Electrochemical reactor of graphene-Ti electrode for treating printing and dyeing wastewater
A printing and dyeing wastewater and reactor technology, which is applied in textile industry wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems that have not been reported, and achieve high removal efficiency, simple operation and management, and stable effluent quality Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
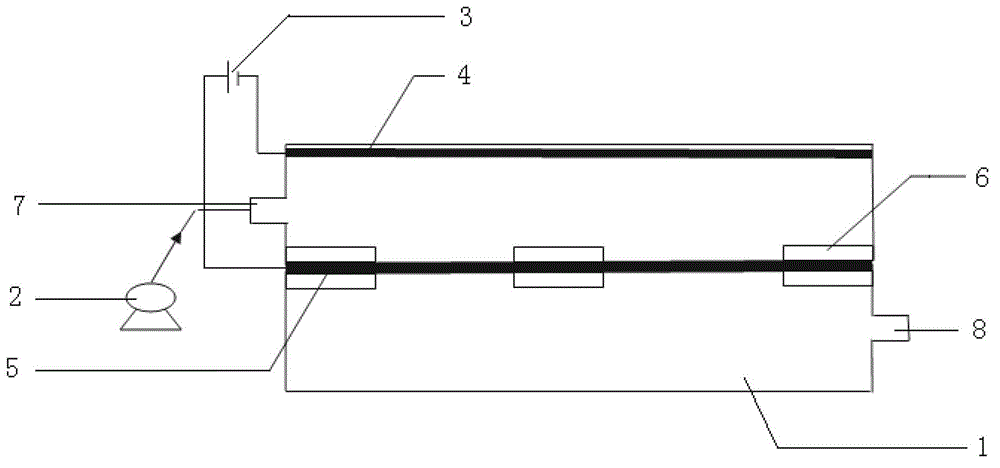
[0028] A novel graphene-Ti electrode printing and dyeing wastewater treatment electrochemical reactor, including a reactor body 1, a pump 2, a power supply 3, a Ti electrode 4, a graphene film electrode 5 and a bracket 6, the reactor body 1 is a hollow structure, and the bracket 6 is a metal grid structure and is set at 1 / 2 height of the inner wall of the reactor body 1, and the Ti electrode 4 has a thickness of 0.3mm and an area of 0.15m 2 The metal Ti sheet is arranged on the top of the reactor body 1, and the graphene film electrode 5 is covered and arranged on the support 6. The area of the graphene film electrode 5 is the same as the cross-sectional area of the reactor body 1, and the positive electrode of the power supply 3 is the same as the graphene electrode. Thin film electrode 5 is connected, and the negative pole of power supply 3 is connected with Ti electrode 4; Reactor body 1 is also provided with reactor inlet 7 and reactor outlet 8, and reactor inlet 7 is...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A novel graphene-Ti electrode printing and dyeing wastewater treatment electrochemical reactor, the main structure is the same as that of Example 1, the difference is that the graphene film electrode 5 is prepared as follows:
[0035] Dissolve graphene in ultrapure water at a mass volume ratio of 0.5g / L, and ultrasonically disperse it for 5 minutes to prepare graphene hydrogel, and then vacuum filter the graphene hydrogel onto a nylon filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 μm , and dried in a 45°C drying oven to obtain a graphene film electrode.
[0036] The treated printing and dyeing wastewater is collected at the outlet 8 of the reactor and its chromaticity and total organic carbon content (TOC content) are measured. Compared with the printing and dyeing wastewater before treatment, the decolorization rate and TOC removal rate are calculated. The printing and dyeing wastewater treated by the novel graphene-Ti electrode printing and dyeing wastewater electrochemical...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A novel graphene-Ti electrode printing and dyeing wastewater treatment electrochemical reactor, the main structure is the same as that of Example 1, the difference is that the voltage of the power supply 3 is 3.0V.
[0039]The treated printing and dyeing wastewater is collected at the outlet 8 of the reactor and its chromaticity and total organic carbon content (TOC content) are measured. Compared with the printing and dyeing wastewater before treatment, the decolorization rate and TOC removal rate are calculated. The printing and dyeing wastewater treated by the novel graphene-Ti electrode printing and dyeing wastewater electrochemical reactor of this embodiment has a decolorization rate of 97% and a TOC removal rate of 96%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com