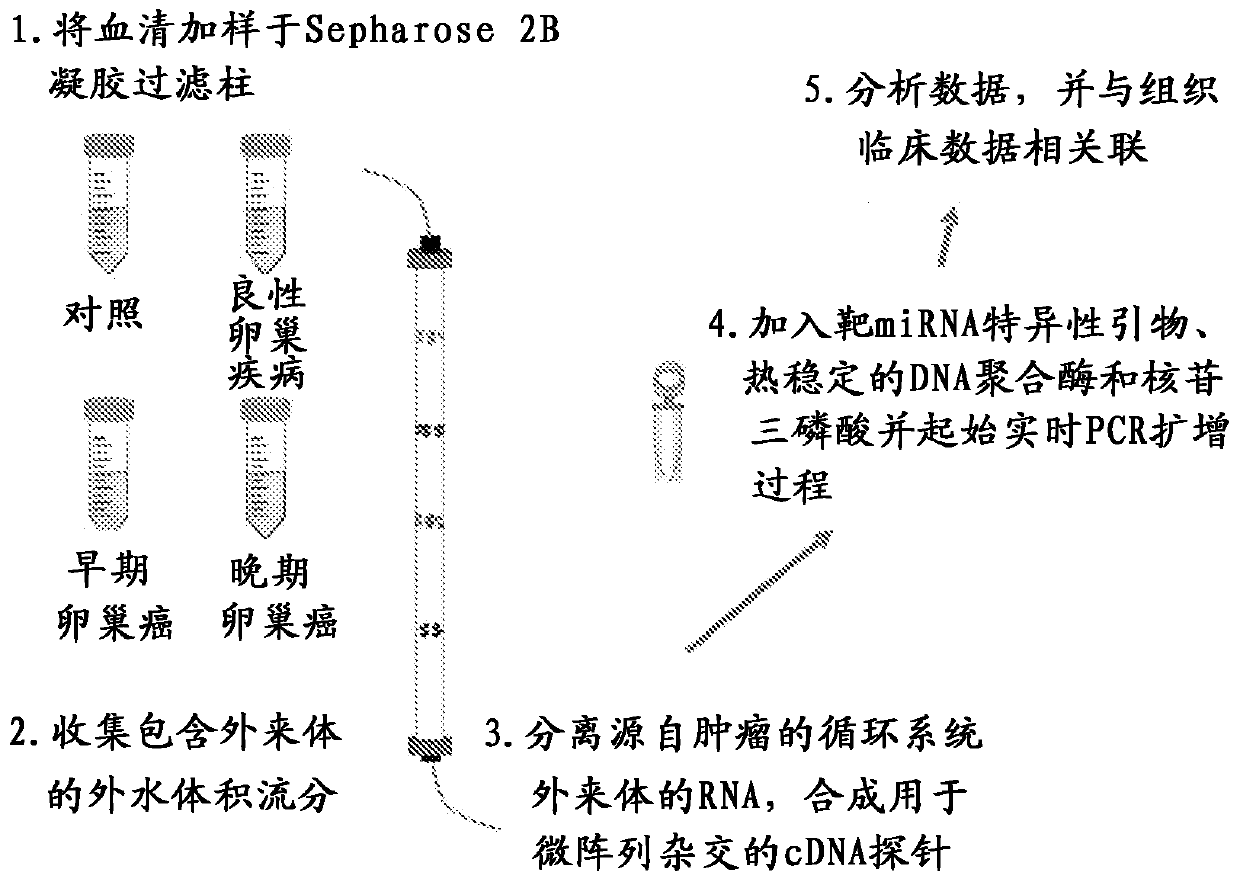
Exosome-associated microRNA as a diagnostic marker
A biomarker and labeling technology, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, coin-operated equipment for distributing discrete items, biological material analysis, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0094] Biopolymer arrays (eg, polynucleotide microarrays) can be fabricated by depositing previously obtained biopolymers (eg, from synthetic or natural sources) on a substrate or by in situ synthetic methods. Methods for obtaining biopolymers by deposition include, but are not limited to: loading a needle or capillary and then contacting a surface, such as described in U.S. Patent 5,807,522; deposition by firing from a pulsed jet such as an inkjet head, such as PCT publication WO 95 / 25116 and WO 98 / 41531 and elsewhere. In situ fabrication methods include those described in US Pat. those methods for polynucleotides. Details of the fabrication of biopolymer arrays by precipitation of previously obtained biopolymers or by in situ methods are further described in US Pat. In fabricating arrays from biopolymers obtained by precipitation or by in situ methods, each area on the surface of a substrate on which an array is to be or has been formed (“array area”) is typically complet...
