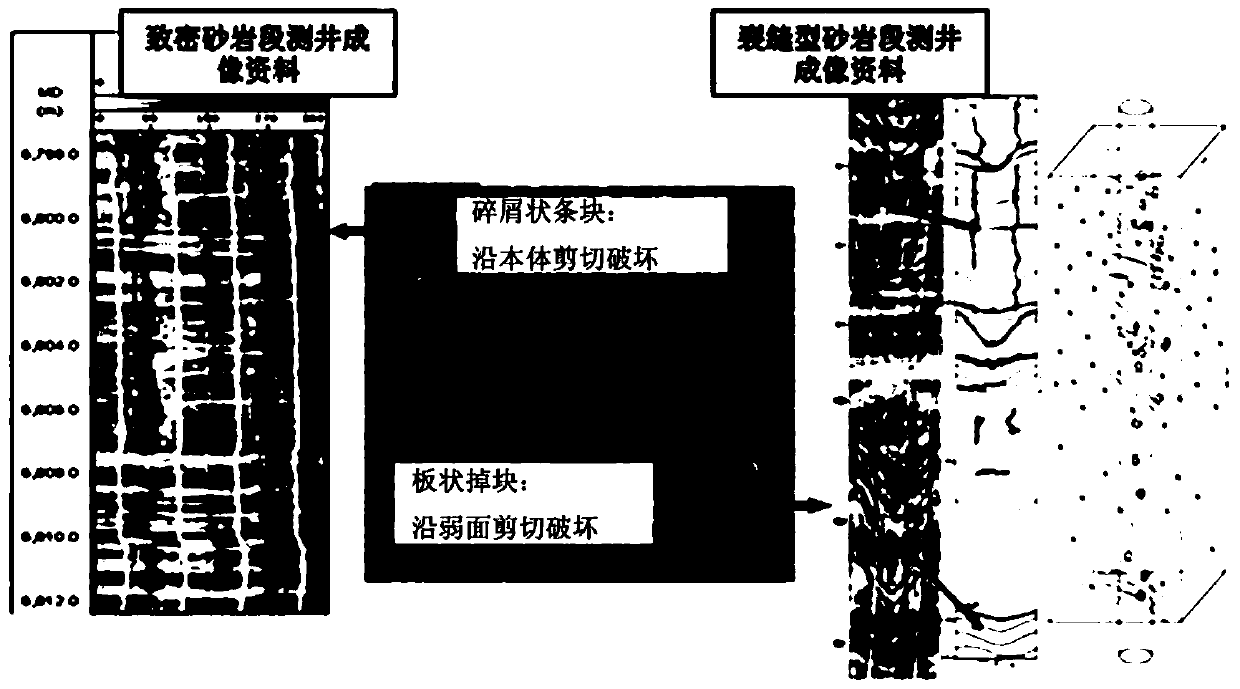
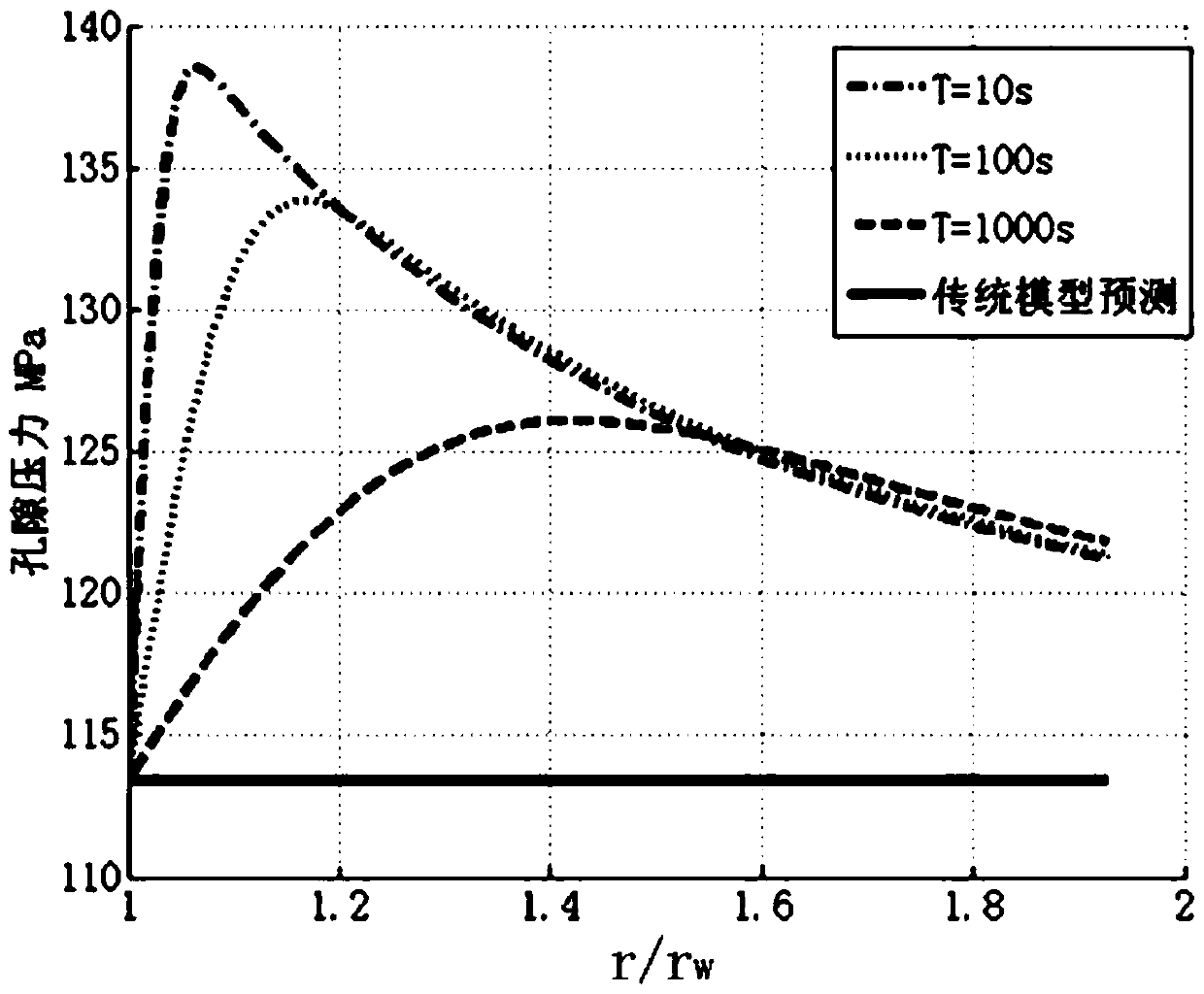
A Method for Predicting the Equivalent Density Window of Collapse Pressure in Weak Face Formation
A technology of collapse pressure and equivalent density, which is applied in the direction of earthwork drilling and production, wellbore/well components, etc., can solve problems such as field operation restrictions, wellbore instability, and inability to fully predict the formation collapse pressure window, so as to prevent complex downhole situations , The effect of preventing the instability of the well wall
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] In this embodiment, combined with the actual situation of a fractured tight sandstone formation in a certain block, the equivalent density window of the collapse pressure of the weak plane formation is predicted. The formation is 100-400m thick and is a set of red clastic rocks, mainly exposed in the northern part of a depression. The formation is divided into three lithological sections, from top to bottom are the first section, the second section and the third section. The first section is 20-70m thick, mainly composed of pebble-bearing sandstone and sandstone, with no fractures, and is a tight sandstone section; the second section is 40-260m thick, mainly composed of fine sandstone interbedded with thin mudstone, and relatively pure mudstone Thin layers appear; the thickness of the third section is 45-100m, mainly composed of maroon conglomerate, glutenite interbedded with pebble-bearing sandstone, and siltstone. Fractures are well developed in the second and third ...
Embodiment 2
