A Pedestrian Navigation Method Based on Relative Pose Measurement
A relative pose and pedestrian navigation technology, applied in the field of navigation and positioning, can solve problems such as loss of navigation and positioning, error accumulation, measurement data including drift, etc., and achieve high-precision positioning and accurate extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] Hereinafter, the preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
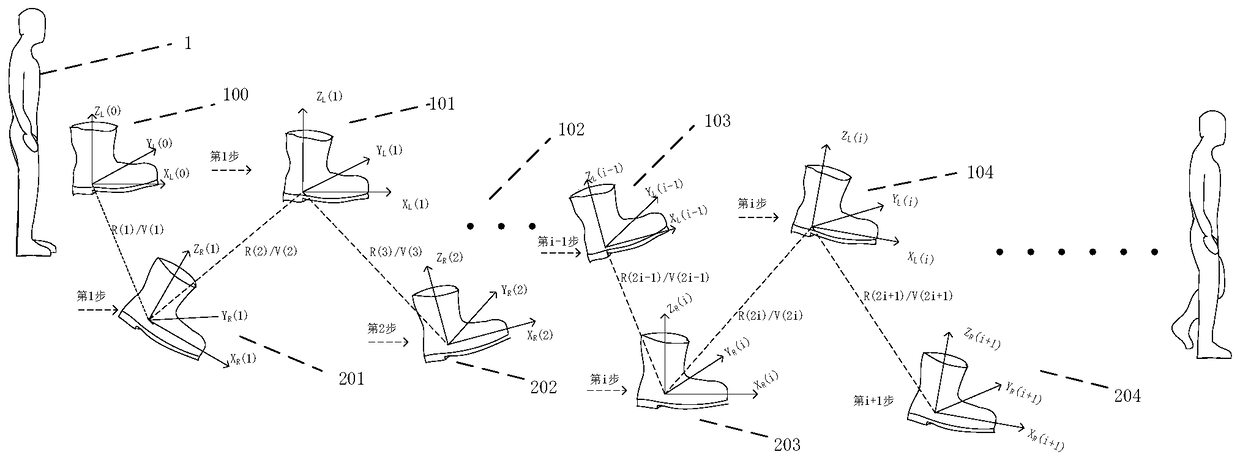
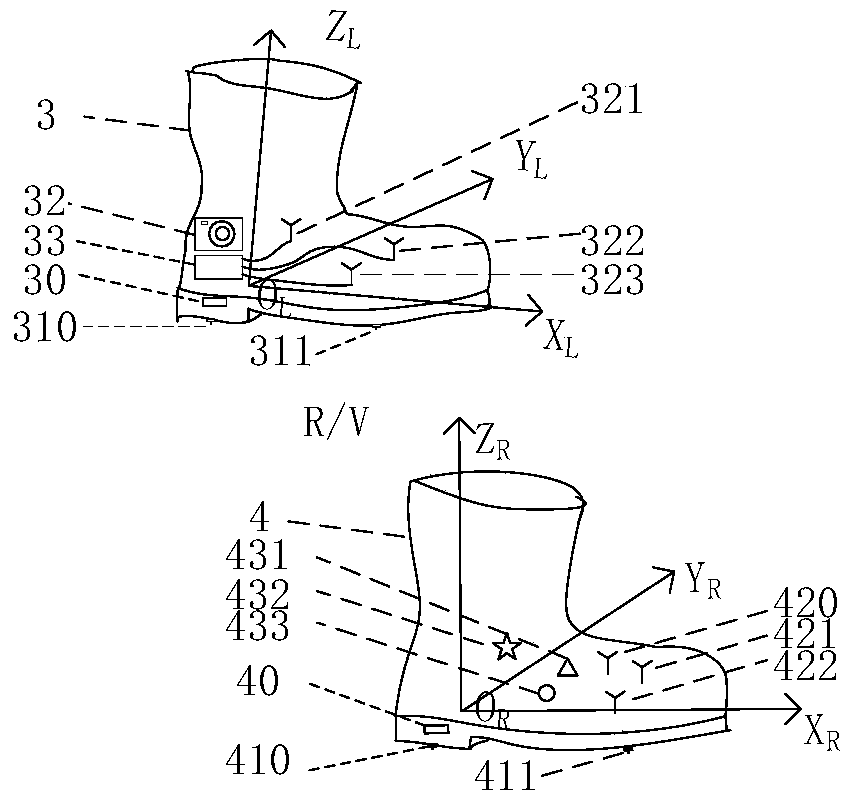
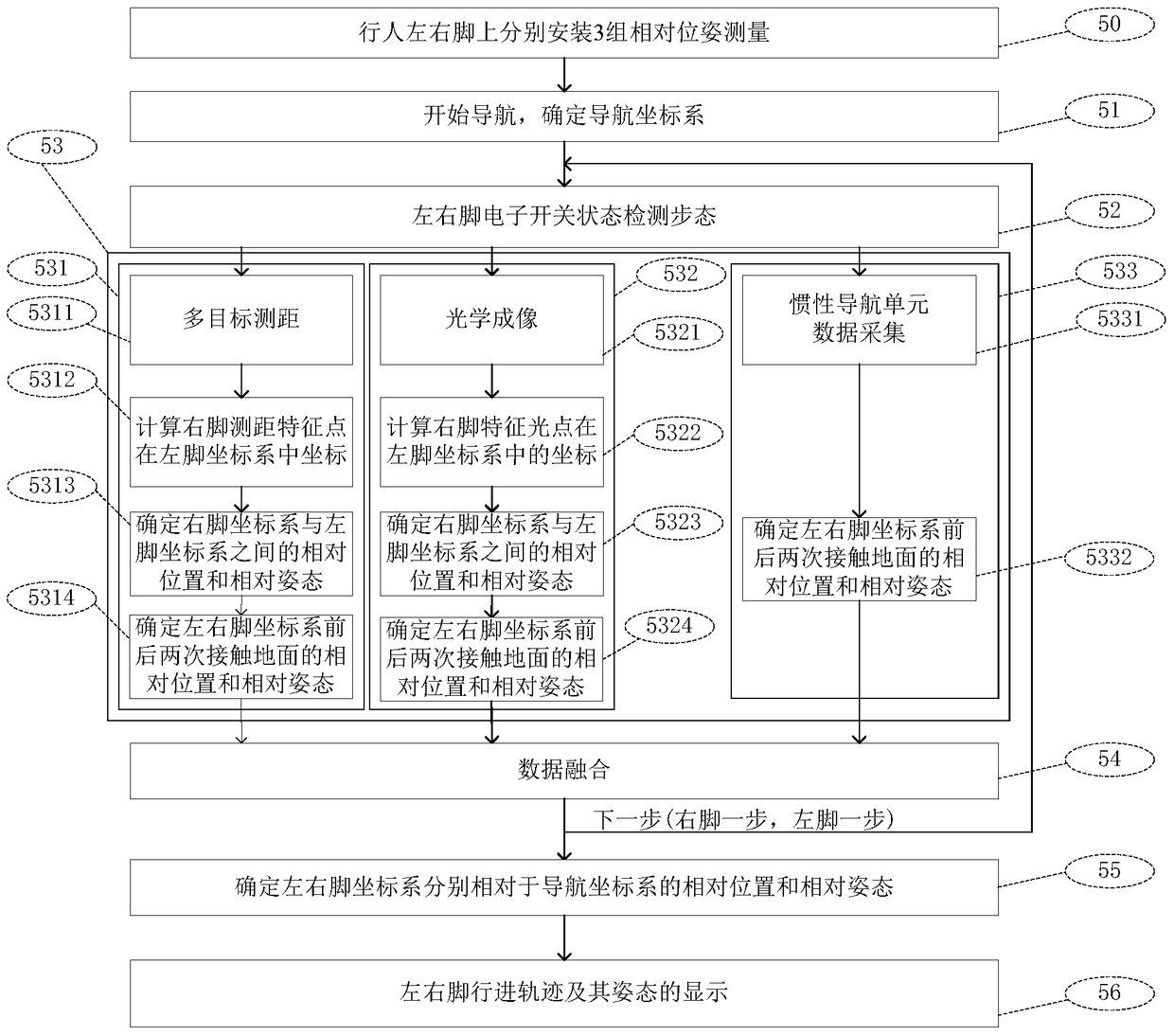
[0022] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a pedestrian navigation method based on relative posture measurement. As shown in the figure, the left foot coordinate system O is constructed on the left foot and right foot of pedestrian 1 respectively. L -X L Y L Z L And the right foot coordinate system O R -X R Y R Z R ,Record the pedestrian’s left foot coordinate system of 100 before the pedestrian takes the first step O L (0)-X L (0)Y L (0)Z L (0); When the left foot steadily stops on the ground, the right foot takes the first step and touches the ground 201, starts the first relative pose measurement, and measures the right foot coordinate system O R (1)-X R (1)Y R (1)Z R (1) Relative to the left foot coordinate system O L (0)-X L (0)Y L (0)Z L (0) relative position V(1) and relative posture R(1), and then when the right foot stops stead...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com