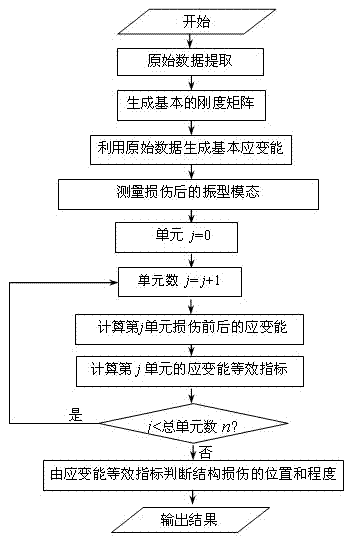
Equivalent modal strain energy damage identification method
A modal strain energy and damage identification technology, which is applied in the testing of machines/structural components, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of low accuracy of damage identification and difficult quantitative identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
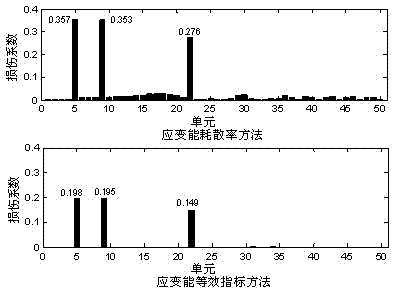
[0070] Example 1: When damage occurs in units 5, 9 and 22, the strain energy dissipation rate method and the strain energy equivalent index method proposed by the present invention are used respectively to carry out damage identification research. The calculation results of the two methods are as follows image 3 shown. From image 3 It can be found that both methods can effectively identify the damage unit, but the strain energy dissipation rate method has low recognition accuracy for the damage degree. The damage values calculated by this method for units 5, 9 and 22 are 0.357 , 0.353 and 0.276, which are quite different from the real values, but the strain energy equivalent index method proposed by the present invention can determine the degree of damage more accurately, and the values calculated for units 5, 9 and 22 are 0.198 and 0.195 respectively and 0.149, the index value is very close to the real damage degree, therefore, the strain energy equivalent index method...
example 2
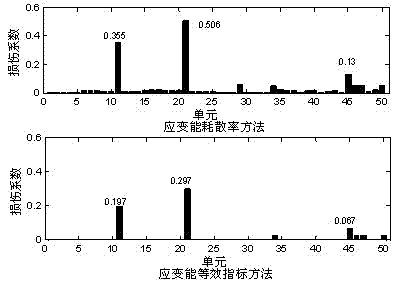
[0071] Example 2: When damage occurs to elements 11, 21 and 45, the strain energy dissipation rate method and the strain energy equivalent index method are also used to carry out damage identification research. The calculation results of the two methods are as follows Figure 4 shown. From Figure 4 It can be found that both methods can effectively identify the location of the damage unit, but the strain energy dissipation rate method is not accurate enough to identify the damage degree. The damage values calculated by the strain energy dissipation rate method for elements 11, 21, and 45 are 0.355, 0.506, and 0.13, respectively, which are quite different from the real values. However, the strain energy equivalent index method proposed by the present invention can more accurately determine the degree of damage, and the values calculated for units 11, 21 and 45 are respectively 0.197, 0.297 and 0.067, which is very close to the real degree of damage. Therefore, the strain ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com