Method For Estimating Optimal Power Flows In Power Grids Using Consensus-based Distributed Processing
An optimal power flow and consistency technology, applied in the power grid field, can solve problems such as the inability to ensure the feasible point of the OPF problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
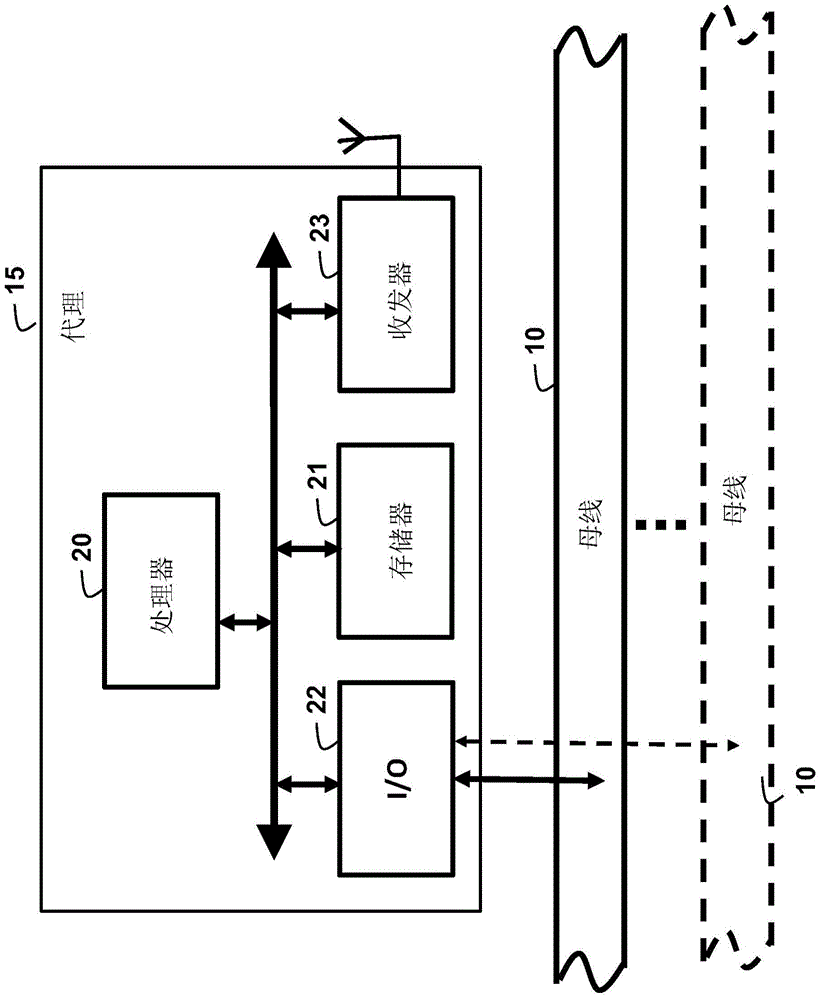
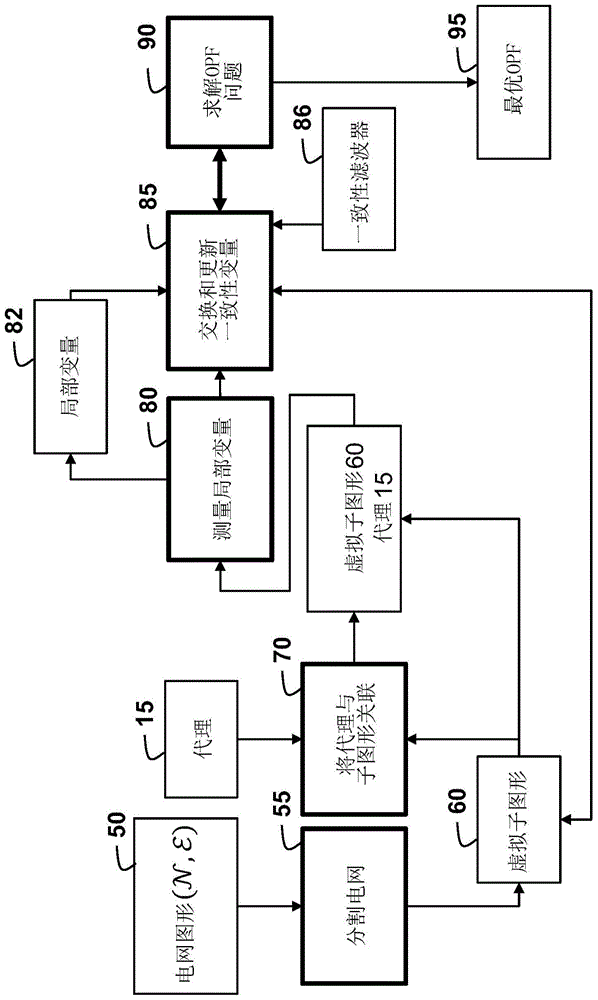
[0025] Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for optimal power flow (OPF) in a power grid using consensus-based distributed processing.
