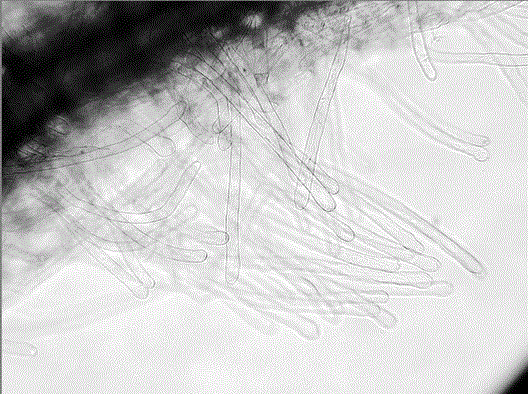
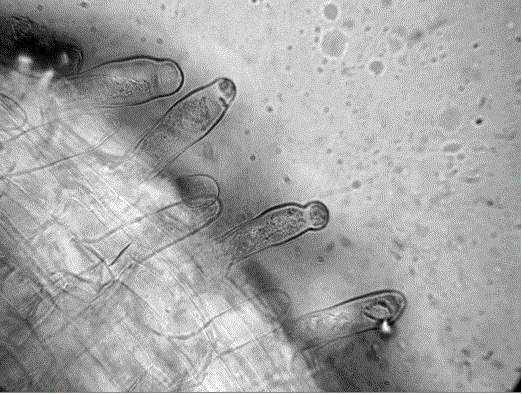
Cultivation method for observing Plasmodium infestation of Brassicaceae plants
A technology of Brassicaceae and Plasmodium, applied in the field of plant pathology research, can solve the problems of unclear observation results, many interference factors, complicated operations, etc., and achieve the effect of convenient and clear observation, high transparency of root hairs, and convenient observation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Take fresh root tissue of Cruciferous plants infected by Plasmodium brassicae and crush it, filter it through gauze with a pore size of 25 μm, and centrifuge the filtrate at a speed of 3000 r / min for 9 minutes to remove Supernatant, then add an appropriate amount of distilled water to the sediment, centrifuge at a speed of 4000r / min for 12min, remove the supernatant, then add an appropriate amount of distilled water to the sediment, centrifuge at a speed of 4000r / min for 12min, remove the supernatant solution, and then distilled water was added to the precipitate to suspend the precipitate until 1×10 7 CFU / mL of Plasmodium brassicae bacteria liquid, stored at 4°C for later use;
[0024] (2) Sow sterilized cruciferous seeds in the sterilized quartz sand, soak the quartz sand and seeds with MS basic culture solution, and put them under the light intensity of 100μmolphotons / (m 2 .s), light time of 16h, temperature of 22°C, and humidity of 75% or more, cultivate until ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] (1) Take fresh root tissue of Cruciferous plants infected by Plasmodium brassicae and crush it, filter it through gauze with a pore size of 25 μm, and centrifuge the filtrate at a speed of 3000 r / min for 9 minutes to remove Supernatant, then add an appropriate amount of distilled water to the sediment, centrifuge at a speed of 4000r / min for 12min, remove the supernatant, then add an appropriate amount of distilled water to the sediment, centrifuge at a speed of 4000r / min for 12min, remove the supernatant solution, and then distilled water was added to the precipitate to suspend the precipitate until 1×10 7 CFU / mL of Plasmodium brassicae bacteria liquid, stored at 4°C for later use;
[0032] (2) Sow sterilized cruciferous seeds in the sterilized quartz sand, soak the quartz sand and seeds with MS basic culture solution, and put them under the light intensity of 100μmolphotons / (m 2 .s), the light time is 18h, the temperature is 20°C, and the humidity is above 75%, cultiv...
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) Take fresh root tissue of Cruciferous plants infected by Plasmodium brassicae and crush it, filter it through gauze with a pore size of 25 μm, and centrifuge the filtrate at a speed of 3000 r / min for 9 minutes to remove Supernatant, then add an appropriate amount of distilled water to the sediment, centrifuge at a speed of 4000r / min for 12min, remove the supernatant, then add an appropriate amount of distilled water to the sediment, centrifuge at a speed of 4000r / min for 12min, remove the supernatant solution, and then distilled water was added to the precipitate to suspend the precipitate until 1×10 7 CFU / mL of Plasmodium brassicae bacteria liquid, stored at 4°C for later use;
[0040] (2) Sow sterilized cruciferous seeds in the sterilized quartz sand, soak the quartz sand and seeds with MS basic culture solution, and put them under the light intensity of 100μmolphotons / (m 2 .s), light time of 17h, temperature of 21°C, and humidity above 75%, cultivate until the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com