Longitudinal minimal-invasion bone cutter for tubular bones
An osteotomy and longitudinal technology, which is applied in the field of osteotomy devices, can solve the problems that the osteotomy device cannot perform longitudinal osteotomy of tubular bones, the wounds around the wound at the osteotomy site are damaged, the operation of the osteotomy device is inconvenient, etc. Connection area, quick recovery, easy separation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
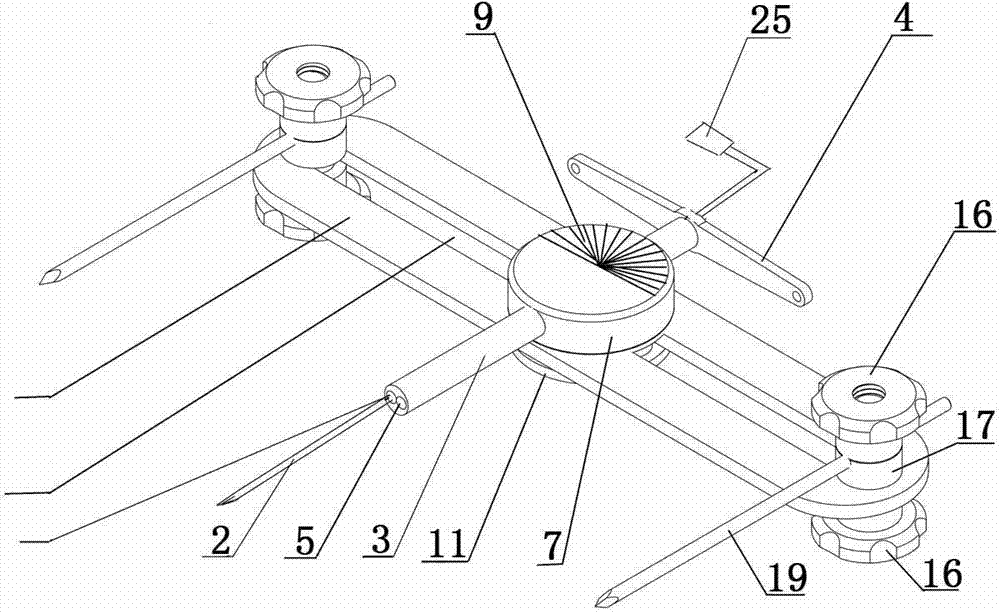
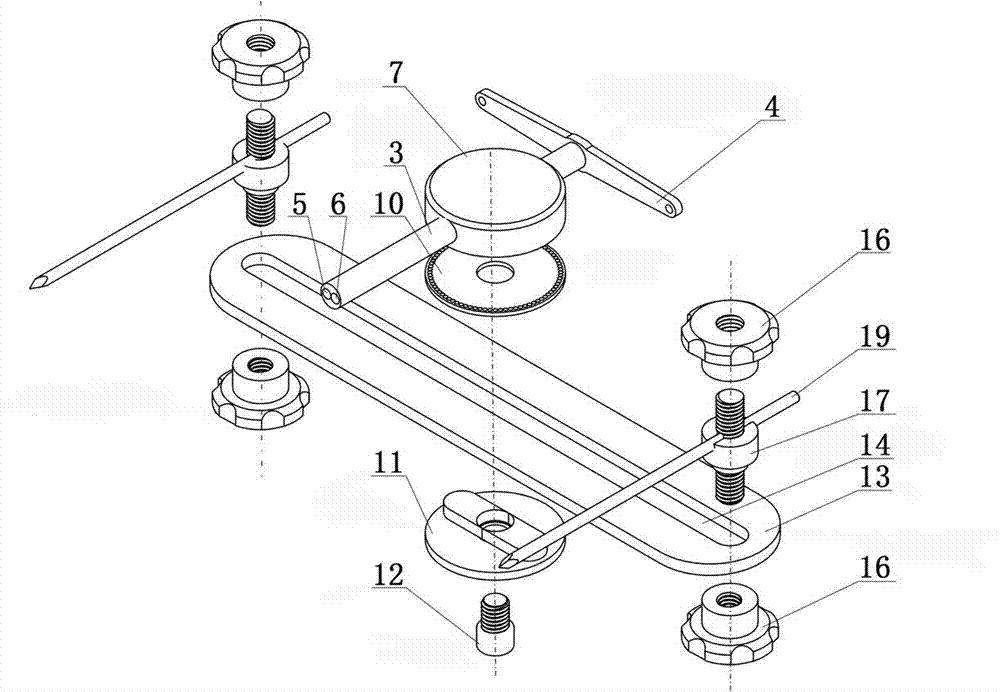
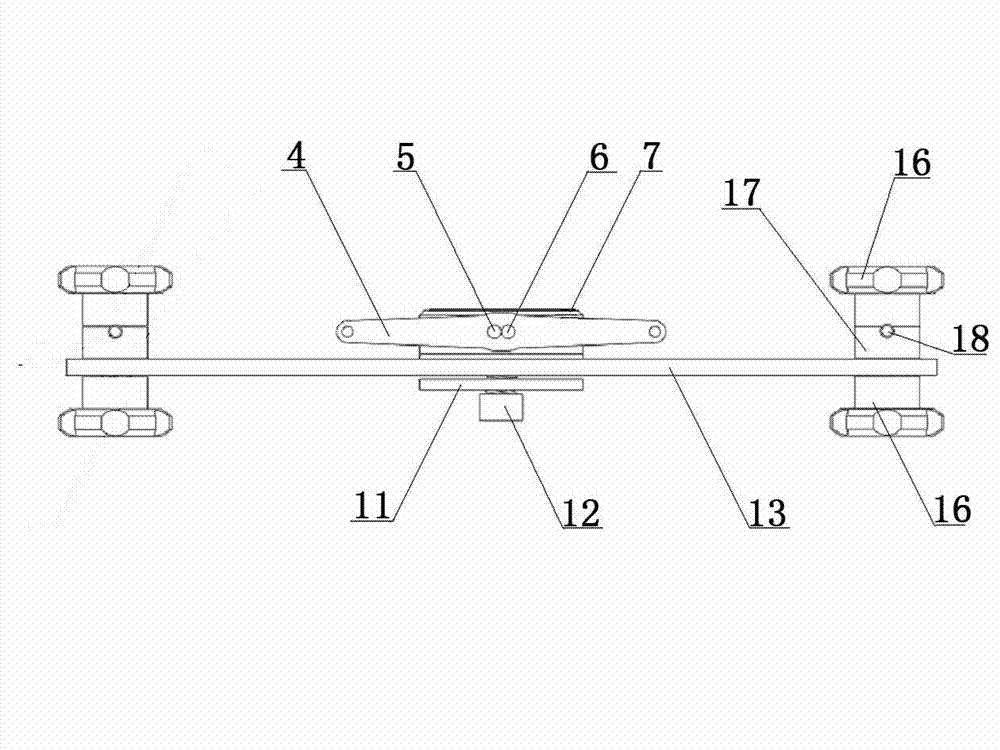
[0039] Embodiment one, see figure 1 , figure 2 , Figure 5 Shown, the operation steps of the present invention when carrying out rectangular osteotomy are as follows:
[0040] Before the operation, first determine the positioning point of the upper end of the surgical bone and the positioning point of the lower end of the surgical bone, cut a small opening in the soft tissue, put the osteotomy drill, and perform the upper end osteotomy on the upper and lower ends of the surgical bone respectively Positioning hole and osteotomy positioning hole at the lower end of the bone. Then confirm the osteotomy point according to the position of the pre-designed longitudinal osteotomy line, cut two small incisions in the soft tissue at both ends of the confirmed osteotomy point for use, place the tubular bone longitudinal minimally invasive osteotomy on the operative bone, A pair of auxiliary positioning pins are respectively inserted into and fixed in the upper end osteotomy position...