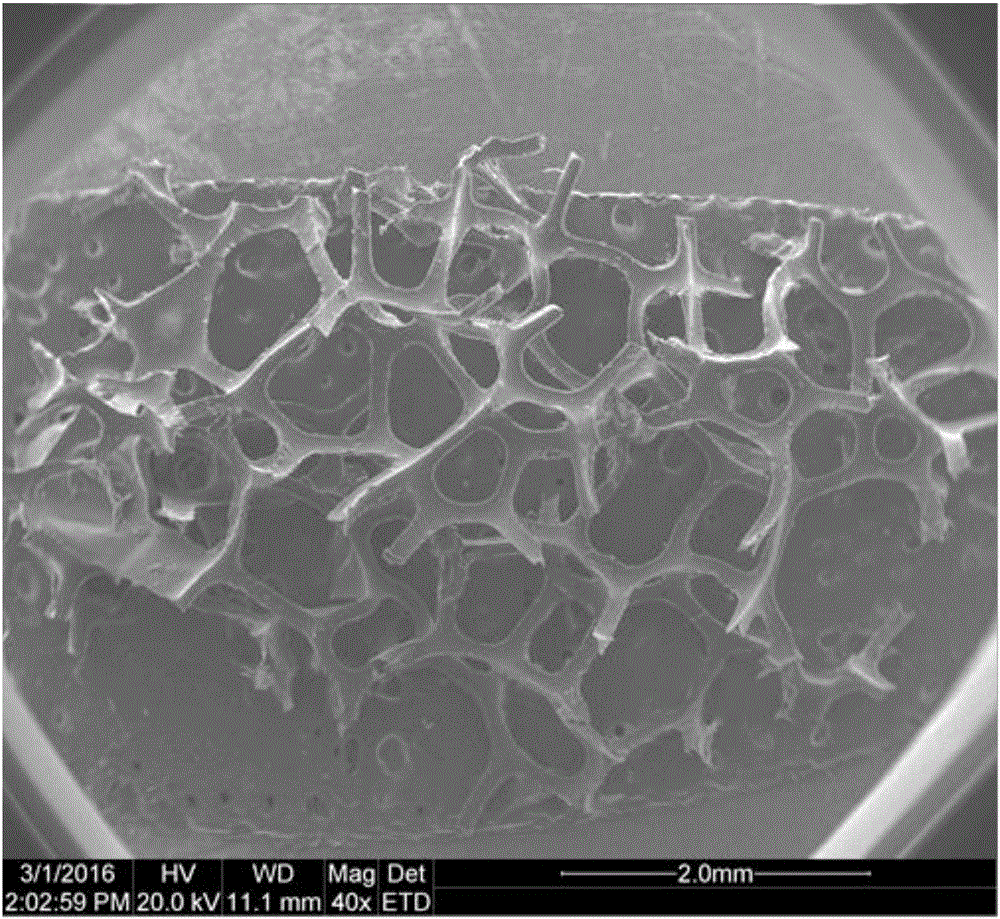
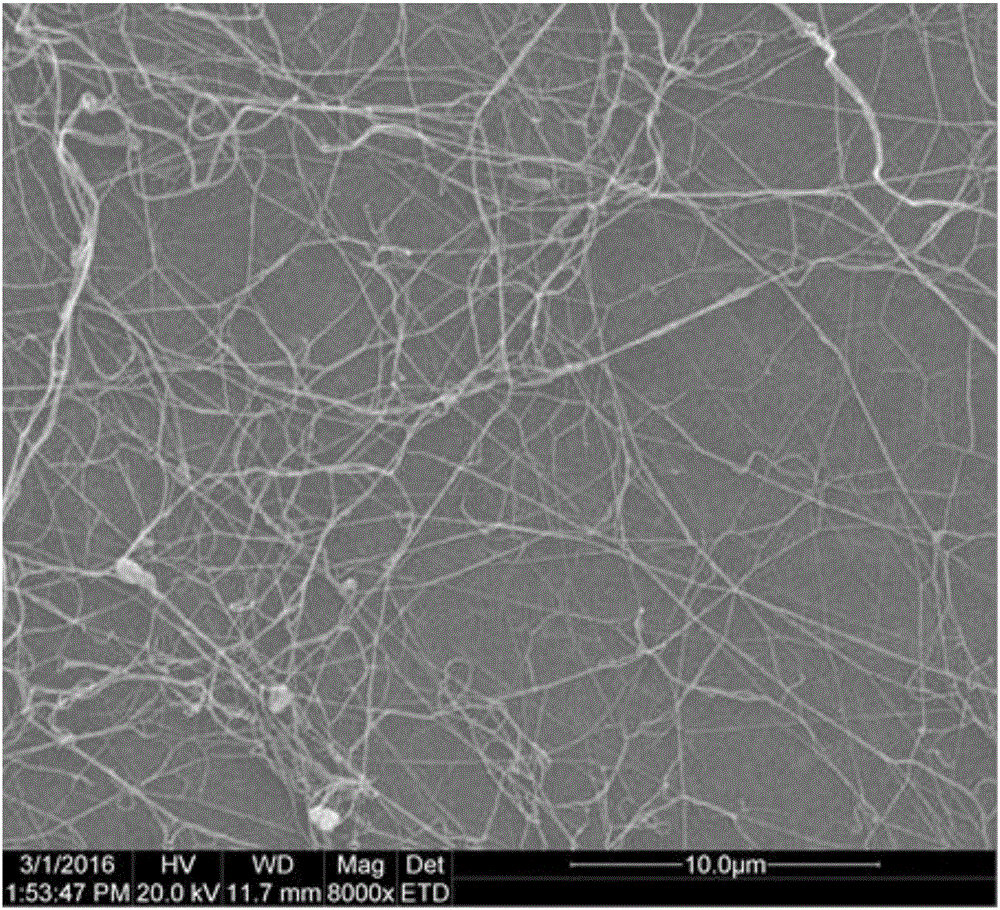
Bacterial cellulose foam fermentation method
A bacterial cellulose and foam technology, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of low fermentation level, unaffordable price, and low output, and achieve the effects of optimal structural strength, improved utilization rate, and excellent performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] A better bacterial cellulose foam fermentation method, comprising:
[0062] 1) Preparation of strains. Take the strains stored at -80°C, transfer them to -20°C for 12 hours, transfer them to 4°C and place them for about 2-4 hours until they are completely dissolved.
