Evading method based on opposite-direction sailing of virtual puffed motion obstacle and UUV
A technology of motion obstacles and obstacles, which is applied in the field of avoidance of motion obstacles and UUV opposite navigation based on virtual puffing, and can solve problems such as difficult to accurately predict the state of motion obstacles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0018] Specific embodiment one: a method for avoiding movement obstacles based on virtual puffing and UUV opposite navigation includes the following steps:
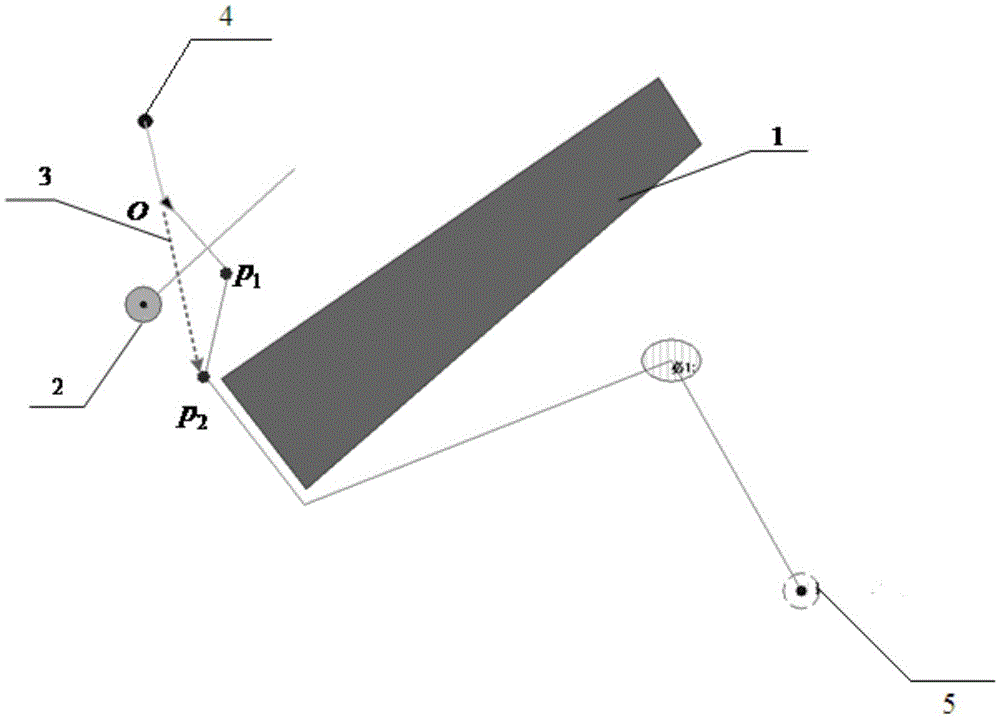
[0019] The guidance direction refers to the direction of the vector formed by the line from the current position of the UUV to the next non-motion obstacle waypoint. The so-called non-movement obstacle waypoint means that the waypoint is not formed by relying on the movement obstacle, but is the vertex of the static environment information in the environment, such as the vertex of the static target (p 2 ), necessary points, recycling points, etc. When the UUV runs to figure 1 At the position shown, when the No. 1 motion obstacle is encountered, the UUV triggers the dynamic programming algorithm to form a new avoidance route, point p 1 is the waypoint formed by the UUV to avoid the No. 1 movement obstacle and relies on the movement obstacle, and the point p 2 is the static target puffed vertex. So according to the def...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: in the step 2, the radius of the region after circular puffing of the dyskinesia is R, and R>obs_r+safe_d.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0025] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is that: the rectangular virtual obstacle generated in the step three is specifically:
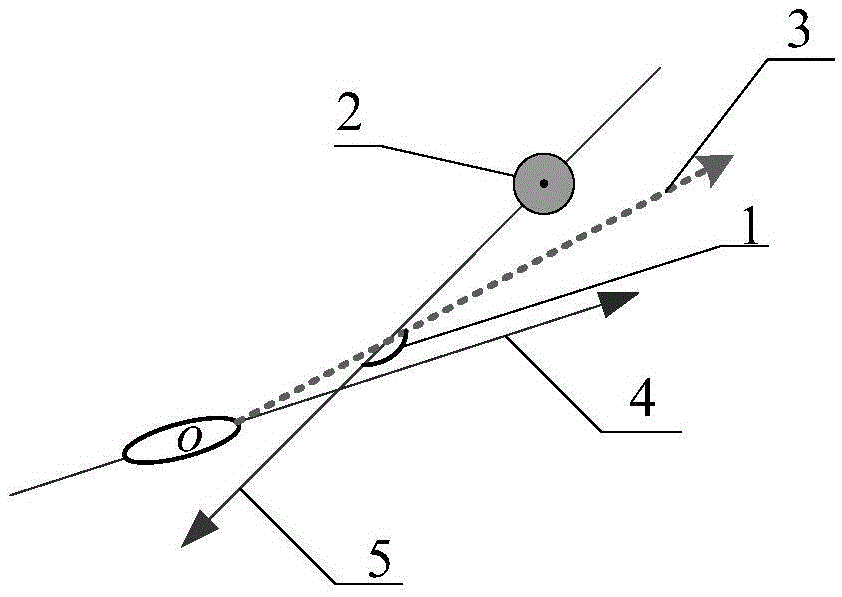
[0026] When the UUV detects that a moving obstacle is approaching, the moving obstacle will generate a rectangular virtual obstacle with a length of L and a width of 2R along the forward direction of the moving obstacle (such as image 3 shown), the relationship between the length of the rectangular virtual barrier and the straight-line distance M from the UUV to the central point of the motion barrier is:
[0027] L=R+λ(M-R)
[0028] Among them, 0<λ<1, λ is the length coefficient of the rectangular virtual obstacle generated by the moving obstacle when sailing in the opposite direction. The larger the λ, the larger the initial length of the rectangular virtual obstacle, and the greater the length change between two adjacent generation, the UUV will generat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com