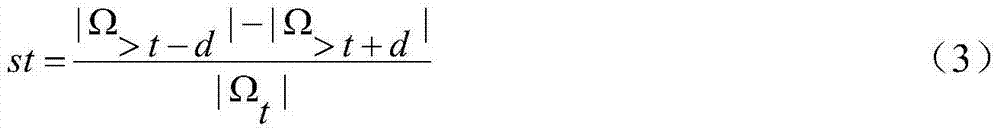Space debris star extraction and positioning method
A technology of space debris and positioning methods, which is applied in image data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., and can solve problems such as difficulty in segmenting adjacent space debris targets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] The specific steps of the space debris star point extraction and positioning method of the present invention are as follows:
[0051] (a) Starry sky image binarization processing:
[0052] For starry sky image I, first count the gray histogram of each pixel in the starry sky image, sort the pixels in the image in ascending order according to the pixel value, and remove the pixel with the smallest gray value λ 1 % of pixels, so that the influence of dark noise on the background can be weakened, and the λ with the highest gray value of the pixel can be removed 2 % of pixels, used to weaken the influence of strong noise and stars on the background estimation, where λ 1 ,λ 2 is the background threshold parameter set. Using the remaining (100-λ 1 -λ 2 )% pixels, obtain the gray mean μ and gray standard deviation σ of the background, and use the threshold μ+κσ to binarize the image, where κ is the segmentation coefficient that needs to be set. The binarization formula i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com