A Tracking Method Oriented to RFID Passive Tags
A passive tag and tag technology, applied in the field of RFID positioning and tracking, can solve problems such as being inferior to active positioning algorithms, increasing computing time, being deeply affected by obstacles, antenna performance, multipath effects and other factors, achieving accuracy and practicality. Sex-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
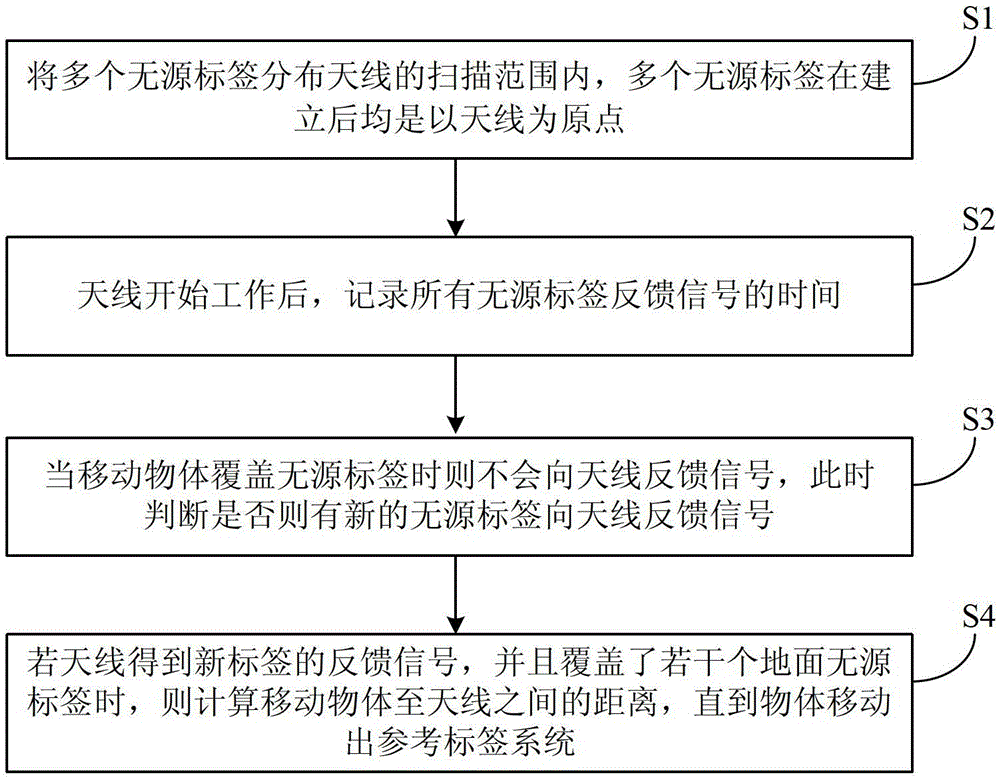
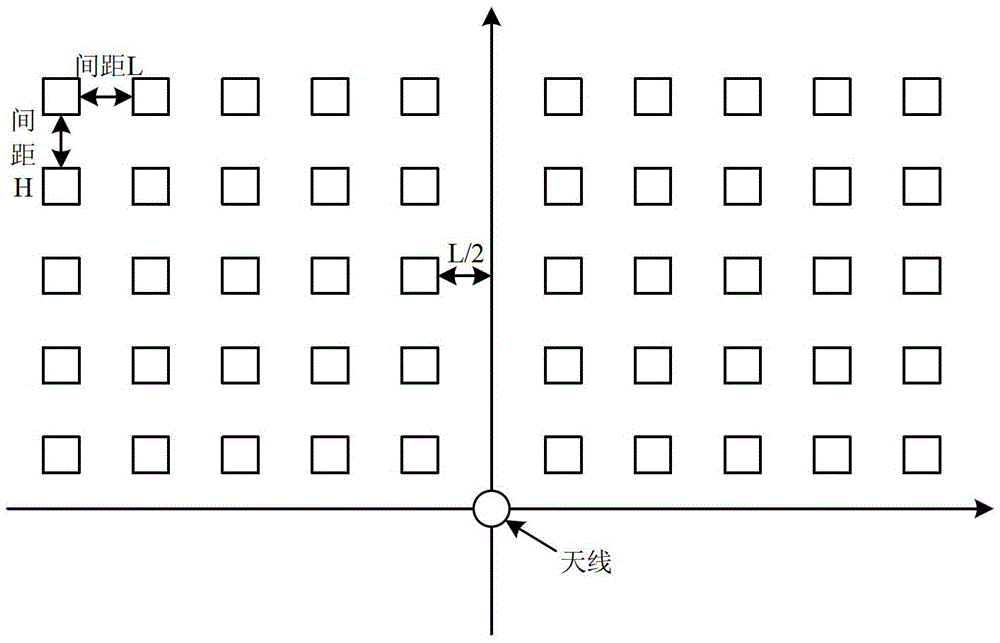
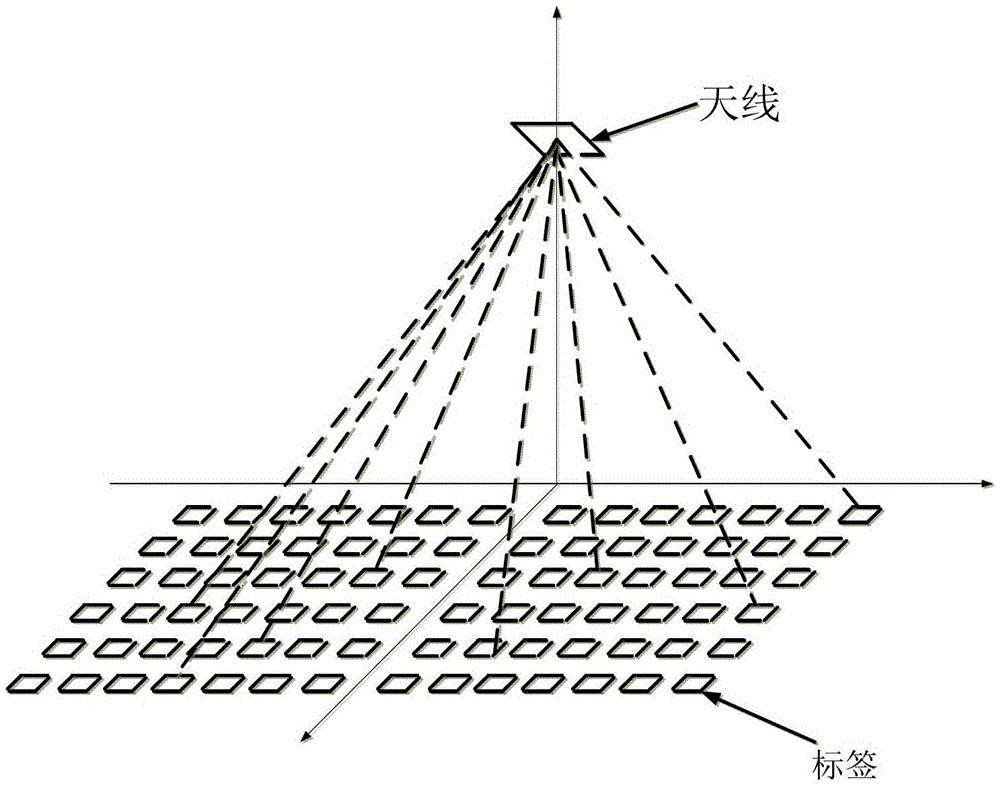
[0027] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, the present invention provides a tracking method for RFID passive tags, including the following steps:
[0028] S1. Distribute multiple passive tags within the scanning range of the antenna. After the multiple passive tags are established, the antenna is the origin.
[0029] Specifically, the passive tags are tiled within the scanning range of the antenna in an arrangement of m*n, where m is the number of rows, n is the number of columns, and both m and n are positive integers greater than 1. Passive tags are laid flat on the ground in the corridor facing the antenna.
[0030] S2. After the antenna starts working, record the time of all passive tag feedback signals.
[0031] Specifically, when the antenna is working normally and no moving objects pass by, each passive tag will feed back a signal to the antenna, and start to work after the antenna stably receives the signal fed back by each passive tag.
[0032] Since there are fewer obstac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com