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment two: see figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 6 As shown, the present invention is also applicable to the longitudinal osteotomy of tubular bone in the way of full incision of soft tissue. When implementing the osteotomy operation, at first the upper and lower osteotomy positioning points of the surgical bone are determined, and then the osteotomy positioning hole 26 at the upper end of the surgical bone and the osteotomy positioning hole 27 at the lower end of the surgical bone are made with the osteotomy drill bit, and according to the pre-designed longitudinal Confirm the osteotomy point at the position of the bone line, and make an incision in the soft tissue along the longitudinal osteotomy position equal to the length of the osteotomy line for use, and place the longitudinal minimally invasive osteotomy of the tubular bone on the operative bone. The operation method and implementation Example 1 is the same.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment three: see figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 7 , Figure 8 As shown, when the present invention performs Z-shaped and S-shaped osteotomies, the operation method is the same as the osteotomy operation steps and methods in Embodiment 1, except that after the longitudinal drilling of the tubular bone and the osteotomy, the upper and lower ends of the tubular bone are drilled horizontally The cutting direction of the osteotomy is opposite to form a longitudinal traction Z-shaped osteotomy site 22 or a longitudinal traction S-shaped osteotomy site 23, and the osteotomy section of the surgical bone is formed into a Z-shape or an S-shape, meeting the needs of longitudinal stretching treatment of tubular bones .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com