[0063] 2) Inoculate 1ml of bacterial solution into 150ml of seed culture solution and incubate at 28°C for 24 hours to become a first-class seed solution.
[0064] 3) Take the first-grade seed liquid and inoculate it into 500ml of fermented liquid, the purpose is to carry out bacterium cell amplification, and the formula of fermented liquid and seed culture liquid is different. Cultivate at 30°C for 18-24 hours.
[0065] 4) Add 1% foaming agent A and 2% foam stabilizer B to the fermentation broth, and mix thoroughly in a 500ml airtight blue cap bottle.
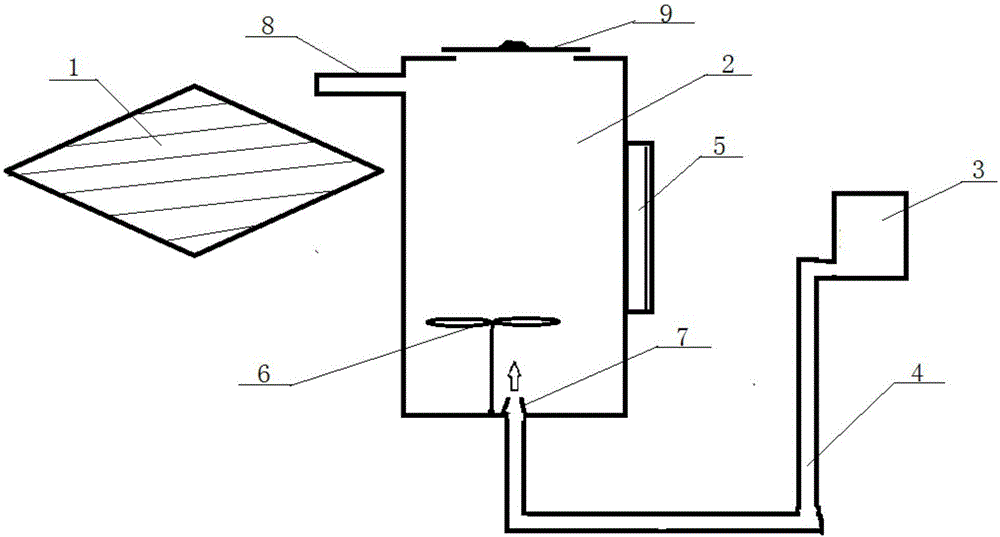
[0066] 5) Pour the fermentation liquid into the foaming cylinder. The foaming cylinder is a high-temperature sterilizable PE barrel with an air inlet a...
Embodiment 2
[0073] A better bacterial cellulose foam fermentation method, comprising:
[0074] 1) Preparation of strains. Take the strains stored at -80°C, transfer them to -20°C for 12 hours, transfer them to 4°C and place them for about 2-4 hours until they are completely dissolved.
[0075] 2) Inoculate 1ml of bacterial solution into 150ml of seed culture solution and incubate at 28°C for 24 hours to become a first-class seed solution.
[0076] 3) Take the first-grade seed liquid and inoculate it into 500ml of fermented liquid, the purpose is to carry out bacterium cell amplification, and the formula of fermented liquid and seed culture liquid is different. Cultivate at 30°C for 18-24 hours.
[0077] 4) Add 5% foaming agent A and 10% foam stabilizer B to the fermentation broth, and mix thoroughly in a 500ml airtight bottle.
[0078] 5) Pour the fermentation liquid into the foaming cylinder. The foaming cylinder is a high-temperature sterilizable PE barrel with an air inlet at the bo...
Embodiment 3
[0081] A better bacterial cellulose foam fermentation method, comprising:
[0082] 1) Preparation of strains. Take the strains stored at -80°C, transfer them to -20°C for 12 hours, transfer them to 4°C and place them for about 2-4 hours until they are completely dissolved.
[0083] 2) Inoculate 1ml of bacterial solution into 150ml of seed culture solution and incubate at 28°C for 24 hours to become a first-class seed solution.
[0084] 3) Take the first-grade seed liquid and inoculate it into 500ml of fermented liquid, the purpose is to carry out bacterium cell amplification, and the formula of fermented liquid and seed culture liquid is different. Cultivate at 30°C for 18-24 hours.
[0085] 4) Add 3% foaming agent A and 6% foam stabilizer B to the fermentation broth, and mix thoroughly in a 500ml airtight bottle.
[0086] 5) Pour the fermentation liquid into the foaming cylinder. The foaming cylinder is a high-temperature sterilizable PE barrel with an air inlet at the bot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com