Automatic welding machine for stator casings
A technology for automatic welding machines and stator casings, applied in welding equipment, welding equipment, auxiliary welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of low processing efficiency and poor quality of stator casings, and improve welding processing quality, processing efficiency, and high accuracy , the effect of reasonable structural design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
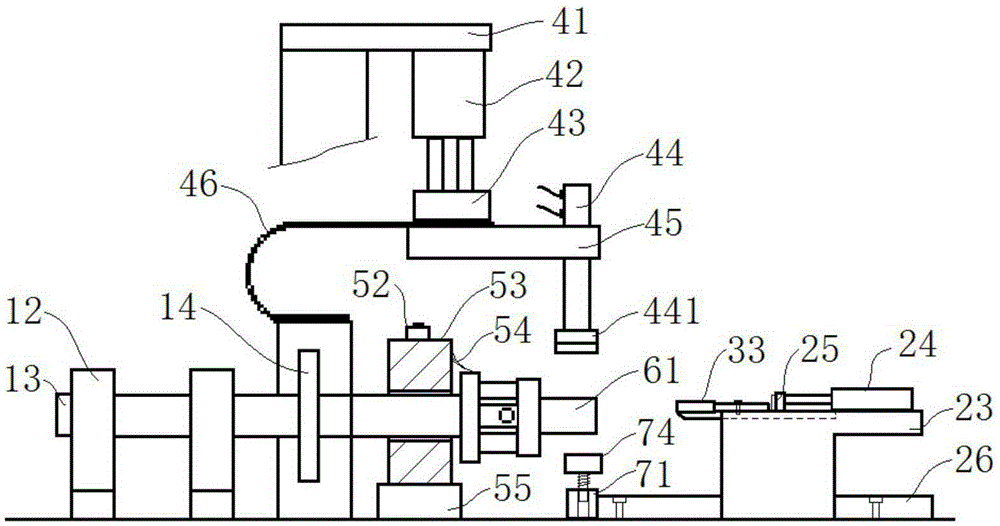
[0036] combine Figure 1 to Figure 7 , a stator shell automatic welding machine in this embodiment includes a control system, a drive mechanism, an element support mechanism, a welding mechanism and a push positioning mechanism, and the drive mechanism includes a motor 11, a bearing seat 12 and a main shaft 13, wherein the motor 11 is a stepping motor, which can accurately control the angular displacement; the main shaft 13 is supported by two parallel bearing housings 12, and the main shaft pulley 14 is installed on the main shaft 13, and the main shaft pulley 14 is output by the power transmission belt and the motor 11. The shafts are connected, the motor 11 controls the rotation of the main shaft 13 through the belt transmission, and the inner ring surface of the transmission belt has stripes to increase the friction to ensure the accuracy of the rotation angle.
[0037] see Figure 6 , the component support mechanism in this embodiment includes a magnetic strip pivot 61, ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] combine Figure 5 , a stator shell automatic welding machine of this embodiment, its basic structure is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that: the welding machine in this embodiment also includes a pressing mechanism, which includes a pressing plate pillar 51, The first platen beam 52, the upper platen 53, the lower platen 55, the second platen beam 56 and the third cylinder 58, the platen pillar 51 is vertically fixed, the upper end of the platen pillar 51 is hinged with the first platen beam 52, and the first platen The crossbeam 52 can rotate around the hinge shaft, and the other end of the first platen crossbeam 52 is fixed on one side of the upper platen 53 by bolts; the other side of the upper platen 53 is fixedly connected with the second platen crossbeam 56; One end of crossbeam pull rod 57 is hinged, and the lower end of crossbeam pull rod 57 is hinged with the piston rod of the 3rd cylinder 58, then can control upper platen 53 to rotate arou...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The basic structure of the automatic stator shell welding machine of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 2, the difference being that the angle between the chamfering slope 312 and the horizontal plane in this embodiment is 45°. In order to visually detect whether the welding interval angles between different magnetic strips are the same, a pointer 54 is fixed on the side of the upper platen 53 towards the chassis 64, and the tip of the pointer 54 rests on the circumferential surface of the end of the chassis 64. Scale marks are provided on the end peripheral surface of the chassis 64 . Every time a magnetic conductive strip is welded, the motor 11 will automatically rotate a set angle, and the cooperation between the pointer 54 and the dial can reflect the accumulated deviation after multiple uses, so as to adjust the equipment in time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com