Method for time synchronization in a communication network
A technology of time synchronization and communication network, applied in the field of communication network, it can solve the problems of unknown frequency and time delay of measurement error of single clock change, inability to coordinate the reference clock, and non-continuous curve trend.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
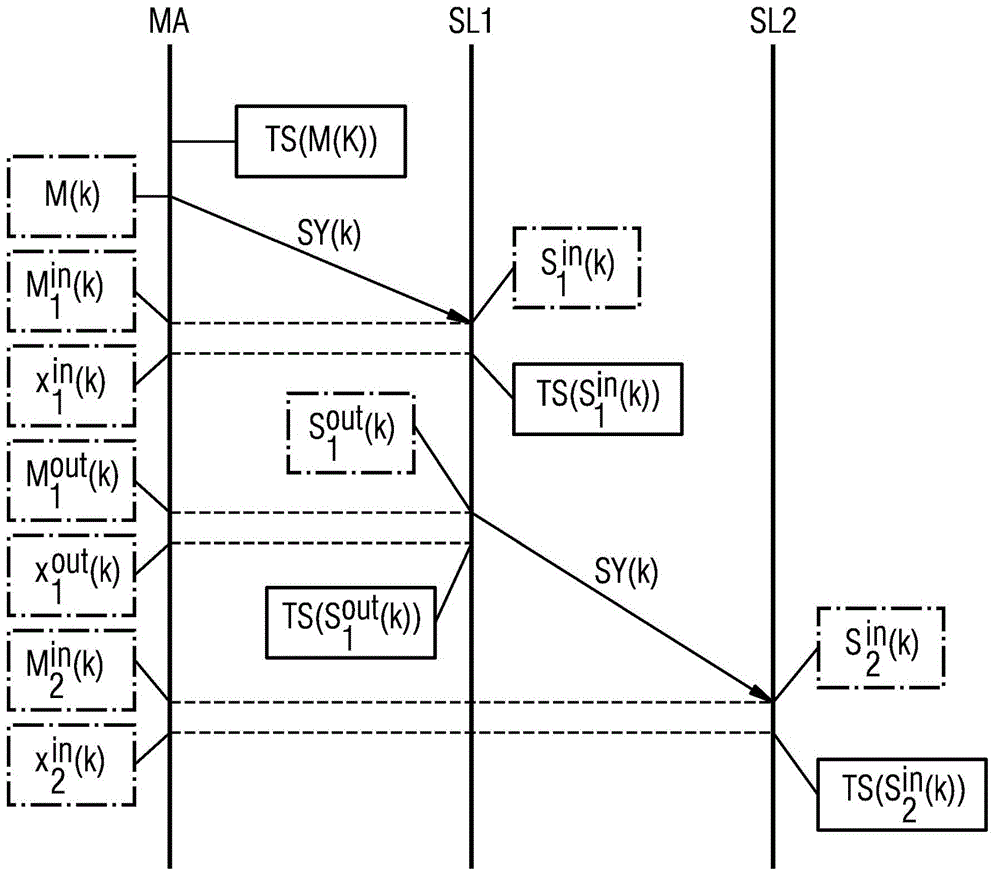
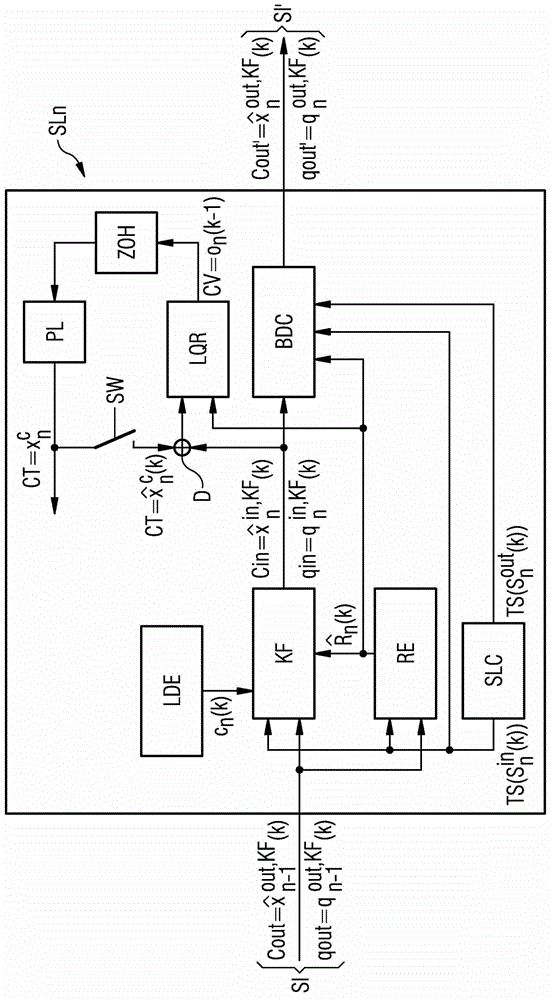
[0048] figure 1 A chain of nodes in a communication network in which an embodiment of the method according to the invention is carried out is shown. The communication network comprises a first node in the form of a so-called master node MA and a plurality of second nodes in the form of so-called auxiliary nodes, wherein in figure 1 Two secondary nodes SL1 and SL2 are shown in . The master node MA includes a reference clock which generates a reference clock frequency. In contrast to this, the individual secondary nodes SL1 , SL2 etc. comprise individual internal clocks which generate corresponding internal clock frequencies. in accordance with figure 1 In the communication network, use a suitable time synchronization protocol, such as the PTP protocol according to the IEEE 1588 standard (PTP=Precision Time Protocol (precision time protocol)), to synchronize the internal clock of each secondary node with the reference clock of the primary node MA . To this end, the synchron...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com