A polynomial method of constructing a non-deterministic (NP) turing machine
A formal, data technique applied in the field of polynomials for constructing non-deterministic (NP) Turing machines, capable of solving problems such as ignorance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
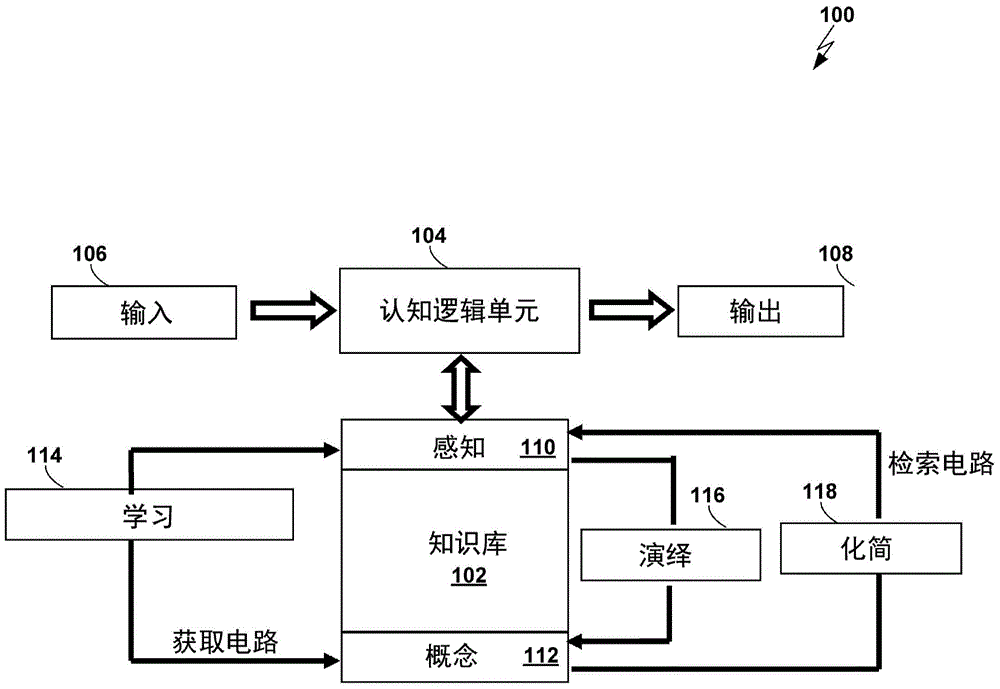
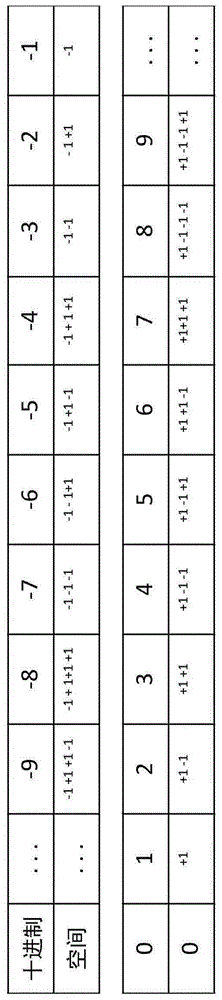
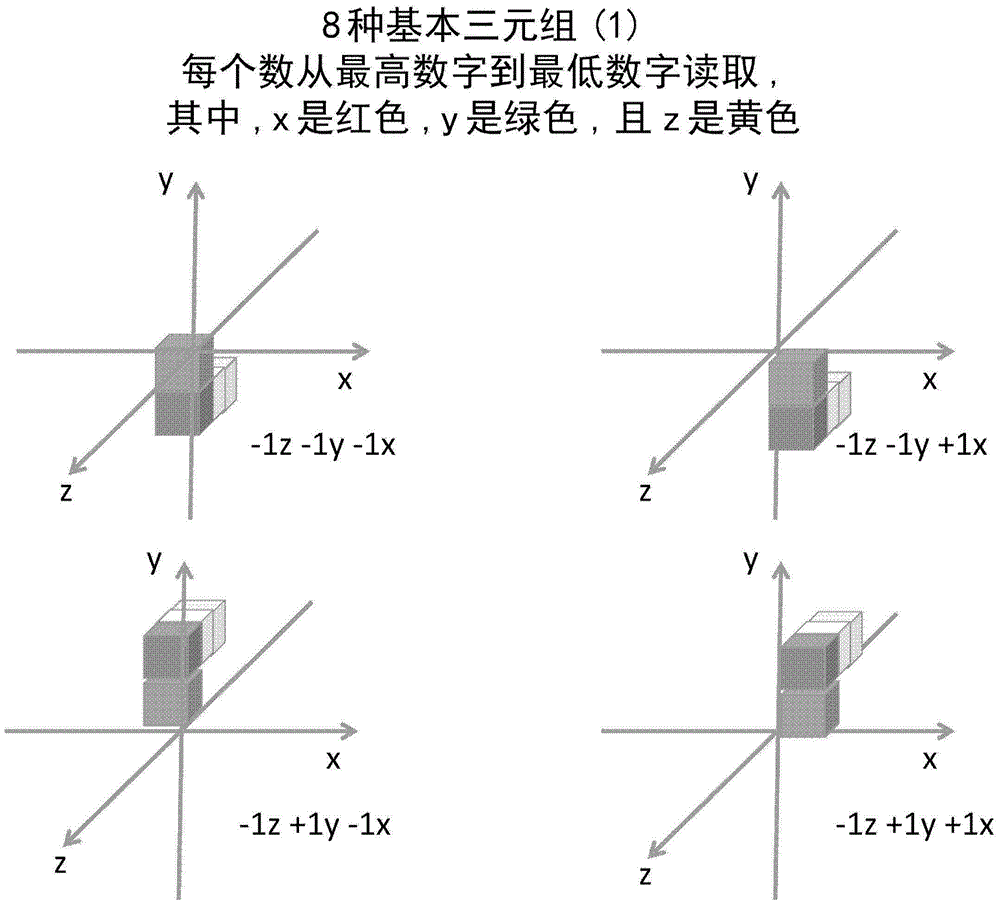
[0025] In general, a non-deterministic Turing machine (NTM) implemented according to an embodiment of the present invention includes four subsystems: (1) a spatial binary enumeration system; (2) a 3-dimensional relational system; (3) a simulated human logic system ; and (4) a bijective collective memory system.
[0026] For example, see figure 1, shows a schematic diagram of a non-deterministic Turing machine (NTM) 100 according to an embodiment of the present invention. NTM 100 includes memory 102 referred to herein as a "bijective set" memory because it contains data representing bidirectional relationships as will be described in more detail below. Memory 102 is also referred to herein as a "knowledge base," as that term is used in US Patent No. 6,611,841. NTM 100 also includes a simulated human logic system 104, which is also referred to herein as a cognitive logic unit or a parallel information processor. Cognitive logic unit 104 does not work in the same way as a trad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com