Linear actuator
A linear motion and drive technology, applied in the direction of electric components, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve problems such as limiting positional relationships, and achieve the effect of easy and simple assembly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
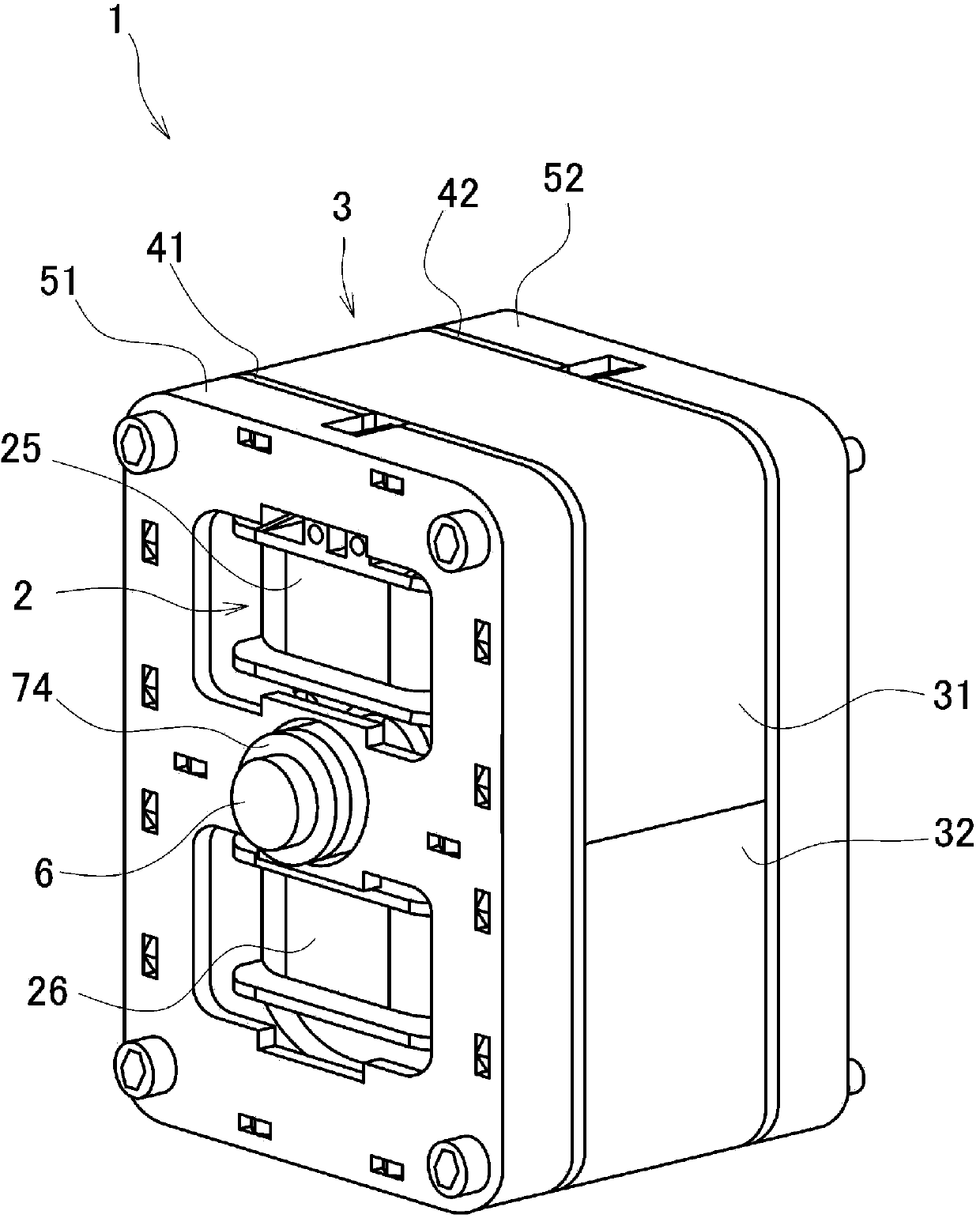
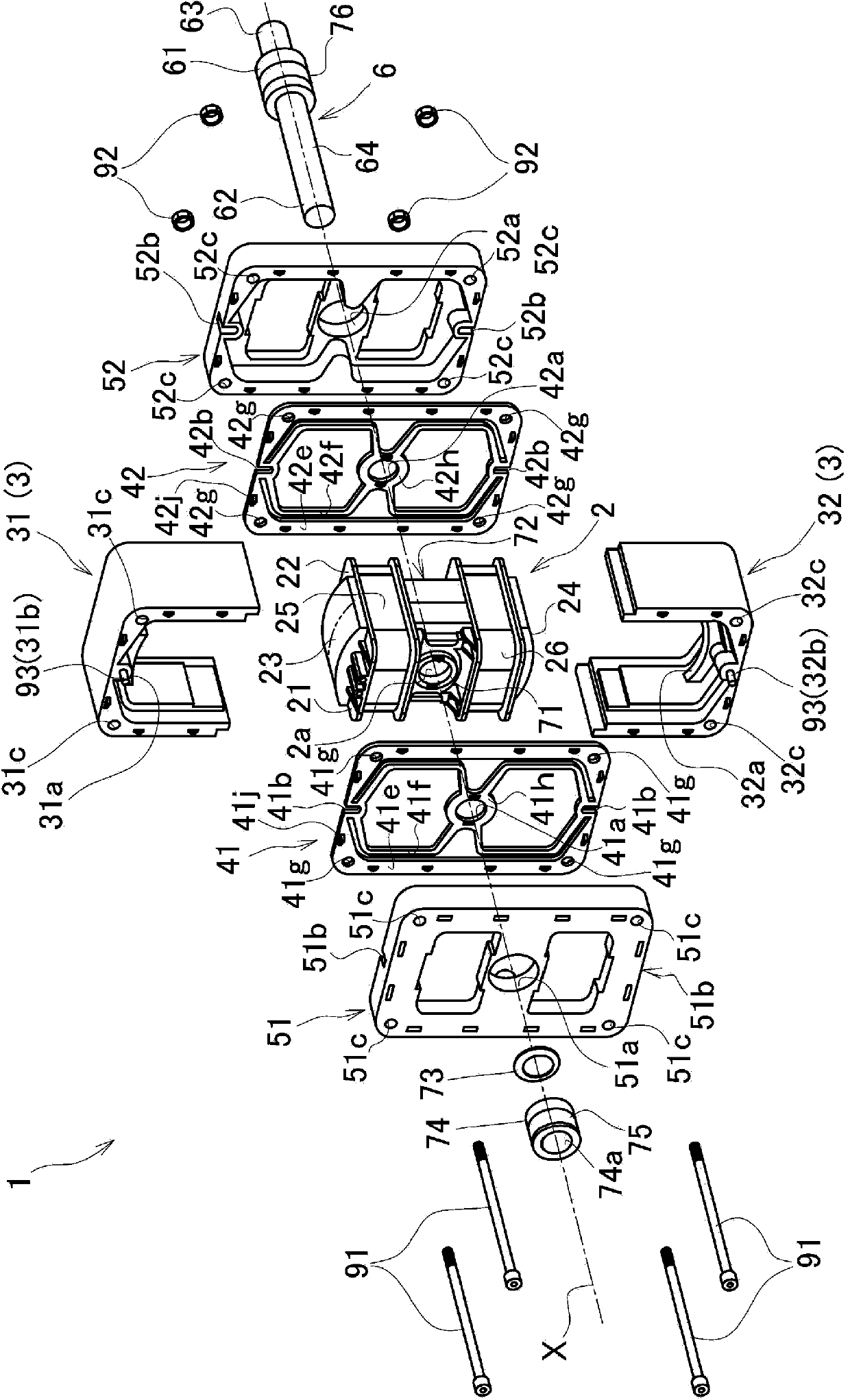
[0063] Such as figure 1 As shown, the linear motion actuator of this embodiment is generally composed of an inner core 2 provided inside, an outer core 3 provided on the outer periphery of the inner core 2 so as to have the same axis as the inner core 2, and the above-mentioned axis. The shaft 6, a pair of leaf springs 41, 42 supporting the outer core 3 on the outer periphery of the shaft 6, and stopper members 51, 52 respectively provided in the front-rear direction of the leaf springs 41, 42 are constituted.
