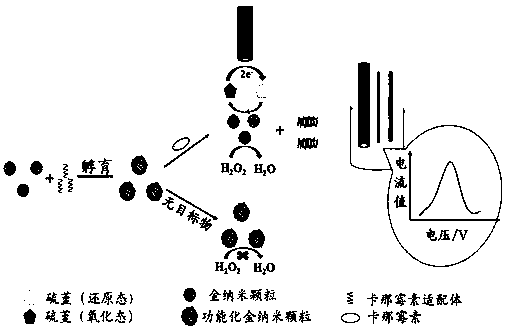
An electrochemical detection method for the detection of kanamycin residues based on nucleic acid aptamers and nano-mimetic enzymes
A nucleic acid aptamer, kanamycin technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of large result error, complicated operation, expensive equipment, etc., and achieve the effects of easy preparation, high sensitivity and high specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
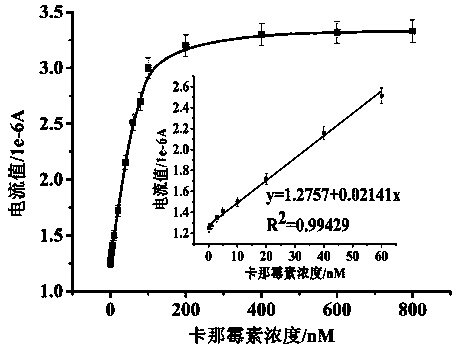
[0031] Example 1. Drawing of kanamycin standard solution peak current value-concentration standard curve
[0032] Specific steps are as follows:
[0033] (1) Preparation of gold nanoparticle mimic enzyme: use tyrosine as reducing agent and capture agent to prepare gold nanoparticle mimic enzyme, boil 300mL ultrapure aqueous solution containing 0.1 mM tyrosine and 0.1 mM KOH for 3-5 minutes, Immediately add 1.02 mL of a 1% chloroauric acid solution by mass to volume and keep it in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes; continue boiling in the boiling water bath until the volume of the solution is reduced to 30 mL to obtain a gold nanoparticle solution; advance the above gold nanoparticle solution Dialysis in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 12kDa treated in boiling water to remove excess KOH, metal ions and tyrosine to obtain a gold nanoparticle mimic enzyme, which is stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for later use;
[0034] (2) Preparation of functionalized gold nanopart...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2. Detection of Kanamycin Residues in Honey Samples
[0046] Here, a standard concentration of kanamycin was added to honey to prepare artificially polluted honey, and a honey sample containing 0-600 nM kanamycin residue was obtained.
[0047] According to the standard detection procedure in Example 1, the artificially contaminated kanamycin in acacia honey was detected.
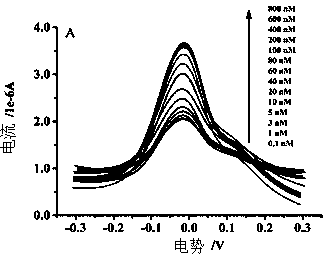
[0048] Get as Figure 5 Shown is the DPV current-potential curve diagram of honey samples detected by differential pulse voltammetry, and Figure 4 The curve showing the relationship between the peak current value and the concentration of kanamycin in the honey sample.
[0049] In the kanamycin concentration range of 1-60 nM, there is a linear relationship between the peak current value and the concentration. The linear regression equations are respectively: y=1.41579+0.0182x, R 2 =0.9978, where y is the peak current value (μA), and x is the concentration of kanamycin in the honey sample (nM). It can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com