A monitoring method of embedded program execution sequence
A program execution and embedded technology, which is applied in the monitoring field of embedded program execution sequence, can solve problems such as multiple faults, residual, and inability to monitor instruction statements, and achieve the effect of improving coverage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings.
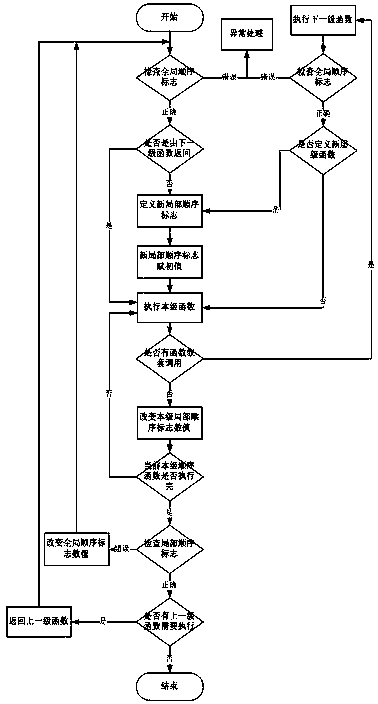
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, the specific steps of the method for monitoring the execution sequence of embedded programs of the present invention are:
[0030] The global sequence flag is judged at the function entry. If it is wrong (not the default value), then exception processing is performed. After the correct pass, it is judged whether the function is returned by the next-level function. If not, define a new local sequence flag ( As the first definition, the corresponding function of this level is the highest level function), and the initial value of the new local sequence flag is assigned, and then go to the next step, if it is returned by the next level function, go directly to the next step;
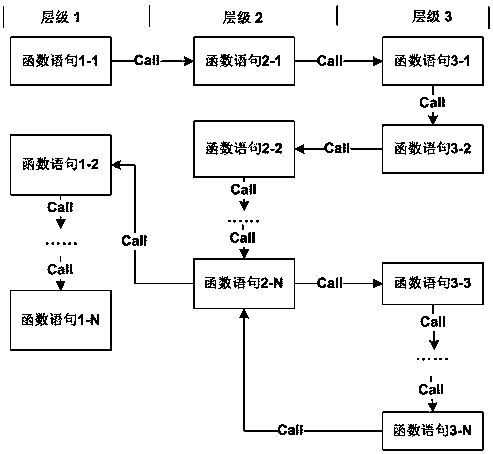
[0031] Next, execute this level function; if there is a nested call to the sublevel function in this level function, enter the next level function, still first judge the global sequen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com