Embodiment 1
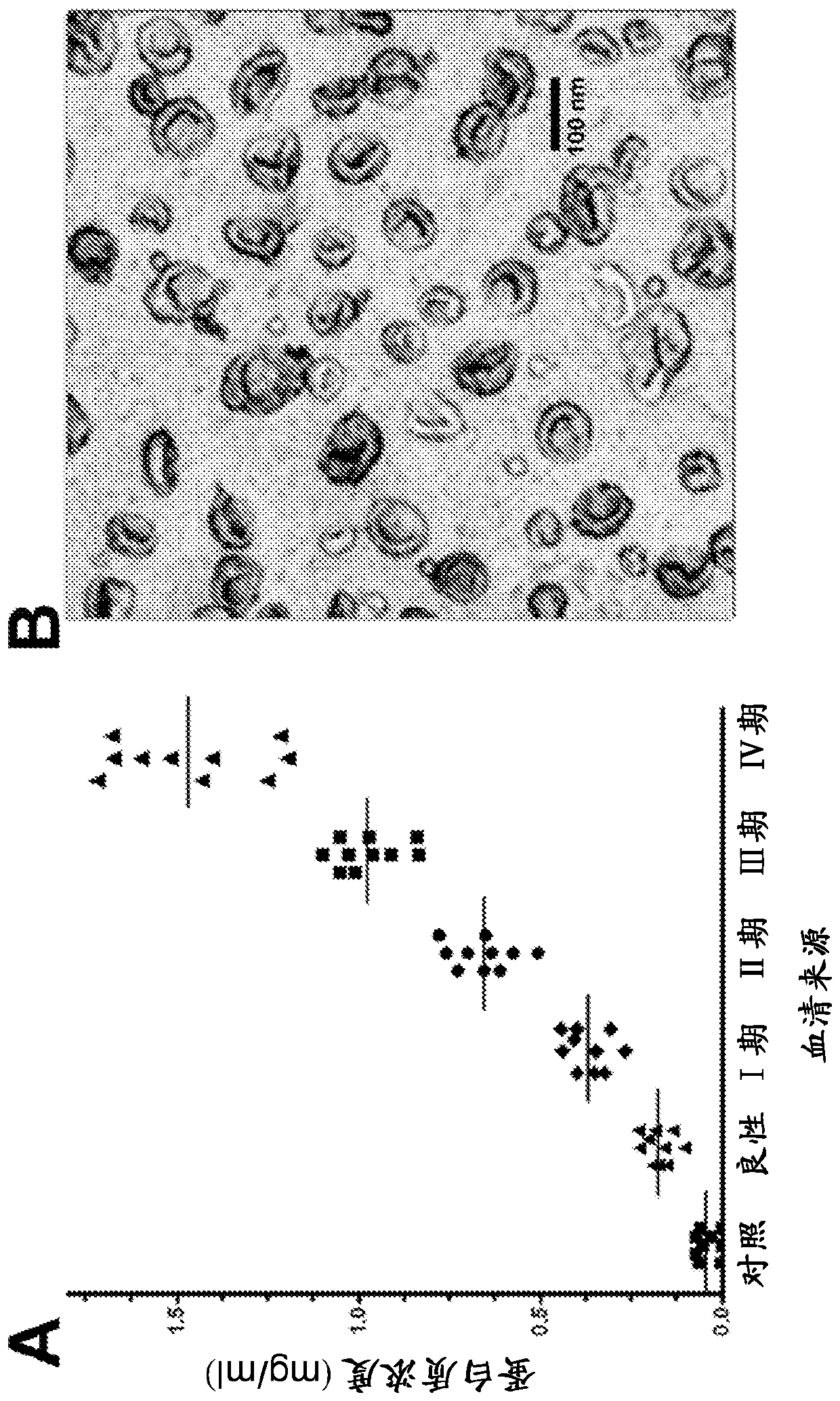
[0117] EPCAM-positive circulating exosomes in women with benign and malignant ovarian disease
[0118] EpCAM-positive exosomes were specifically isolated using magnetic beads of an anti-EpCAM antibody, and the total protein of these circulating exosomes was determined and plotted against the stage of the disease ( image 3 A). The level of EpCAM-positive exosomes in age-matched normal volunteers (controls) was 0.039 ± 0.030 mg / ml of exosomal protein, which represented the background value for the assay. Patients diagnosed with benign ovarian disease had 0.149 ± 0.065 mg / ml of exosomal protein, which was significantly higher than control values. Patients diagnosed with ovarian cancer all presented significantly higher levels of EpCAM-positive exosomes (compared with benign disease or controls). Women with stage I ovarian cancer presented 0.320±0.056 mg / ml of circulating exosomal protein, which was significantly higher than controls and benign disease (p image 3 B). The exoso...
Embodiment 2
[0120] Association of small RNAs with tumor-derived exosomes
[0121] To identify whether these isolated exosomes contain small RNAs, they were examined using Bio-Analyzer2100 ( Figure 4 ). These analyzes identified the presence of significant numbers of small RNAs in the absence of 18S and 28S RNAs that normally occur with cell-derived RNA. These materials were subsequently used for miRNA profiling.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com