Multi-level architecture for data synchronization, data synchronization method and fault handling method
A data synchronization and data technology, applied in data exchange networks, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as low reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
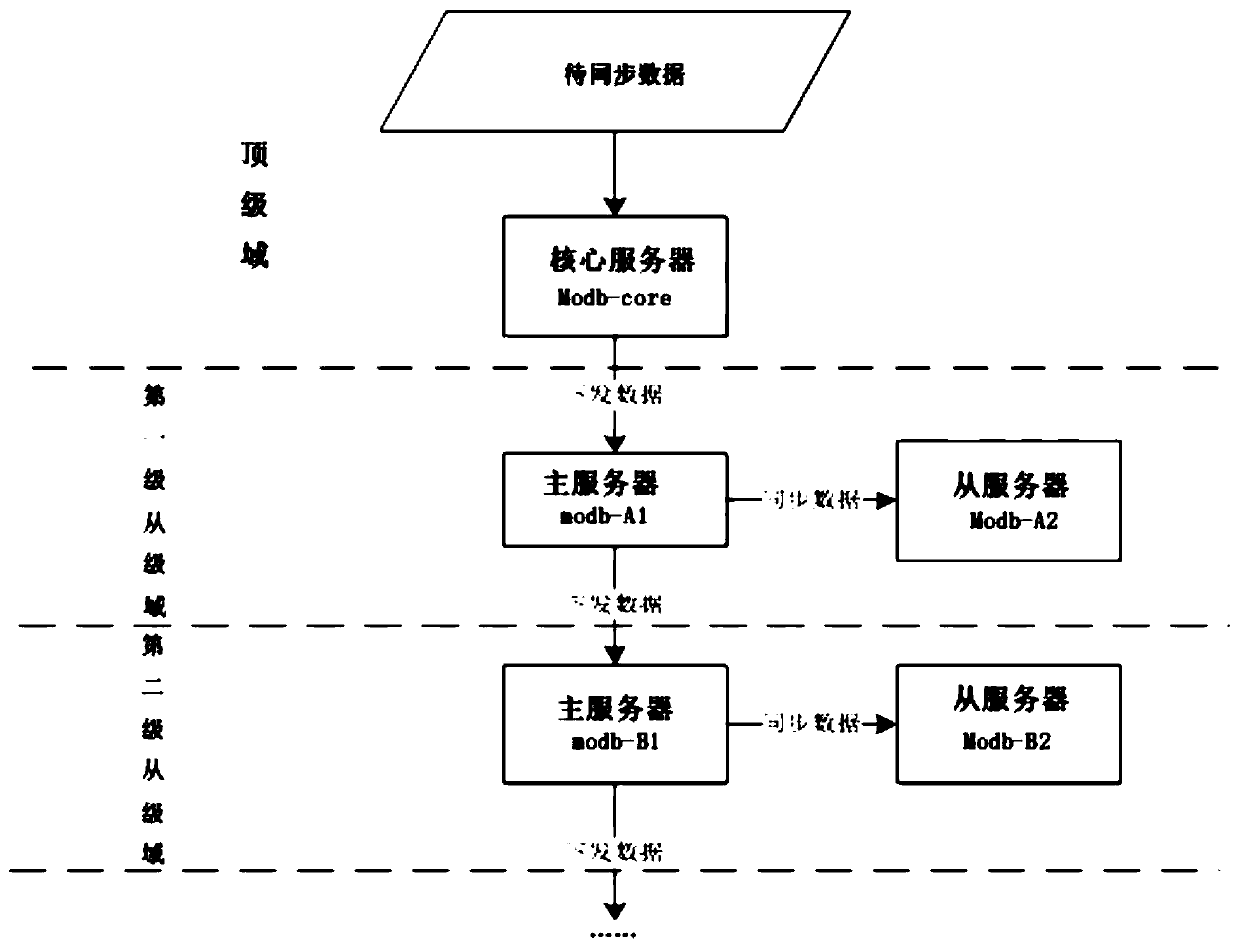
[0061] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a multi-level architecture for data synchronization, including a top-level domain and multiple sequentially connected slave-level domains, the data to be synchronized is delivered from the top-level domain to the first-level slave-level domain, and the first The first-level slave domain then delivers the data to be synchronized to the second-level slave domain and delivers them level by level. Specifically, there is a data delivery link between the first-level slave-level domain and the top-level domain, and there is also a data delivery link between two adjacent slave-level domains.
