Method for reducing plant cell browning risk through absorption of quinone substances with silica gel
A silica gel adsorption and plant cell technology, which is applied in the biological field of plant cells, can solve the problems of plant cell culture system instability, production capacity decline, etc., and achieve high adsorption target specificity, improved capacity, improved stability and efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
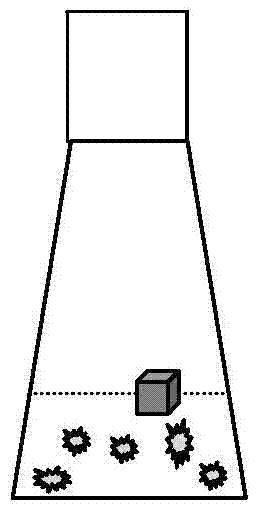
[0028] This example relates to a method for inhibiting the browning of yew cells by using sponge-like silica gel to absorb quinones. Including the following steps:
[0029] (1) Preparation of sponge-like silica gel blocks: Take a food-grade sponge silica gel plate, cut into small pieces of 1 cm square, wash with ultrapure water, sterilize at 121 degrees for 20 minutes, and set aside.
[0030] (2) Establishment of the yew culture system: Take a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask, add 75ml of B5 medium, add 25g / L of sucrose, 4mg / L of plant hormone naphthalene acetic acid, and 0.15mg / L of 6-benzylbenzylaminoadenine , adjust the pH to 5.8, and seal it with a breathable sterile film. Sterilized for later use. After being lowered to room temperature, the yew cells were inoculated, and the inoculation amount was 12g / L (calculated according to the fresh weight of the cells). There were 20 groups in the experiment, and 10 bottles were the experimental group. After the inoculation, a piece of st...
Embodiment 2
[0036] In this example, the regenerated silica gel block used in Example 1 was used as an adsorbent, and the effect of inhibiting the browning of Taxus chinensis cells by adsorbing quinones on the silica gel block after elution and regeneration was investigated.
[0037] After the regenerated silica gel blocks were cleaned with ultrapure water, they were sterilized for use. All the implementation steps are exactly the same as in Example 1 except that the silica gel block used is for elution regeneration.
[0038] During the cultivation process, it was observed that: 5 bottles in the control group had obvious browning, and three of them were severely browned, and the cultures were dark reddish brown. The browning rate was 50%. The silica gel adsorption group was all normal without browning.
[0039] After the culture, samples were taken to measure the cell density and paclitaxel content. It was found that the cell density of the control group was 22±1.9g / L, while the cell den...
Embodiment 3
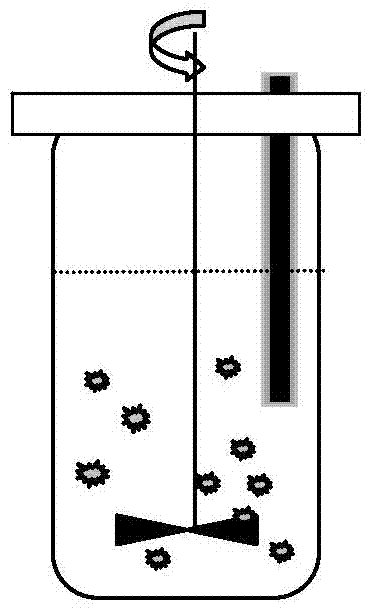
[0042] This example is a method of using rod-shaped silica gel to absorb quinones in a cell reactor to inhibit the browning of Taxus chinensis cells.
[0043] (1) Rod-shaped silica gel preparation: Take a medical-grade silica gel rod with a diameter of 1 cm, cut it into a length of 20 cm, clean it with ultrapure water, and install it on a 2-liter NBS cell culture reactor according to the electrode installation method (such as figure 2 as shown, figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the application of rod-shaped silica gel to adsorb quinones in the yew cell culture in the reactor; the thick rod extending into the yew culture at the lower end on the right represents the rod-shaped silica gel adsorption material, and the thorny ball represents the yew cell mass).
[0044] (2) Establishment of yew culture system: prepare 1 liter of B5 medium, which contains 4 mg / L of plant hormone naphthalene acetic acid, 0.15 mg / L of 6-benzylbenzylaminoadenine, and 25 g / L of sucrose, and adjust...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com