Blood volume measurement method and blood volume measurement device
A measurement method and blood volume technology, applied in blood flow measurement, diagnostic recording/measurement, blood vessel assessment, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in measuring blood pressure, impossibility of calibration, imposition on patients, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
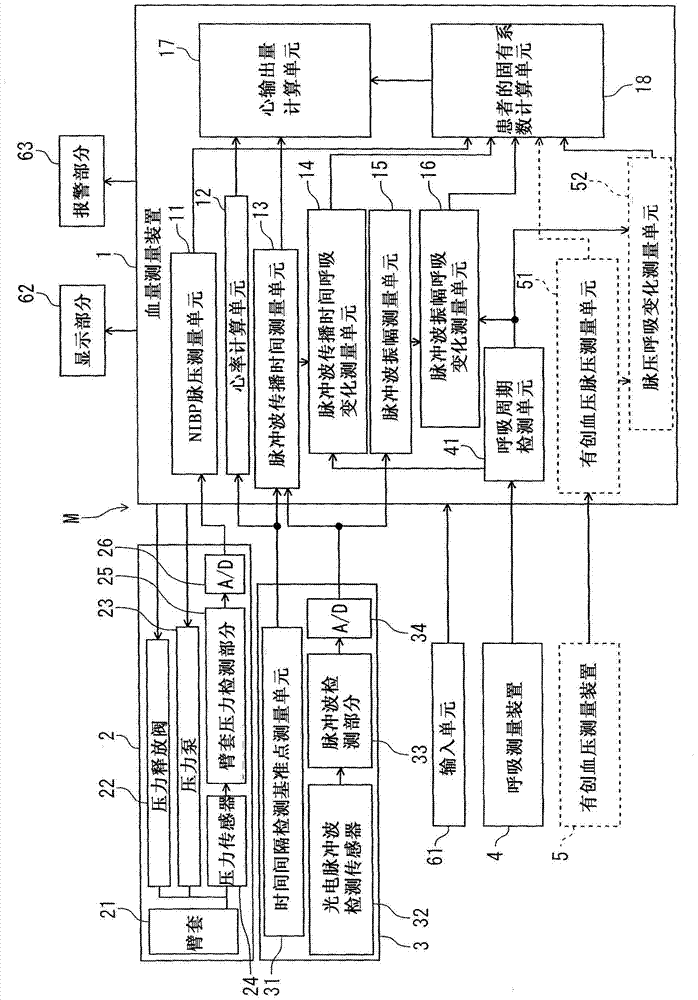
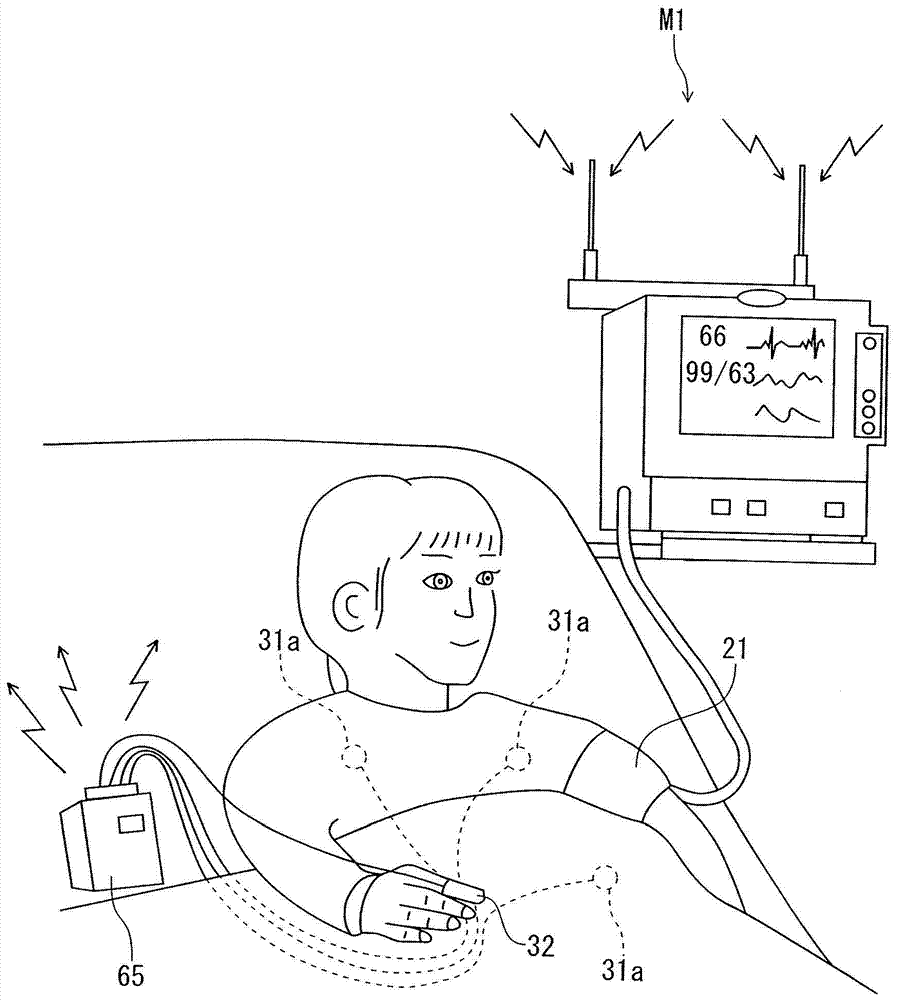
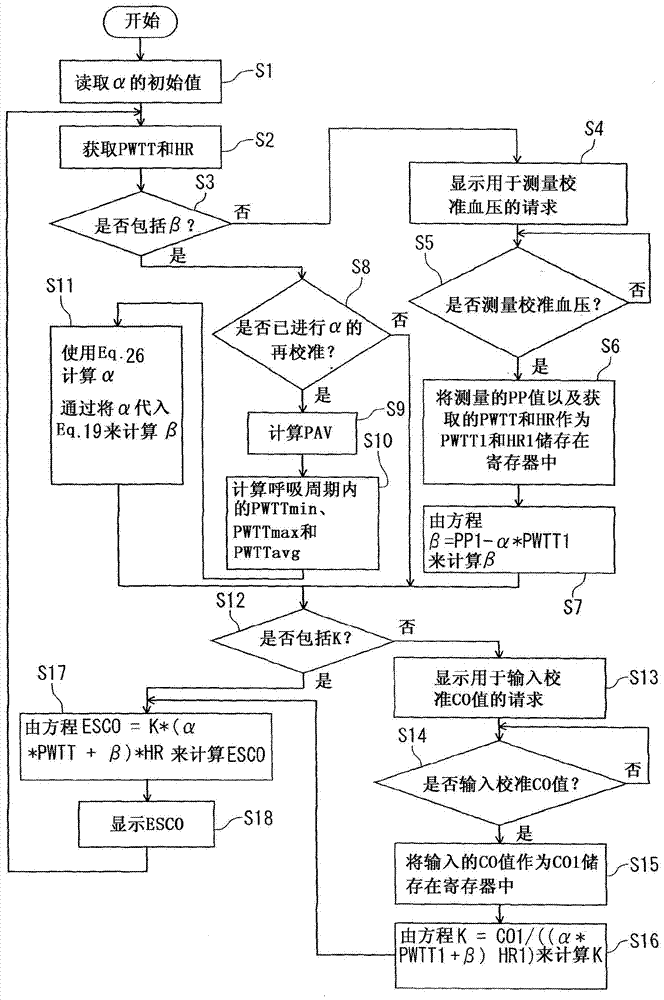
[0032] Exemplary embodiments of the blood volume measuring method and measuring device of the present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0033] First, the principle of measuring cardiac output (cardiac output: CO) will be explained below.
[0034] According to the Windkessel model as an index for diagnosing blood vessels, the flow rate determined by subtracting the blood volume (Qs) flowing out to the periphery during systole from the blood volume flowing into the aorta during systole, that is, the stroke volume (SV) ( SV–Qs), which can be expressed in terms of aortic compliance (C) and pulse pressure [PP: difference between systolic (highest blood pressure) and diastolic (lowest blood pressure)] as follows:
[0035] SV–Qs=C*PP (Eq.1)
[0036] The volume of blood outflow to the periphery (Qd) during diastole becomes equivalent to SV–Qs. Flow Qs is determined by dividing arterial systolic pressure (V) by vascular resistance (R), a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com