[0062] Each slave domain includes multiple servers, one of which is the master server and the others are slave servers. The master server is used to receive the data to be synchronized and forward the data to be synchronized to each slave server in the slave domain after it completes the data synchronization , receive the data to be syn...
Embodiment 2
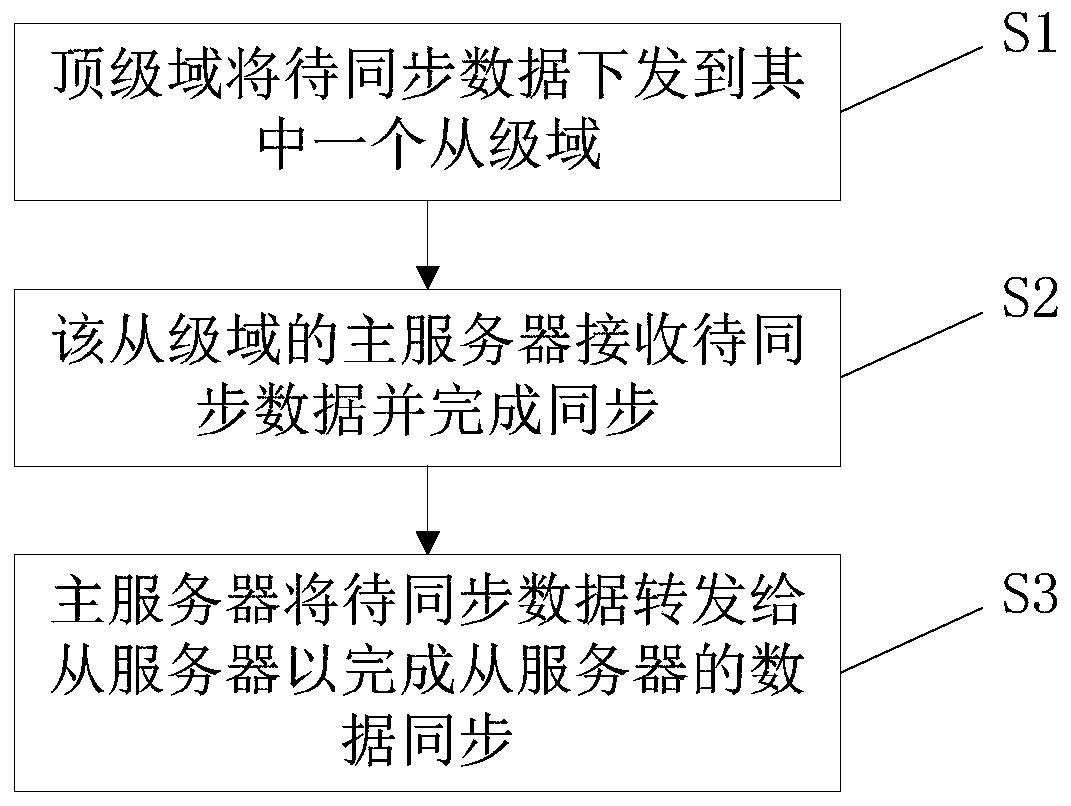
[0065] This embodiment provides a data synchronization method, which is based on the multi-level architecture described in Embodiment 1 above, such as figure 2 with 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0066] S1: The top-level domain sends the data to be synchronized to one of the subordinate domains, and the data to be synchronized may be generated by the top-level domain;
[0067] S2: The master server of the slave domain receives the data to be synchronized and completes the synchronization;
[0068] S3: The master server forwards the data to be synchronized to the slave server to complete the data synchronization of the slave server.
[0069] The data synchronization method provided in this embodiment is based on the multi-level architecture provided in Embodiment 1 above. Therefore, correspondingly, this method can reliably complete the synchronization of the data to be synchronized from the top-level domain to the subordinate-level domain.
[0070] Specifically,...
