Fast recognition algorithm of similarity data in big data set
A recognition algorithm and similarity technology, applied in the field of big data processing, can solve the problems of occupying a large amount of CPU time and memory space, increasing the time and space overhead, and reducing the performance of similarity data recognition, so as to ensure the validity and accuracy, and the calculation cost is fixed. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
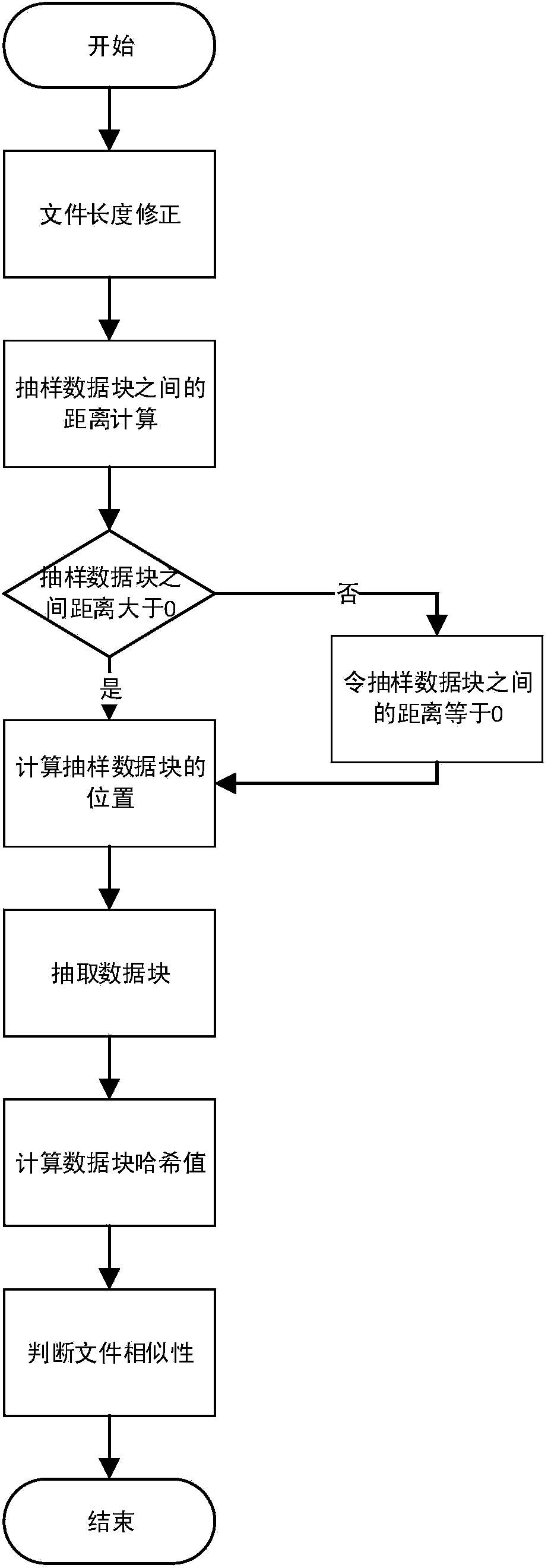
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, the algorithm flow process of the present invention has the following steps:
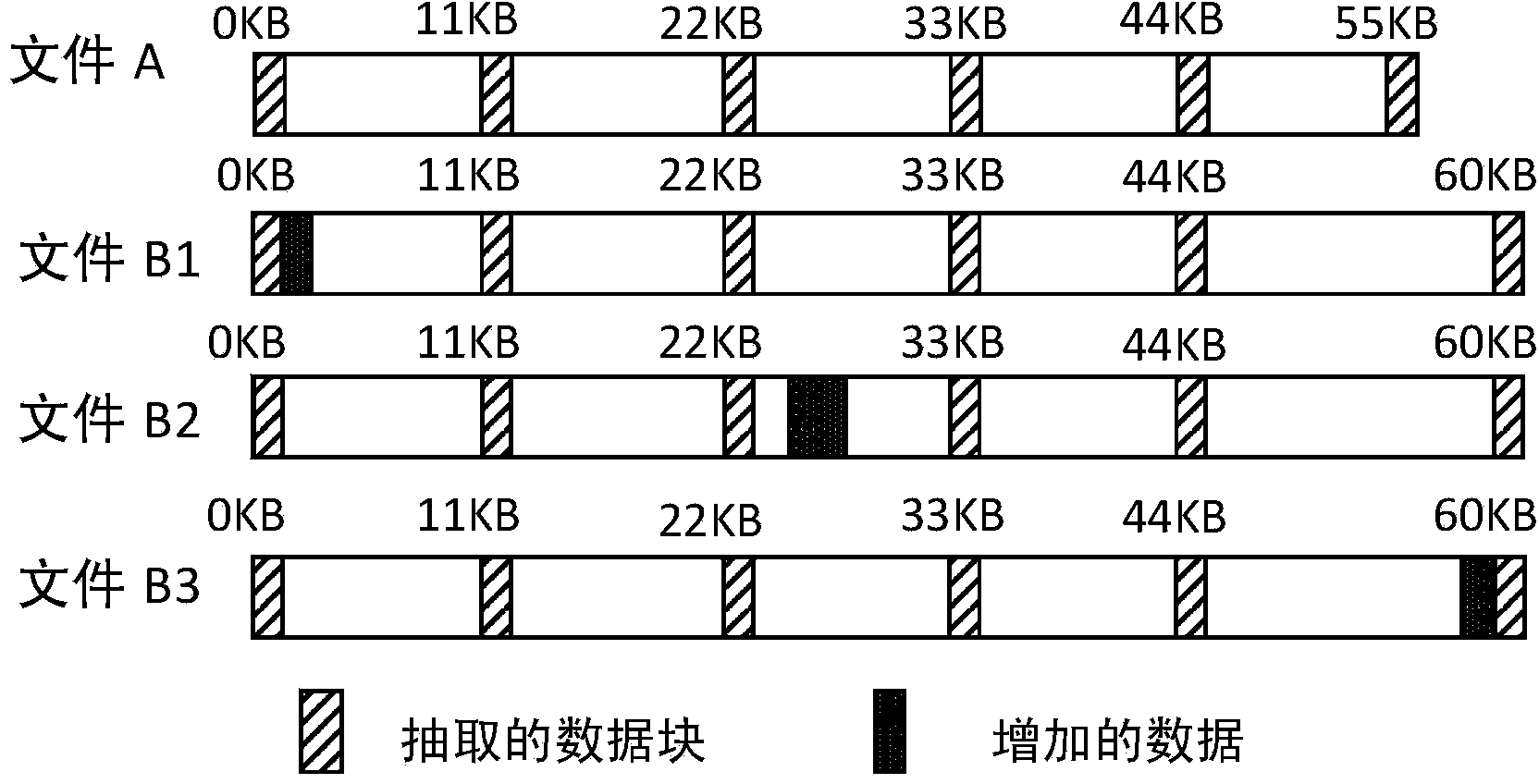
[0037] (1), the correction of data file length, before carrying out similarity judgment to data file, at first obtain the length of data file, the length of data file is divided by a position influence factor, then the quotient that obtains is multiplied by position influence factor, Finally, the resulting product is used as the corrected data file length. The correction of the length of the data file is to avoid the failure of similarity data identification due to the offset of the sampling data position due to the modification of the data file.
[0038] (2), calculate the distance between the sampled data blocks, subtract the length of the data file after correction from the product of the length of the sampled data multiplied by the number of sampled data blocks, and then divide the obtained difference by the difference of the number of sampled data blocks minus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com