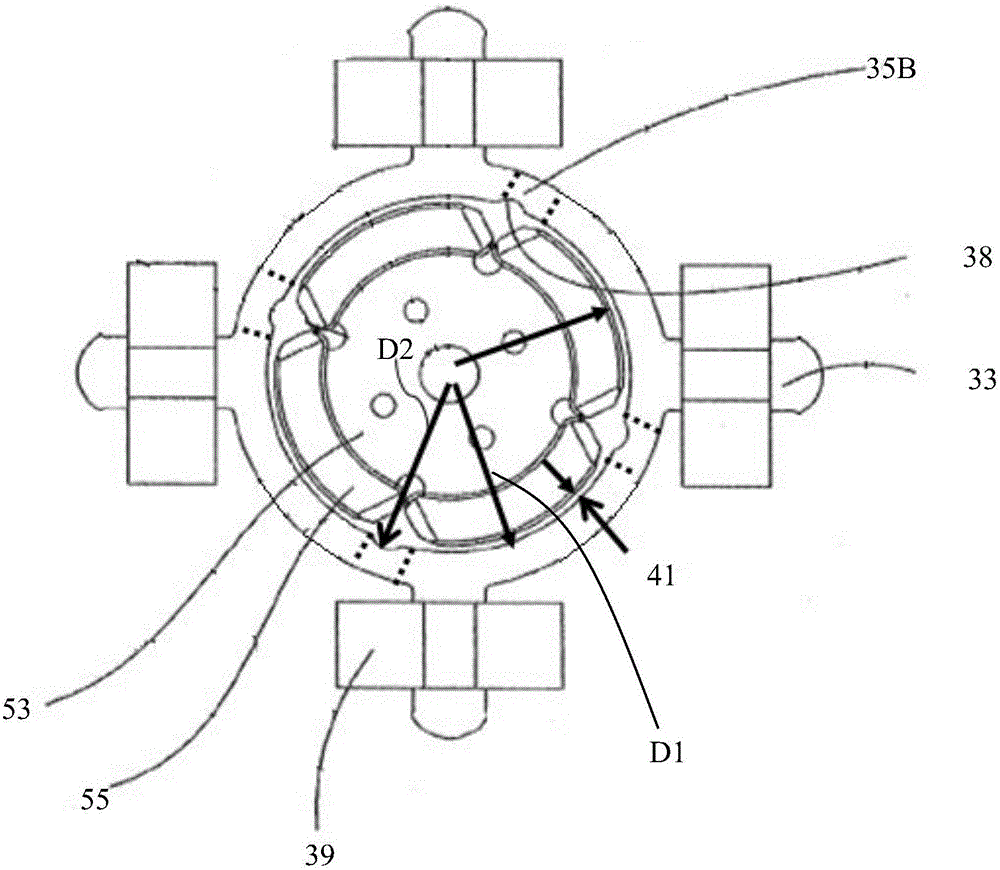
[0064] Please refer to Figure 10 , different from the first embodiment, in this embodiment, grooves 37 are formed on the outer peripheral surface of the inner ring part corresponding to the area of the magnetic bridge, the number of grooves 37 is only one, and its shape is, for example, square, Certainly also can be circular arc or any other shape.
[0065] In this embodiment, the pole shoes 35 between adjacent tooth bodies are also provided with positioning grooves 38. The difference is that the positioning grooves 38 in this embodiment are located in the inner ring formed by connecting pole shoes of several tooth bodies. The invisible positioning groove is between the outer peripheral surface and the inner peripheral surface of the part, preferably, close to the inner peripheral surface of the inner ring part. In this way, the distance between the first arc portion and the second arc portion of the pole piece 35 and the rotor axis is equal.
[0066] In this embodiment, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com