Embodiment 3
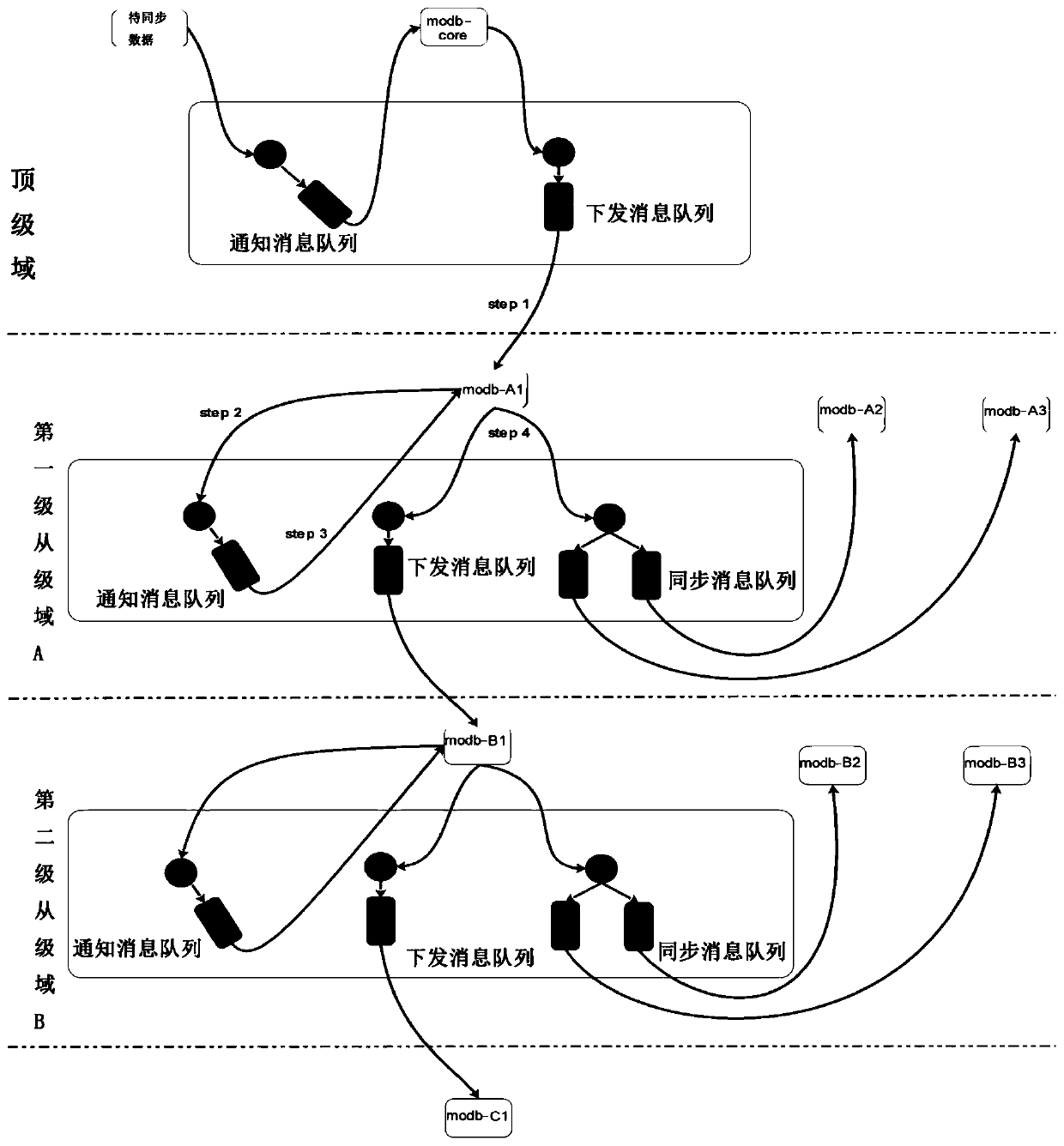
[0094] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment provides a data synchronization method, which is also based on the multi-level architecture provided by the above-mentioned embodiment 1. This embodiment uses a message queue to realize the storage of synchronization messages. The messages stored in the message queue of the slave-level domain or the top-level domain realize the level-by-level delivery and synchronization of data, and the slave servers in the slave-level domains of all levels also realize data synchronization by subscribing to the messages stored in the message queue of the same level. For the convenience of description, in this embodiment, only three servers are set in each secondary domain, one of which is the master server and the others are slave servers. The data synchronization method specifically includes the following steps:
[0095] 1) After the top-level domain business modifies the database, if it is necessary to notify the subordinate domains, a mess...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com