Mesh subdivision method based on laplacian coordinates
A grid subdivision and target grid technology, applied in image data processing, 3D modeling, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of no analytical form and complexity of subdivided surfaces
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
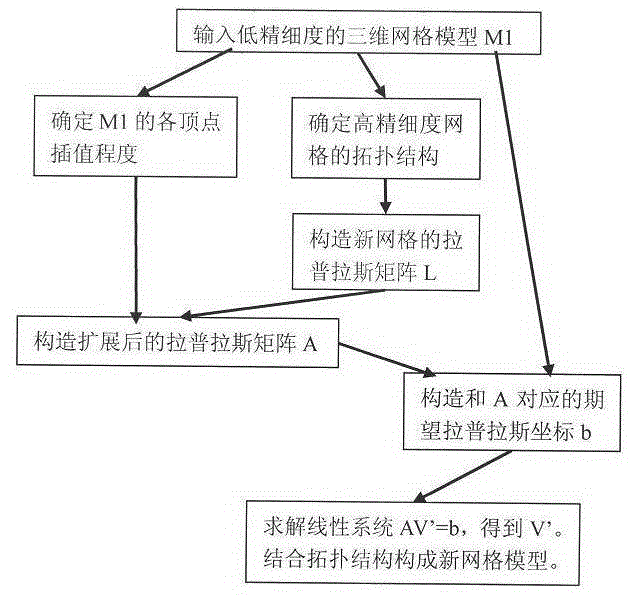
[0021] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
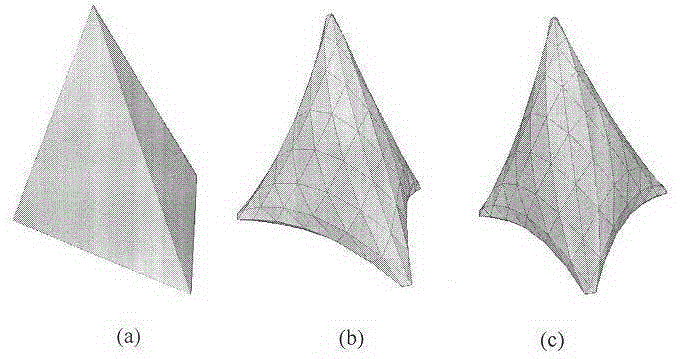
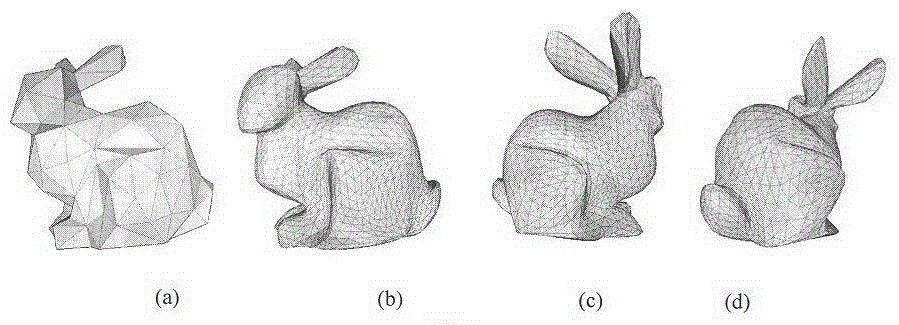
[0022] First, input a low-precision 3D mesh model and set it to M1. It includes the set of vertices V={v0,v1,...,vi,...}, the set of edges E={e0,e1,...,ej,...}, and the set of faces F={f0,f1,...,fk,... }. May wish to set the number of vertices to N.
[0023] In order to determine the degree of interpolation or approximation of each vertex in V, it is necessary to determine an approximation value cvi for each vertex vi. This value can be any positive number. When the value is larger, it means that the corresponding vertices in the new grid are closer to the original vertices, that is, closer to the interpolation. When the value is infinite, the original vertex is interpolated. When the value is smaller, it means that the point is more free, and its position is determined by the smooth factor.
[0024] The user can specify the interpolation degree value in the follo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com