Organic compositions to treat HSF1-related diseases
A technology of composition and disease, applied in the field of RNAi agent, human subject in pathological state, able to solve the problem of inactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0140] Several specific specific embodiments of the disclosure herein are described below.
[0141] In one embodiment, the disclosure herein relates to a composition according to any of the foregoing embodiments for use in a method of treating HSF1-related diseases in an individual, the method comprising administering to the individual a therapeutically effective amount of Of the composition.
[0142] Several specific specific embodiments of this embodiment are described below.
[0143] In one embodiment, the disclosure herein relates to a composition according to any of the above embodiments for use in a method of inhibiting HSF1 expression in an individual, the method comprising administering to the individual a therapeutically effective amount of according to any of the above embodiments Of the composition.
[0144] One embodiment of the disclosure herein is the use of the composition according to any of the above embodiments in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of...
Embodiment 1
[0929] Example 1. Sequence of RNAi agent against HSF1
[0930] Table A1 above provides a list linking the names of RNAi agents against HSF1 to the target sequence SEQ ID NO, as well as unmodified and modified variants. The actual sequence is provided below.
[0931] Table 1 provides the sequence of the target sequence (sense and antisense).
[0932] Table 2 provides exemplary unmodified variants (sense and antisense) of RNAi agents against HSF1.
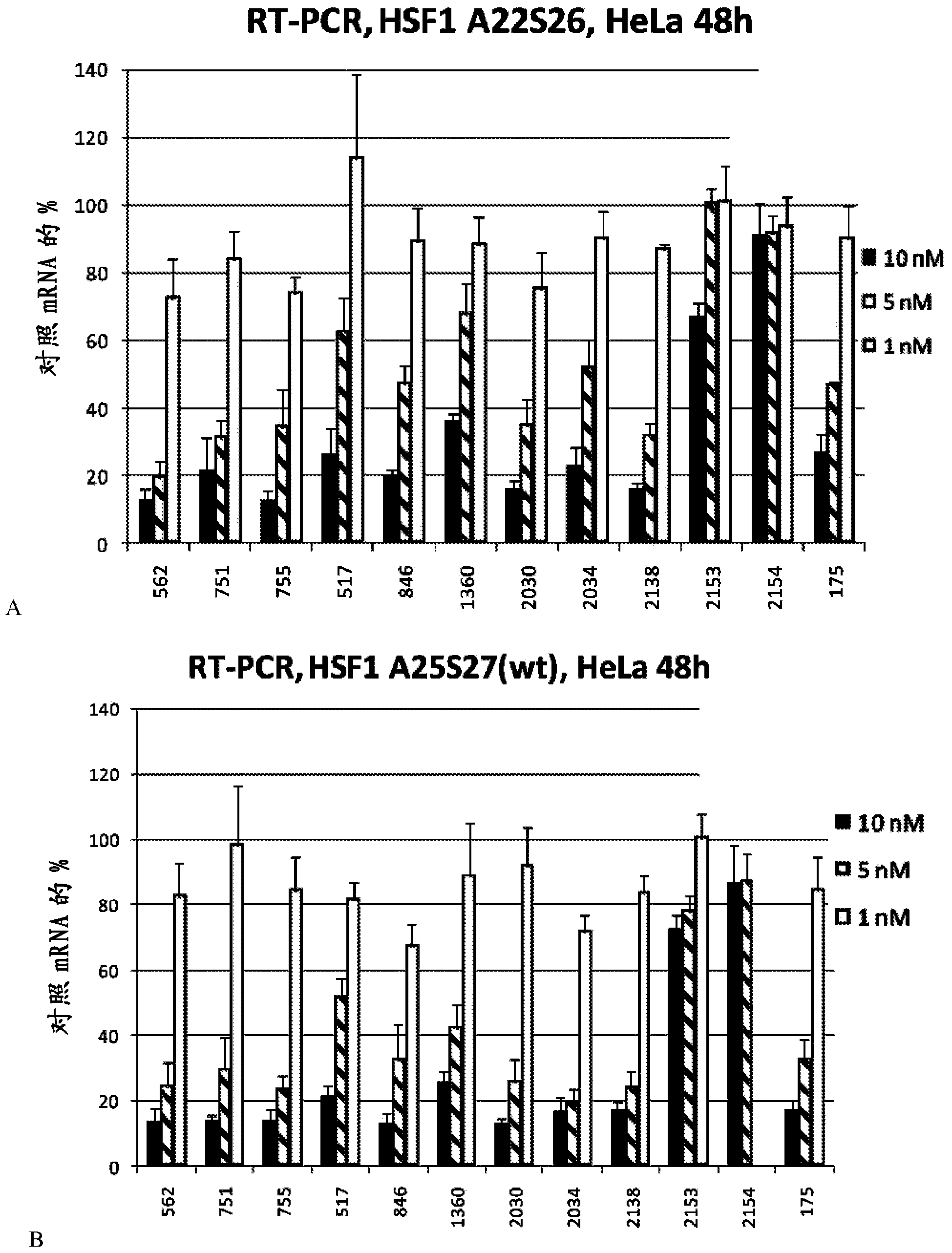
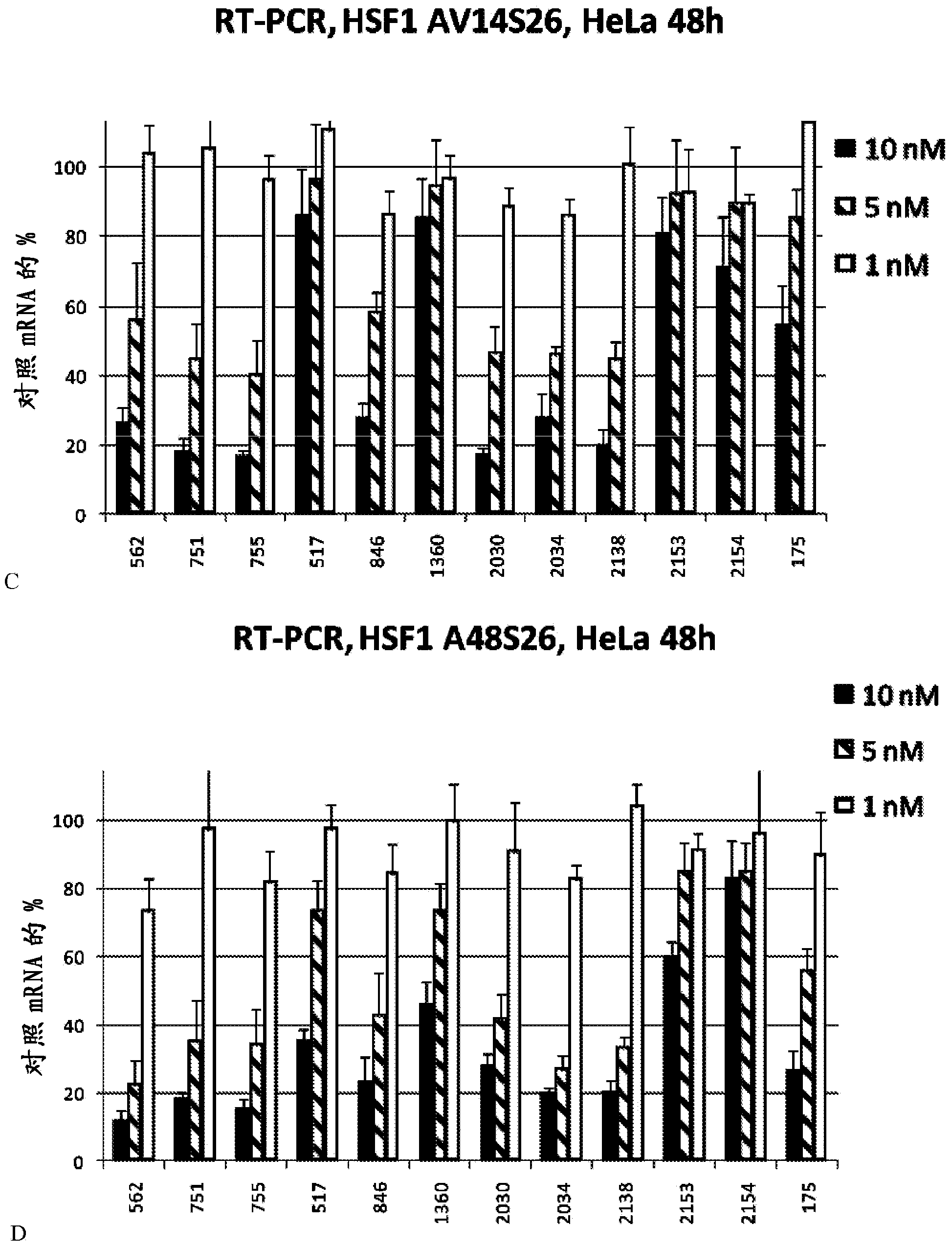
[0933] Table 3 provides exemplary modified variants (sense and antisense) of RNAi agents against HSF1. Seven different chemical modifications are presented to multiple nucleotide duplex sequences. For each of them, the prefix of the duplex name indicates the position (nt) of the HSF1 transcript. Therefore, hs_HSF1_562_ starts at nt562 of the HSF1 transcript. Therefore, all RNAi agents with the same prefix (for example, hs_HSF1_562_) have the same nucleotide sequence despite the difference in chemical modification. The suffix (for exampl...
