Method for measuring the concentration of gas molecules in the respiratory and circulatory system in exhaled breath
A circulatory system and gas molecule technology, which is applied to the structural details of gas analyzers, measuring devices, and analyzing gas mixtures, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
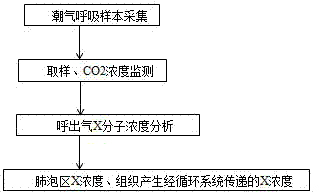
[0056] Taking the measurement of the NO concentration of the respiratory and circulatory system gas in exhaled air as an example, an application embodiment of the present invention is introduced.
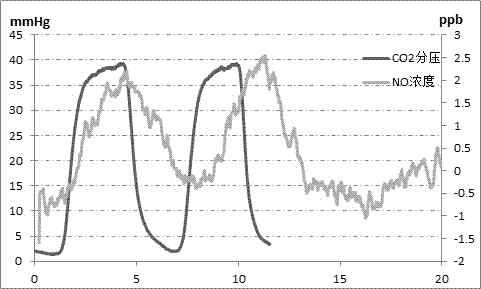
[0057] The subject breathes with normal tidal flow (expiratory flow rate 200ml / s), observes the CO2 curve, after the breathing is balanced, the sampling starts, collects two tidal exhaled breaths for the instrument, analyzes the NO concentration in it, and the exhaled breath displayed by the CO2 curve State, measure the exhaled NO concentration in the alveolar region of the exhaled breath at least two times. The sampled gas flow rate (about 10ml / s) and the analyzed gas flow rate (about 1ml / s) have been calibrated in advance, which is equivalent to the exhaled gas per second can be measured on the sensor for 10 seconds, and the measurement time is magnified by 10 times. The end time of the above-mentioned exhalation sampling is consistent with the inflection point time when the zero ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com