Method for verifying safety of SM2 signature algorithm based on improved difference error attack
A technology of error attack and improved difference, which is applied in the direction of secure communication device, user identity/authority verification, digital transmission system, etc., and can solve problems such as irrecoverability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
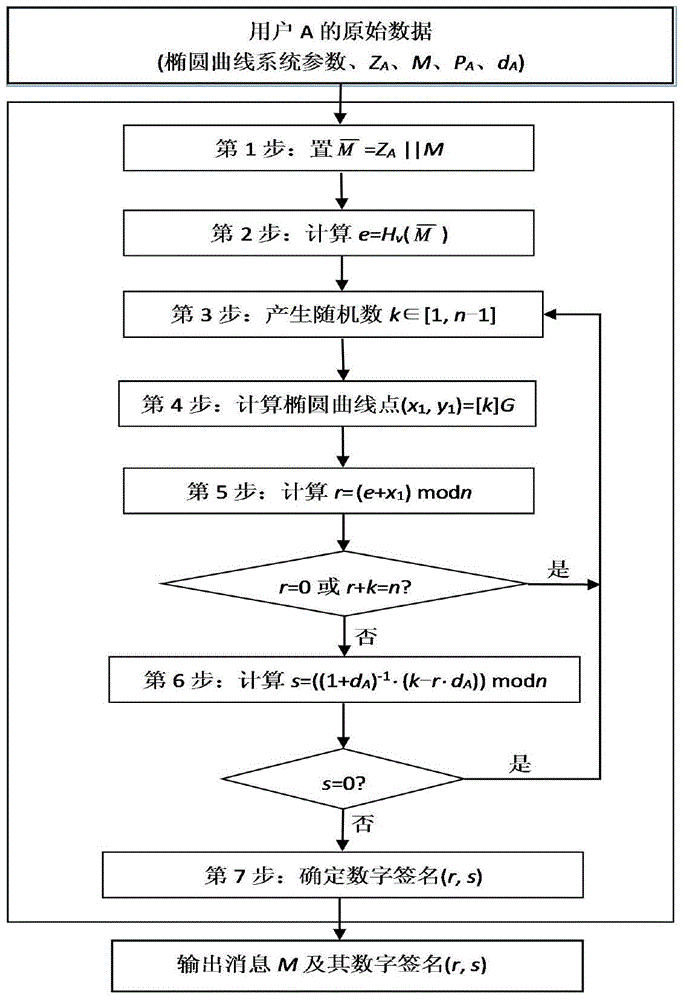
[0075] The following describes the present invention in further detail with reference to the accompanying drawings and an example, but the scope of the present invention is not limited in any way. In the embodiment, an experiment in which the error attack method of the present invention performs a lattice attack on the SM2 signature algorithm is used as an example to illustrate the effectiveness of the present invention.
[0076] 1) In the i-th iteration of the SM2 signature scalar multiplication operation, an error is injected to change part of the bit value of the intermediate y coordinate. In an implementation of SM2(F p -256) The signature algorithm is signed in the 32-bit chip of the signature algorithm, and the 248 rounds of point multiplication of the binary scalar multiplication iteration from right to left is about to end (you can check the injected error energy trace, and filter to meet the error injection time requirement ’S signature), to store the result Q 248 The ch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com