Elliptic curve encryption method comprising error detection
An elliptic curve encryption, elliptic curve technology, used in the countermeasures of attacking encryption mechanisms, public keys for secure communication, instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
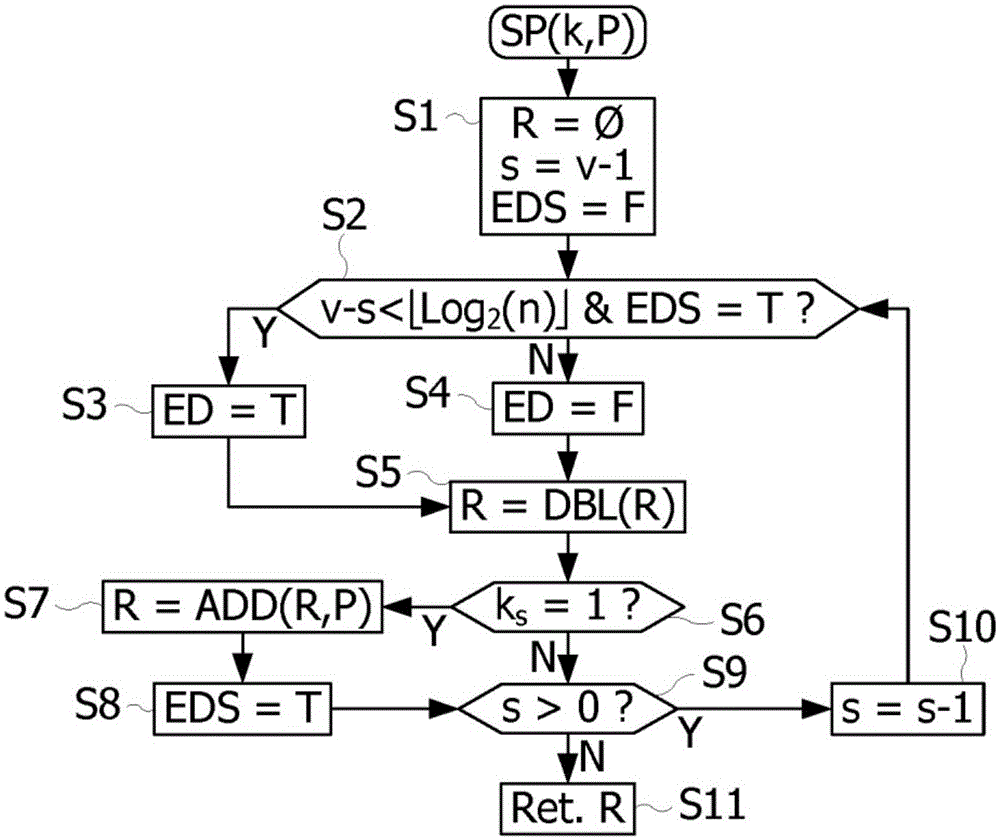
[0025] Elliptic curve cryptosystems generally require the definition of so-called "domain" parameters. In GF(p) or GF(2 m ) type Galois field, these parameters include: a large prime number p or a large integer m; the generation point or base point G of coordinates Gx and Gy in the Galois field; the prime number n called "order" of point G, such that is the point at infinity or the neutral element in the Galois field; the parameters defining the elliptic curve; the number f called the "cofactor", generally equal to 1, 2, or 4, so that f·n represents the number of points of the elliptic curve. In a Galois field of type GF(p), an elliptic curve may for example have a shape such as E(a,b):y 2 =x 3 The equation of +ax+b. In this elliptic curve, the opposite point of a point P with affine coordinates (x, y) is a point -P with coordinates (x, -y).
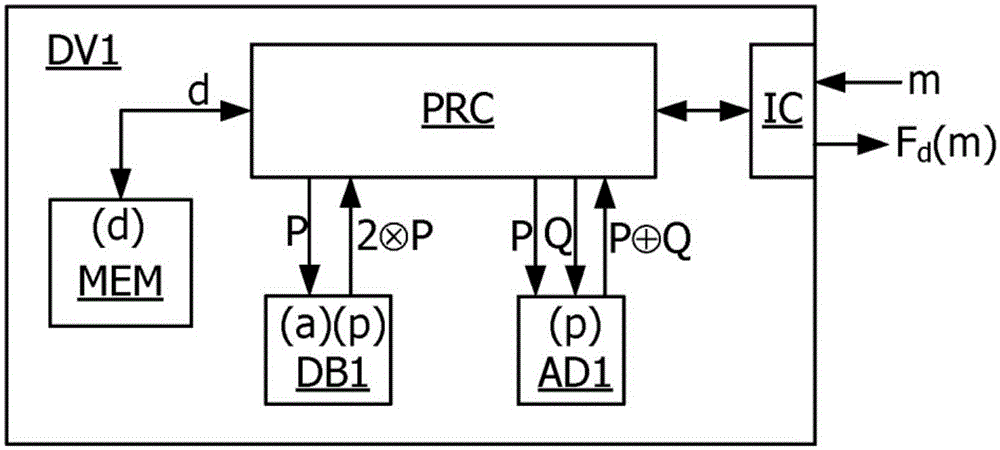
[0026] figure 1 An electronic device DV1 is represented in the form of a block diagram, configured to perform cryptographic cal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com