A stitching method and system for digitized x-ray images
A line image and image technology, applied in image data processing, graphic image conversion, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency and long time-consuming stitching process, and achieve the effects of improving efficiency, reducing stitching time, and avoiding difficulties in feature point extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
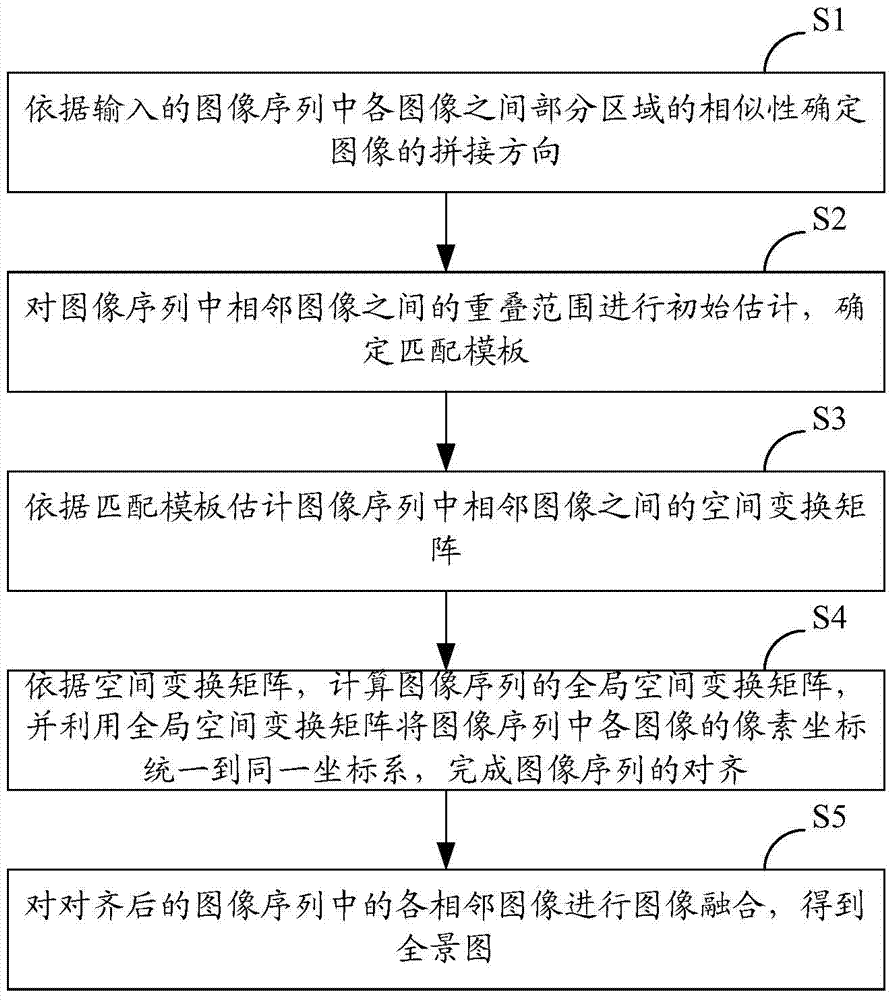
[0047] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a splicing method of digitized X-ray images, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0048] S1: Determine the stitching direction of the images according to the similarity of partial regions between the images in the input image sequence.
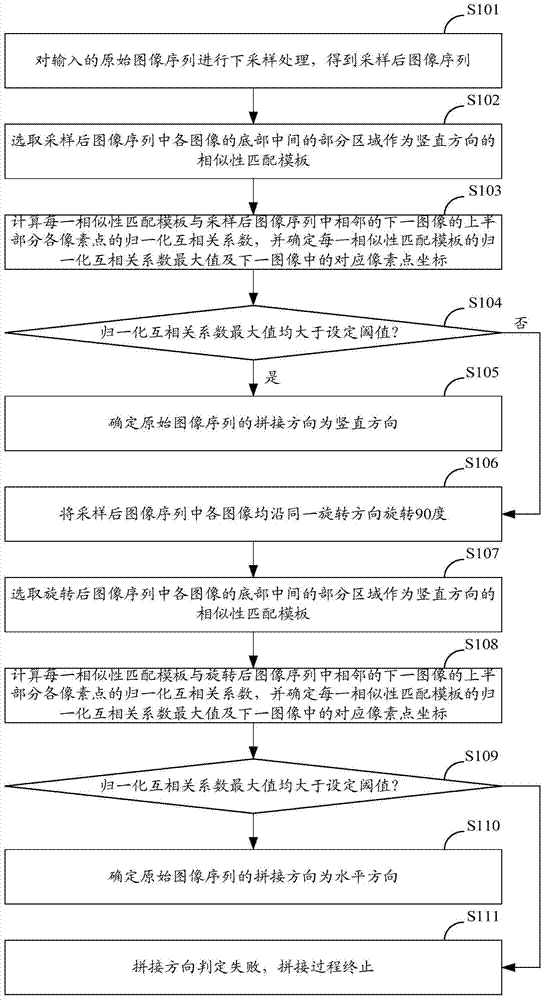
[0049] Further, as figure 2 As shown, step S1 may further include the following steps:
[0050] S101: Perform down-sampling processing on an input original image sequence to obtain a sampled image sequence.
[0051] In the present invention, in order to reduce the calculation amount of the subsequent image alignment process, it is necessary to perform down-sampling processing on the original image sequence, so as to reduce the size of the image to be processed subsequently and improve the processing speed.
[0052] Assume that the input original image sequence I={I containing n images 1 ,I 2 ,...,I n}, the corresponding image sequence after downsampling processing...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a splicing method of digitized X-ray images, such as Figure 10 shown. Different from Embodiment 1, the following steps are also included between step S4 and step S5:
[0113] S6: Determine the effective overlapping area between adjacent images according to the pixel coordinates of each image in the image sequence in the same coordinate system, and perform exposure compensation on the image sequence.
[0114] Further, as Figure 11 As shown, step S6 comprises the following steps again:
[0115] S61: Determine an effective overlapping area between adjacent images according to the pixel coordinates of each image in the sampled image sequence in the same coordinate system.
[0116] S62: Calculate in turn the median value of the pixel intensity difference of the corresponding pixel in the effective overlapping area between adjacent images in the sampled image sequence.
[0117] S63: In the sampled image sequence and the ori...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a mosaic system of digitized X-ray images, such as Figure 13 shown, including:
[0122] The splicing direction determination module 1 is used to determine the splicing direction of the images according to the similarity of the partial regions between the images in the input image sequence; the matching template determination module 2 is used to perform overlapping ranges between adjacent images in the image sequence The initial estimation is to determine the matching template; the spatial transformation matrix estimation module 3 is used to estimate the spatial transformation matrix between adjacent images in the image sequence according to the matching template; the alignment module 4 is used to calculate the global space of the image sequence according to the spatial transformation matrix transformation matrix, and use the global space transformation matrix to unify the pixel coordinates of each image in the image sequen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com