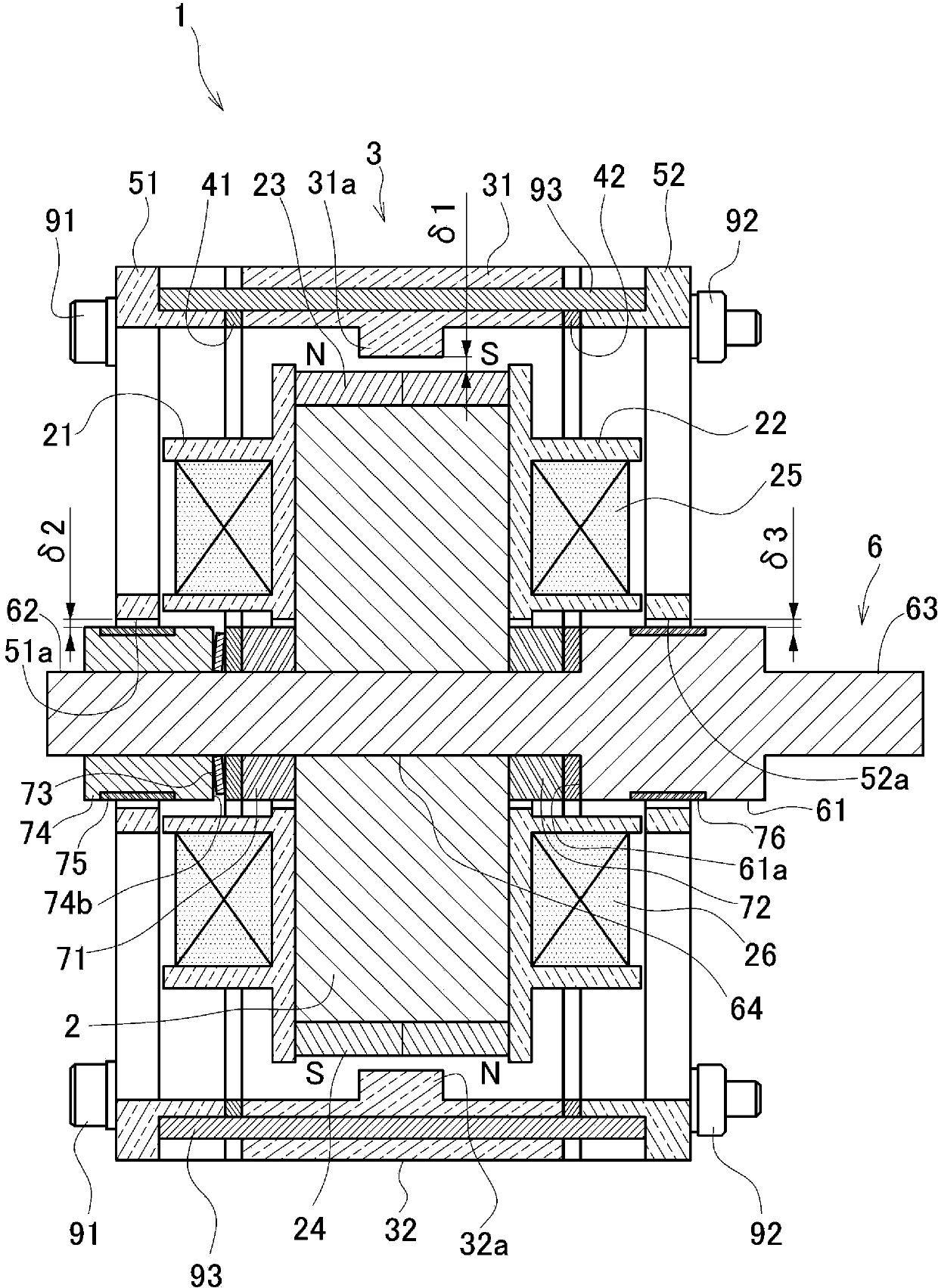
[0064] use figure 2 The central cross-sectional view shown further details the structure.
[0065] The shaft 6 is formed in a cylindrical shape extending from the rear end portion 63 on the right side in the figure toward the top end portion 62 on the left side in the figure, and the shaft 6 has a large diameter portion 61 formed on the right side in the figure relative to the center in the longitudinal direction. .
[0066] A portion from the end surface 61 a of ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0146] Figure 12 It is a figure which shows the sectional view of the linear motion actuator 101 which concerns on the 2nd Embodiment of this invention, and the same code|symbol is attached|subjected to the part common to 1st Embodiment.
[0147]In this embodiment, compared with the case of the first embodiment, the number of caulking parts formed in the inner core 102, spacers 171, 172, leaf springs 141, 142, outer core 103, and stopper members 151, 152 is reduced. . Therefore, there is an advantage that the yield at the time of processing improves.
[0148] The specific positional relationship of the riveting part is as follows: Figure 13 As shown, between the inner core 102, the spacers 171, 172, and the leaf springs 141, 142 function as engaging portions, one riveting portion 102k1 is provided near each of the through holes 102a, 171a, 172a, 141a, and 142a. , 171k1, 141k1, 142k1.
[0149] In this embodiment, the inner diameter D6 to the inner diameter D10 of each thr...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0155] Figure 14 It is a diagram showing an exploded perspective view of a linear motion driver 201 according to a third embodiment of the present invention, and the same reference numerals are attached to the parts common to the first embodiment and the second embodiment.
[0156] In the present embodiment, the permanent magnets 223 and 224 are formed into flat plates based on the structure of the first embodiment, and the inner core 202 and the core covers 221 and 222 for mounting the permanent magnets 223 and 224 are changed to be compatible with the permanent magnet 223. , 224 corresponds to the shape. In addition, the magnetic pole portions 231 a and 232 a facing the permanent magnets 223 and 224 also have flat surfaces corresponding to the permanent magnets 223 and 224 .
[0157] Forming the permanent magnets 223 and 224 in flat form as described above facilitates the processing of the permanent magnets 223 and 224 and reduces the number of parts removed during process...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com