[0026] grid representation
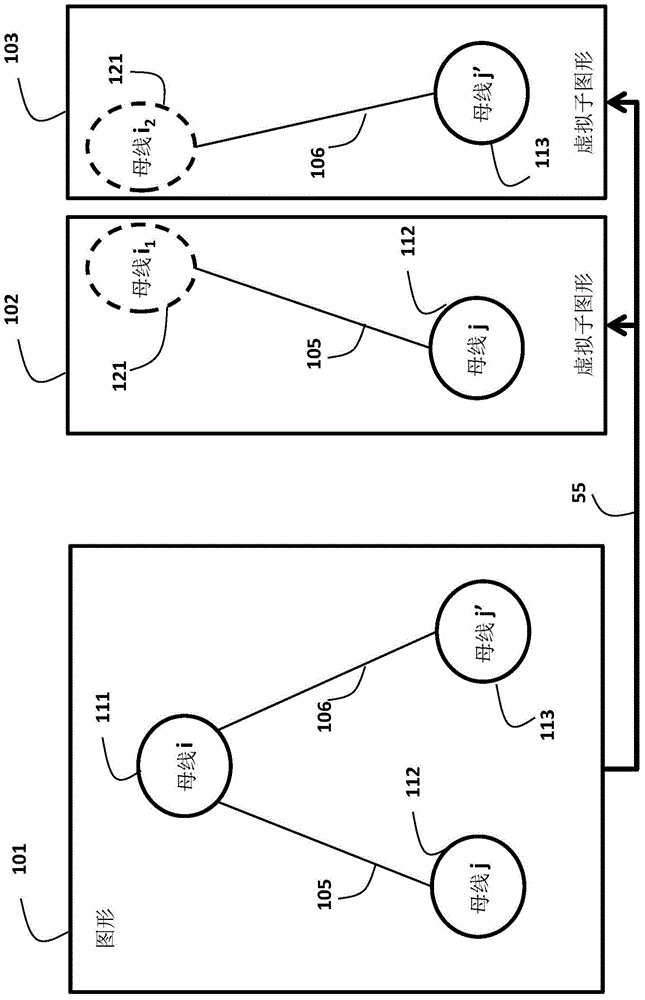
[0027] Such as Figure 1B As shown, we model the grid as a graph 50, where the vertex set Including all buses in the grid, the links ε between vertices are the elevated or underground transmission lines connecting the buses.
[0028] Each bus Can be connected to generator or load. The set of buses connected to the generator is represented as For convenience, the bus connected to the generator is referred to as the generator bus. A bus without any generators is called a loaded bus. We use i~j to denote that bus i is connected to bus j.
[0029] The active and reactive generated power at bus i is expressed as with The power demand at bus i is expressed as The complex voltage at bus i is denoted as V i = e i +jf i , where e i is the real part (Re) of the voltage, f i is the ima...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com