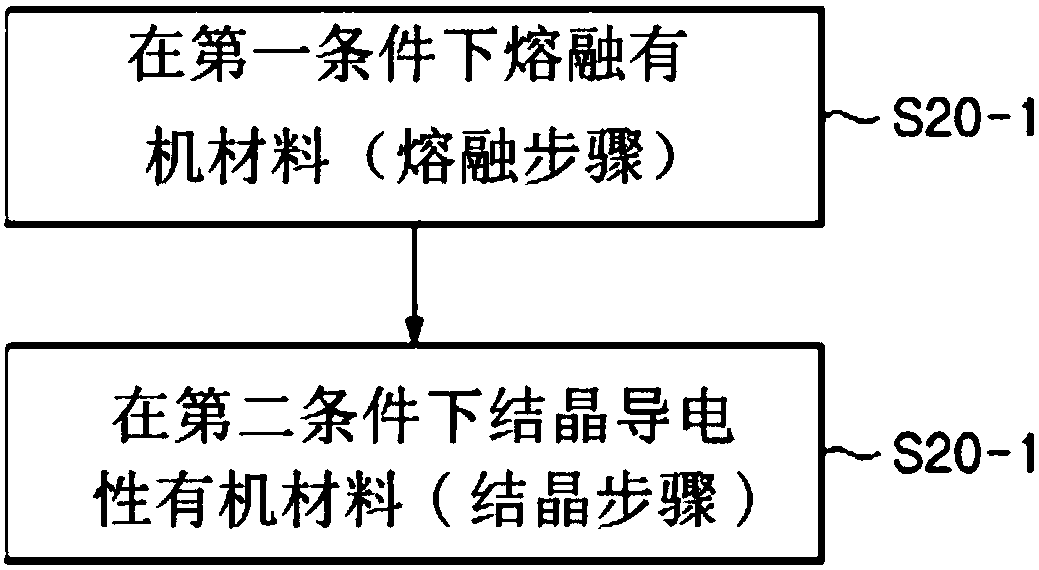
Use the organic material of ionic liquid to purify the method and device
A technology of organic materials and ionic liquids, which is applied in the field of purifying organic materials to achieve the effects of low cost, easy design and control of purification process, and wide temperature range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Example 1 is the use of (Omim) (TFSI) ionic liquid to purify the conductive organic material N', N'-bis-(1-naphyl)-N(N'-bis(1- Naphthyl)-N,), N'-diphenyl-1 (N'-diphenyl-1), 1'-biphenyl-4 (1'-biphenyl-4), 4'-diamine (hereinafter referred to as "NPB"). The chemical formula of NPB is shown by the following (chemical formula 4).
[0100] (chemical formula 4)
[0101]
[0102] Figure 6 It is a scanning electron micrograph of NPB before purification. exist Figure 6 It was confirmed that the shape of NPB ions before purification was amorphous with a size of about 1-2 μm. Furthermore, when the purity of NPB before purification was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (High Performance Liquid Chromatography), the purity was as low as 82.4%.
[0103] The low-purity NBP before pulverization is mixed with (Omim) (TFSI) ionic liquid (ionic liquid / NPB=0.5 / 0.01g) with the mixing ratio of 2wt%, in the heat treatment environment that keeps argon (Ar) environment...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2 is an example of purifying NPB as an organic material by using (Bmin)(TFSI) ionic liquid. Compared with the examples, only the ionic liquid is changed from (Omin)(TFSI) to (Bmin)(TFSI), but the process conditions are the same.
[0109] Figure 10 and Figure 11 Scanning electron microscope photographs of NPB crystals purified at 110°C and 170°C are shown, respectively, and the purity of each case was analyzed by HLPC.
[0110] From Figure 10 and Figure 11 It can be seen from the photographs of the scanning electron microscope of , that when crystallized at a relatively low temperature of 110° C., circular plate-shaped crystals of about 10 to 20 μm are formed. In the case of crystallization at a relatively high temperature of 170° C., larger and uniform elongated crystals of about 30 to 40 μm are formed. In addition, HPLC purity analysis data confirmed that high-purity NPB of 99.67% and 99.83% was obtained when the crystallization temperature was 110°C and...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Embodiment 3 utilizes (Omim) (TFSI) ionic liquid to purify the conductive organic material tris-(8-hydroxyquinoline) aluminum (three-(8-hydroxyquinoline) aluminum, hereinafter referred to as Alq3) example. Compared with Example 1, only the organic material is changed from NPB to Alq3, and other process conditions are the same. The chemical formula of Alq3 is shown below (chemical formula 5).
[0113] (chemical formula 5)
[0114]
[0115] Figure 12 It is a scanning electron micrograph of low-purity Alq3 before purification, Figure 13 It is a scanning electron micrograph of a high-purity Alq3 crystal purified at a crystallization temperature of 170°C. From Figure 12 , 13 It can be seen that, according to the purification method of the present invention, uniform pocket-shaped crystals of about 5 to 10 μm are obtained. In addition, as a result of HPLC analysis, it was also confirmed that Alq3 crystals were obtained at a level similar to that of NPB in Example ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com