Method for determining thickness of blades of hydraulic torque converter based on water-drop-shaped airfoil function
A hydraulic torque converter and blade thickness technology, applied in the field of hydraulic torque converter, can solve problems such as relying on experience design, distortion of coordinate conversion process, and complicated design process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
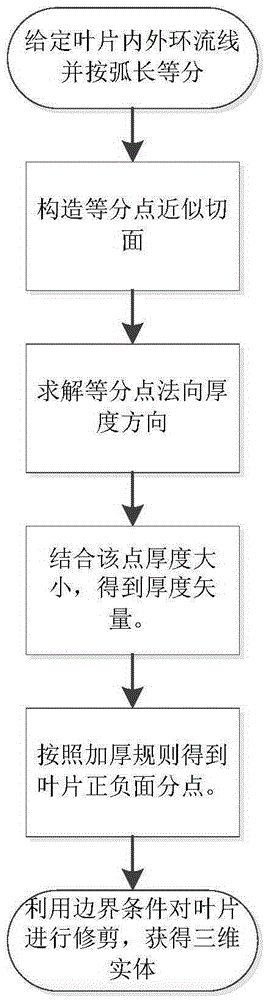
[0027] The present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and a design example of the turbine blades of the twin-turbine hydraulic torque converter.
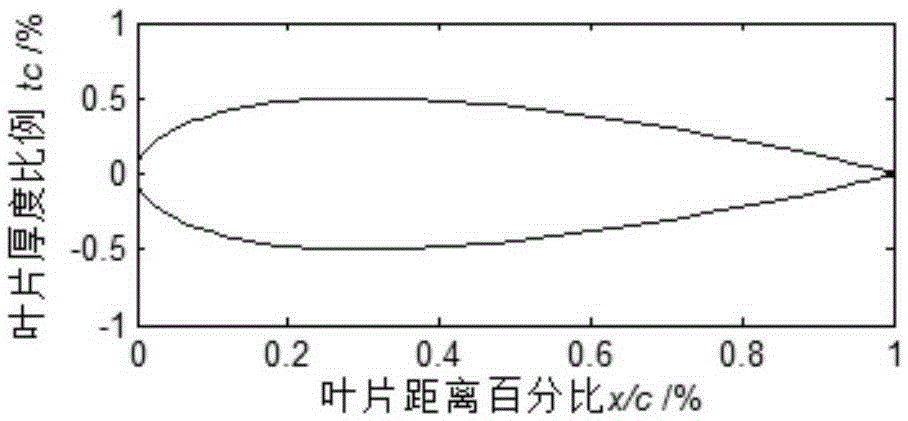
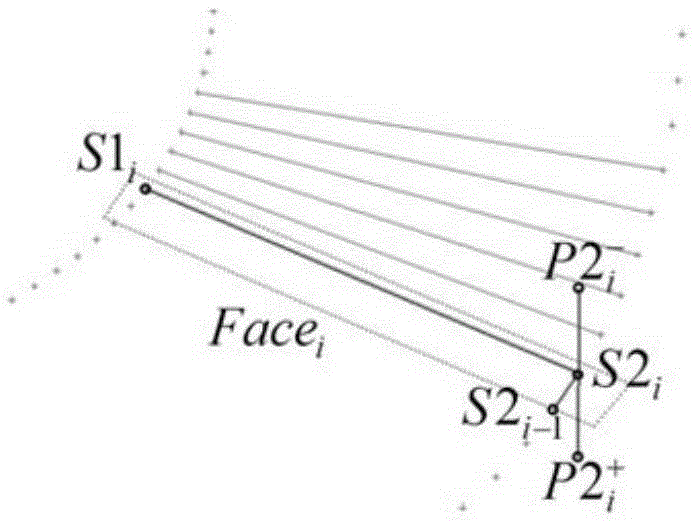
[0028] Usually, the first turbine and guide wheel of the twin-turbine hydraulic torque converter are in the shape of a blunt inlet and a slender water drop at the outlet. When designing a hydraulic torque converter blade, the middle flow surface is usually thickened, but since the bone line of the blade is generally straight, to design a drop-shaped blade shape, it is necessary to put forward higher requirements for the blade thickening method. Require. For the traditional design methods, such as the equiangular projection method, the design is more difficult and requires repeated attempts by the designer. The present invention introduces the thickness vector, and applies the drop-shaped thickness function value to the thickness vector. Through the thickness design vectori...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com