[0244] In this embodiment, combined with the actual situation of a fractured tight shale formation in a certain block, the collapse pressure equivalent density window of the formation with weak planes is predicted. Its prediction method, principle, beneficial effect, etc. are the same as those in Example 1, except that the parameter values of shale weak plane formation are shown in Table 2.1.
[0245] Table 2.1 Parameter values of shale weak plane formation
[0246]
[0247] Substituting the parameter values in Table 2.1 into the model for calculation, the calculation results are as follows Figure 8 and Figure 9 Shown: If the allowable borehole expansion rate is given as 13%, the lower limit of the equivalent density of the collapse pressure of the tight shale section is 1.1g / cm 3 ; The lower limit of the collapse pressure equivalent density of the fractured shale section is 0.95g / cm 3 , the upper limit is 1.35g / cm 3 . Therefore, the collapse pressure equivalen...
Embodiment 3
[0249] In this embodiment, combined with the actual situation of a fractured tight carbonate formation in a certain block, the collapse pressure equivalent density window of the formation with weak planes is predicted. Its prediction method, principle, beneficial effect, etc. are the same as those in Example 1, except that the parameter values of shale weak plane formation are shown in Table 3.1.
[0250] Table 3.1 Values of various parameters in weak carbonate formations
[0251]
[0252]
[0253] Substituting the parameter values in Table 3.1 into the model for calculation, the calculation results are as follows Figure 10 and Figure 11 Shown: If the allowable diameter enlargement rate is given as 12%, the lower limit of the collapse pressure equivalent density of the tight carbonate formation is 1.45g / cm 3 ; The lower limit of the collapse pressure equivalent density window of fractured carbonate formations is 1.5g / cm 3 , the upper limit is 1.6g / cm 3 . The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com