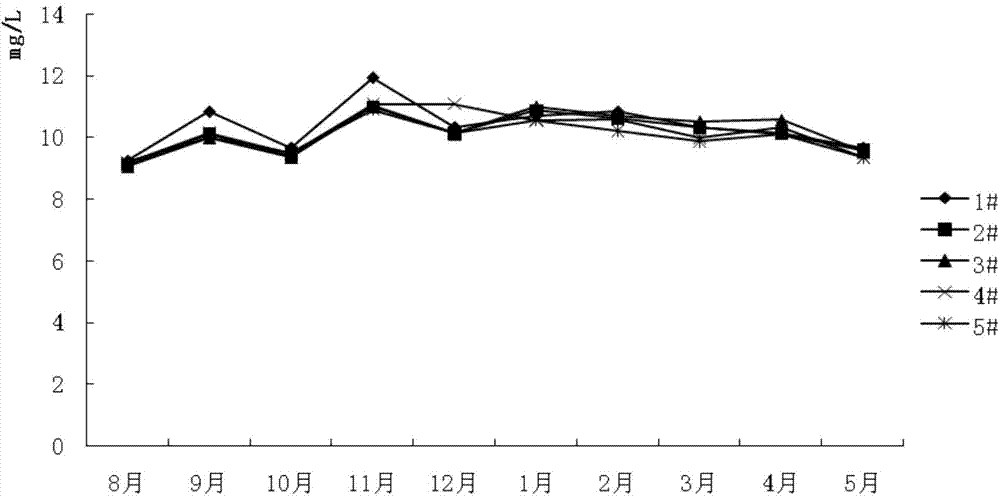
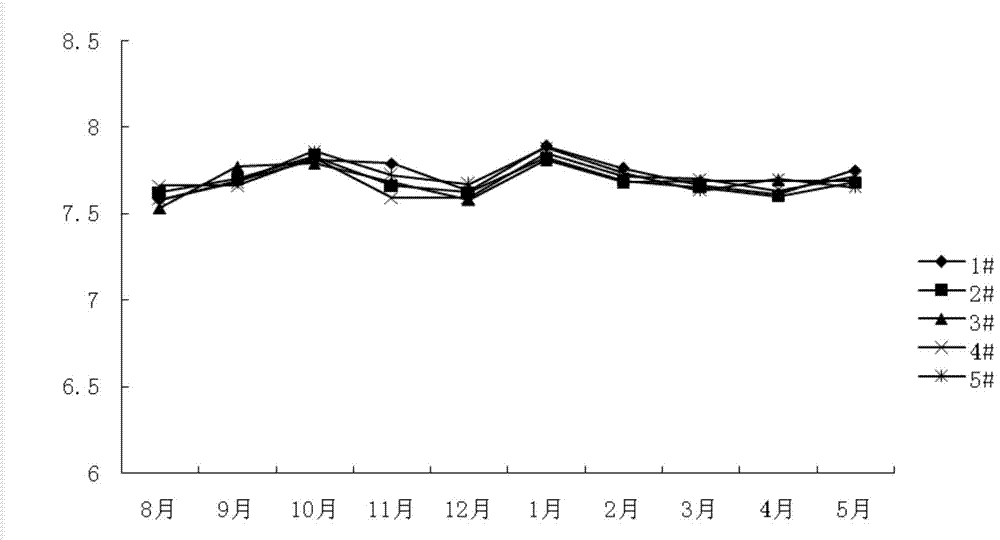
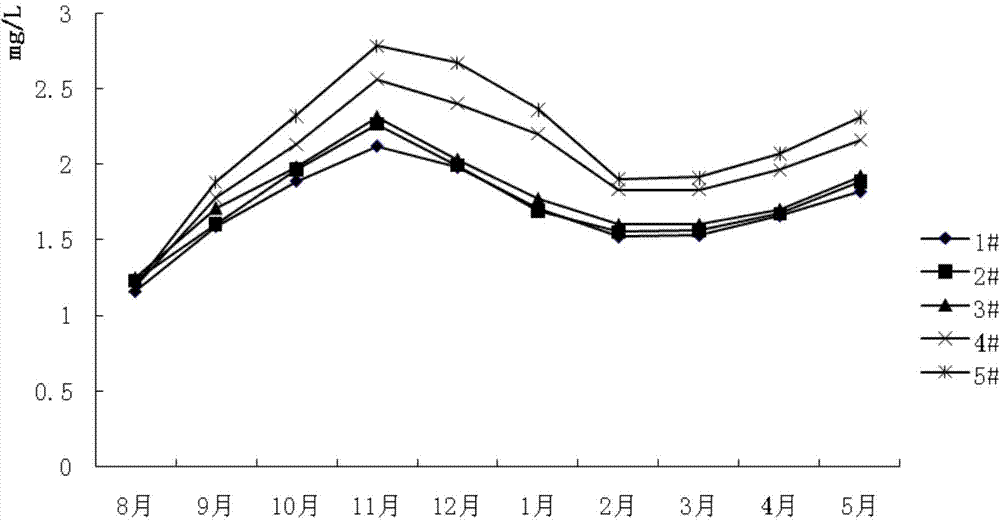
Method for ecologically breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and Odontobutis obscura in pond by utilizing artificial ecological base
An artificial ecology and ecological breeding technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, applications, fish farming, etc., can solve the problems of artificial ecological base and few applications, which are conducive to habitat and predation, improve survival rate, and improve the quality of life. social and economic effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method for applying an artificial ecological base to ecological breeding in ponds of giant river prawns and snakehead snakeheads, comprising the following steps:
[0038] 1. Pond selection: Choose 5 ponds with good water sources and convenient drainage, with an area of 4.5, 4.6, 4.7, 4.5 and 5.1 mu respectively. , each pond is equipped with a 0.2kw / acre bottom aerator and a 0.5kw / acre submersible pump.
[0039] 2. The layout of the artificial ecological base in the pond and the formation of biofilm: In late June, the pond was strictly dredged and disinfected with quicklime. After a week, the artificial ecological base was placed in the pond, and the artificial ecological base was connected by ropes in the pond. Arranged in a Z" shape, the ropes are fixed on the edge of the pond with bamboo, and the density of the ecological base is 100, 75, 50, 25 and 0m respectively 3 / mu. After the artificial ecological base is laid out, the pond is filled with water, and then o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com