Embodiment 1A
[0934] Example 1A. HSF1 RNAi agent sequence and target sequence
[0935] Table 1. HSF1 RNAi agent target sequence
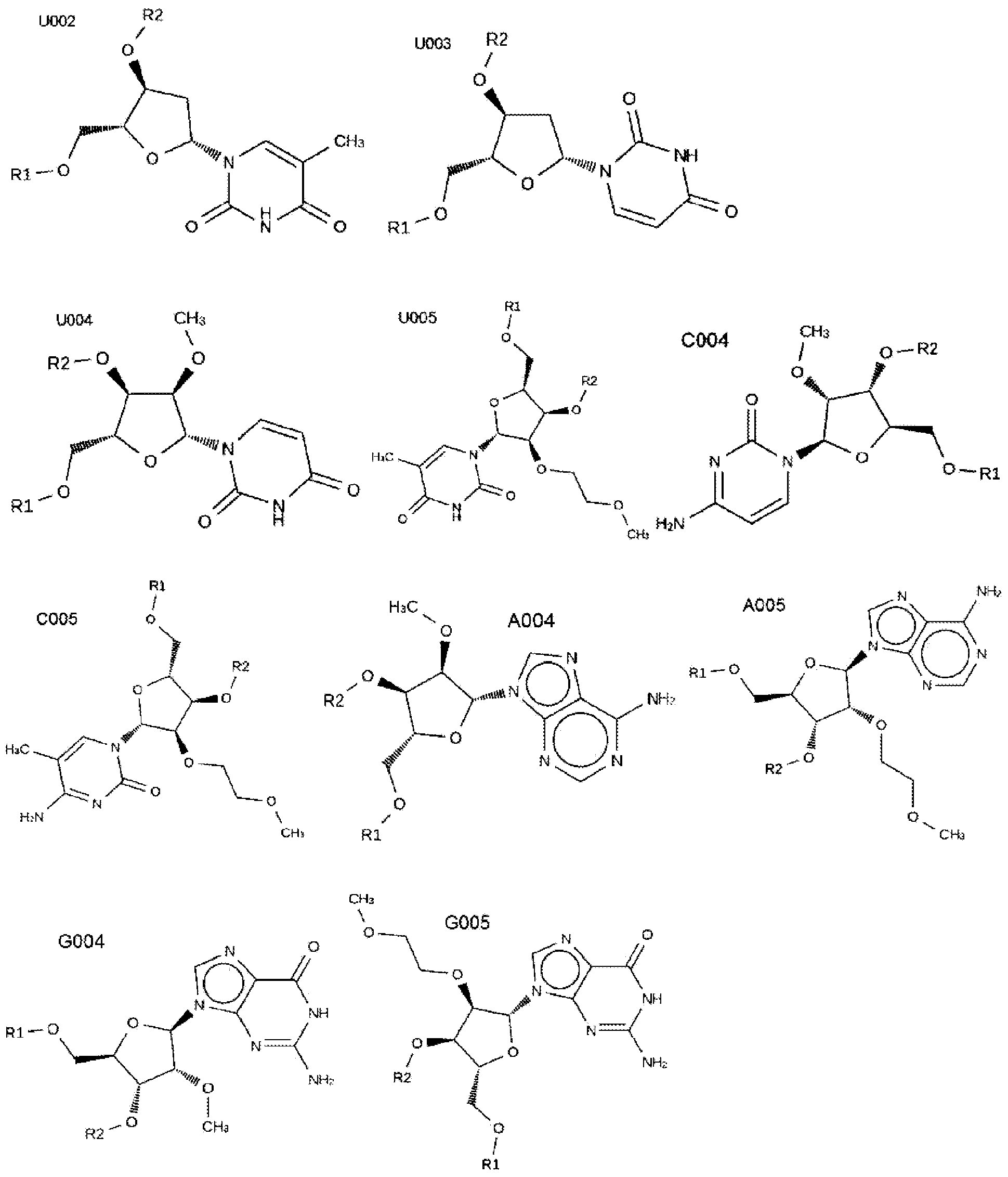
[0936] Provide the name of the HSF1 RNAi agent, as well as the antisense sequence (AS) and sense sequence (S) against the target sequence (each sequence name starts with hs_HSF1_*, where * is the name provided in each line; for example, "175_A22_S26" Same as "hs_HSF1_175_A22_S26", etc.). Note that the target sequence is presented as DNA (with DNA nucleotides and T instead of U). The corresponding RNAi agent will contain the corresponding RNA sequence (with RNA nucleotides and U instead of T). The RNAi agent may optionally further include terminal UU or TT on either or both strands, and may include modifications, as shown in the modification example group below.
[0937] In various embodiments, it refers to "RNAi agent (having) Table 1 (sequence)", "RNAi agent comprising a first strand and a second strand, wherein the sequence of the first strand includes (or) the seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com