Method and apparatus for dynamic wavelength allocation in Wavelength switched optical networks
An optical network and wavelength technology, applied in the field of optical telecommunications and data networks, which can solve problems such as inefficient resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
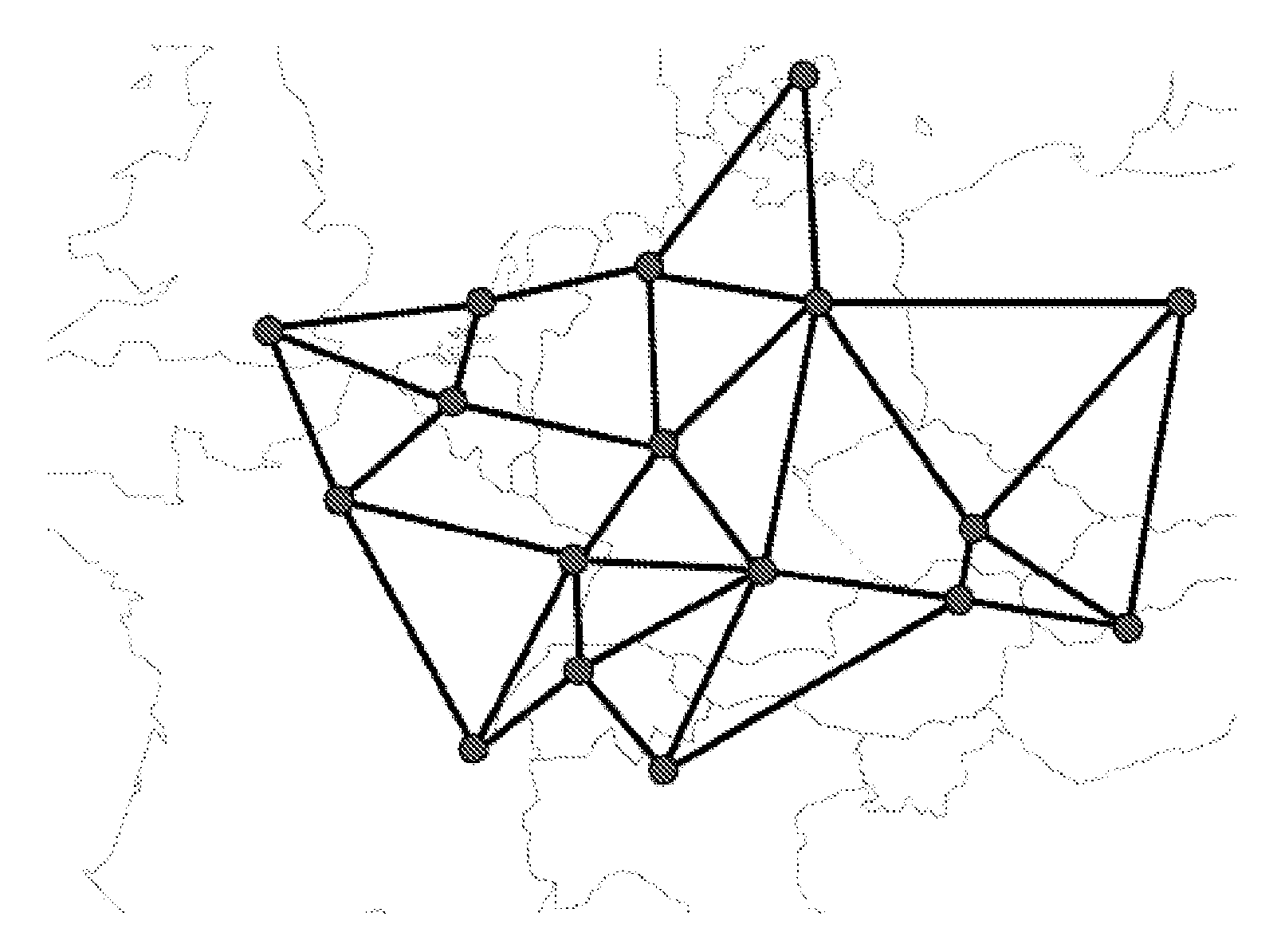
[0021] To illustrate an embodiment of the invention, consider a transparent optical network with N nodes and L bidirectional links. It is also assumed that the network is a Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) network. However, the invention is equally applicable to WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) networks. In such DWDM networks, adjacent wavelength channels are spectrally separated by a constant amount (eg, 100GHz). The wavelength carriers are sorted in ascending order. assuming w 0 is the lowest wavelength channel in the DWDM comb (or multiplex) (at wavelength λ 0 operation), w 1 (at wavelength λ 1 operation) is away from w 0 nearest channel. In general, in a DWDM multiplex, there are 40 wavelengths (channels), with indices from 0 to 39. Each node and link supports transmission and reception at 10Gbit / s and 40Gbit / s, and each link supports W wavelengths per direction (in this example, W=40). In alternative embodiments, there are 80 or even 160 channe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com