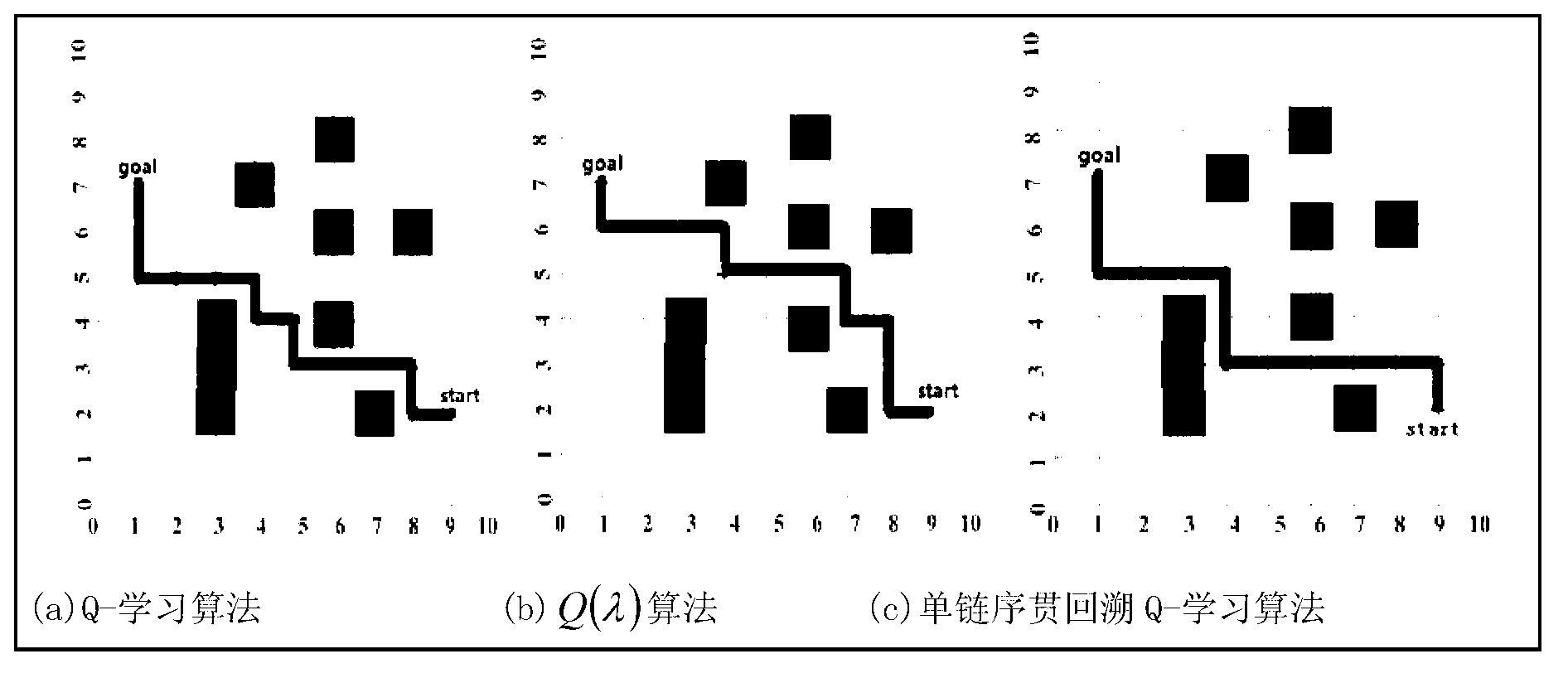
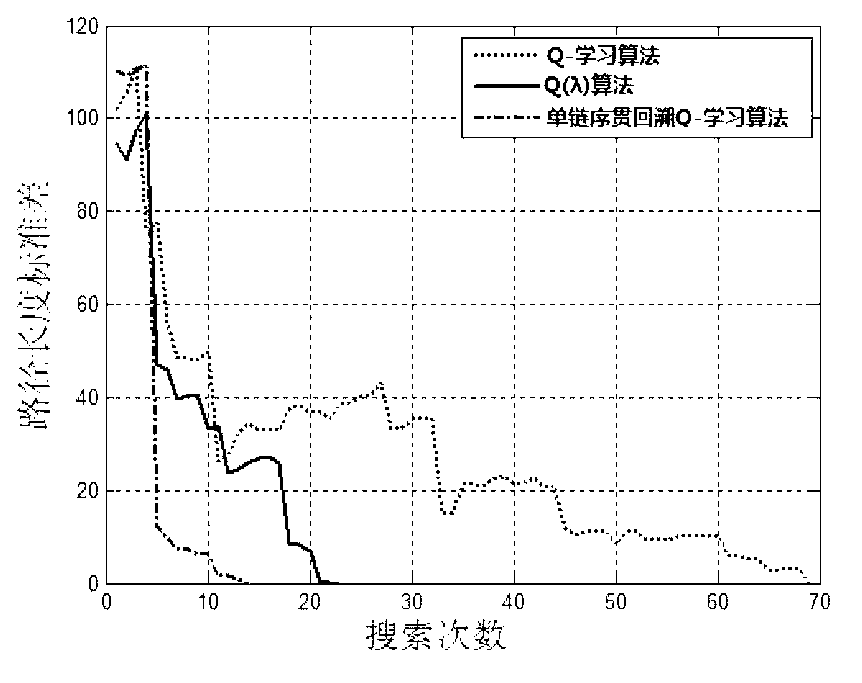
Mobile robot path planning algorithm based on single-chain sequential backtracking Q-learning
A mobile robot and path planning technology, which is applied in the direction of two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problems of long learning time and slow convergence speed, and achieve the effect of short learning time, high learning efficiency and improved learning efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
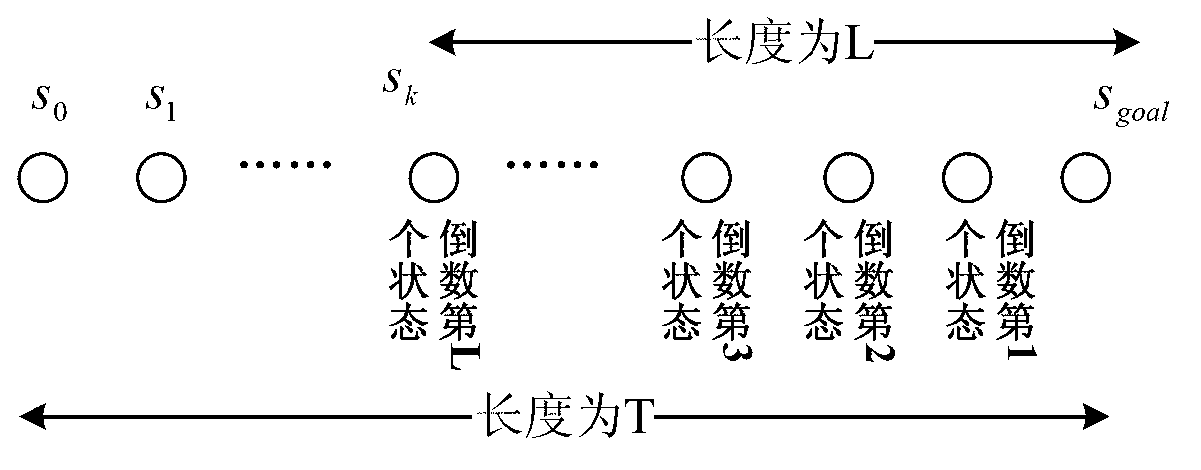
[0043] 1. Q-learning algorithm
[0044] The Q-learning algorithm is an iterative algorithm that assigns a corresponding Q value to each state-action pair. The Q value is defined as the sum of reinforcement learning discount rewards. If an action strategy changes the state of the environment, it will obtain a strengthening signal. According to Strengthen the signal, iteratively update the Q value, the Q value corresponding to the correct action will continue to increase, and the Q value corresponding to the wrong action will continue to decrease, until the Q value of each state-action pair stabilizes and converges, the optimal path from the starting point to the target point is determined up. The iterative process is as follows:
[0045]
[0046] where s 0 Indicates the initial state (starting position) of the robot, s 1 Indicates the state of the robot (the location in the environment) at t=1, ..., s n Indicates the state of the robot (the location in the environment) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com