Zero-charge starting and stopping circuit of inverter
A technology of stopping circuit and inverter control circuit, applied in the direction of electrical components, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problems of inverter bridge arm interference conduction, main circuit risk competition, electrical arcing and other problems, to eliminate device out-of-control , Avoid related damage, eliminate the effect of electrical arcing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] Embodiments of the present invention are described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings,
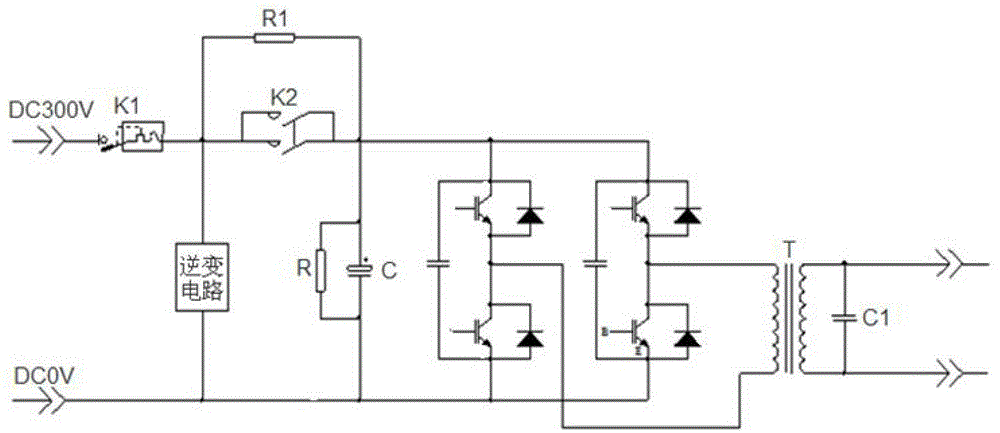
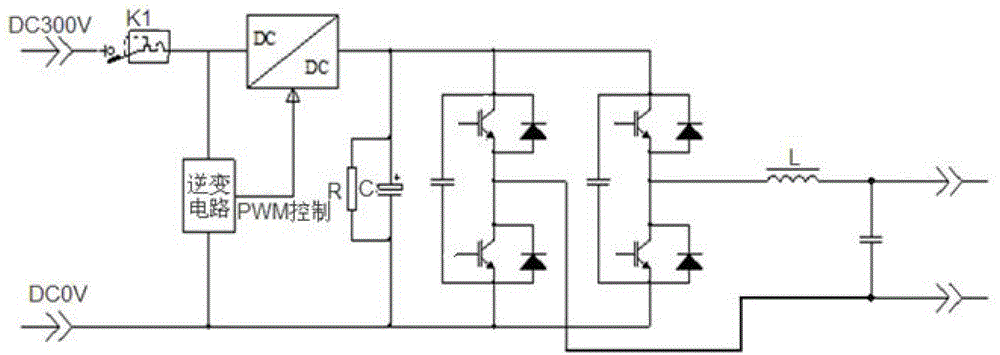
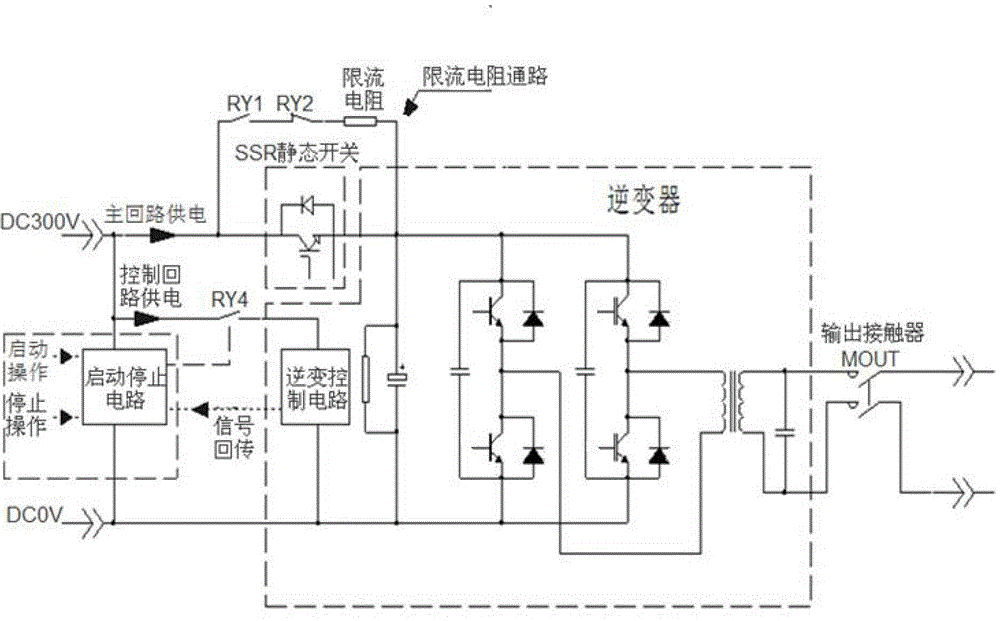
[0034] An inverter zero-charge start and stop circuit, such as image 3 As shown, including the current limiting resistance of the inverter, the DC bus capacitor, and the inverter control circuit, the innovation of the present invention is that it divides the power supply of the inverter into two parts, the main loop power supply and the control loop power supply. Loop power supply is to connect a circuit connected in series with relays RY1 and RY2 on the node between the positive terminal of the power supply and the current limiting resistor, and connect an SSR static switch to the node between the positive terminal of the power supply and the current limiting resistor and the DC bus capacitor to realize the main circuit Power supply control, the power supply of the control loop is to connect the start-stop circuit between the positive and negativ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com