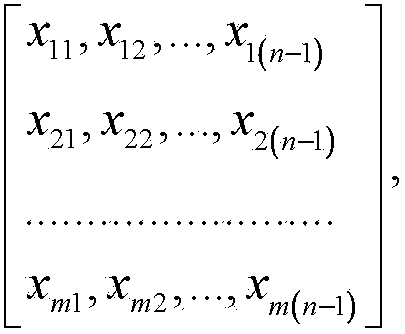Method for optimizing design on number of regulating stage nozzles of steam turbine based on improved genetic algorithm
A technology for improving genetic algorithm and optimization method, which is applied in the field of design optimization of the number of nozzles in the regulating stage of steam turbines, and can solve the problems of small valve opening in the working load area, inability to guarantee fully open or fully closed state, and inconsistency with the theme of the times.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
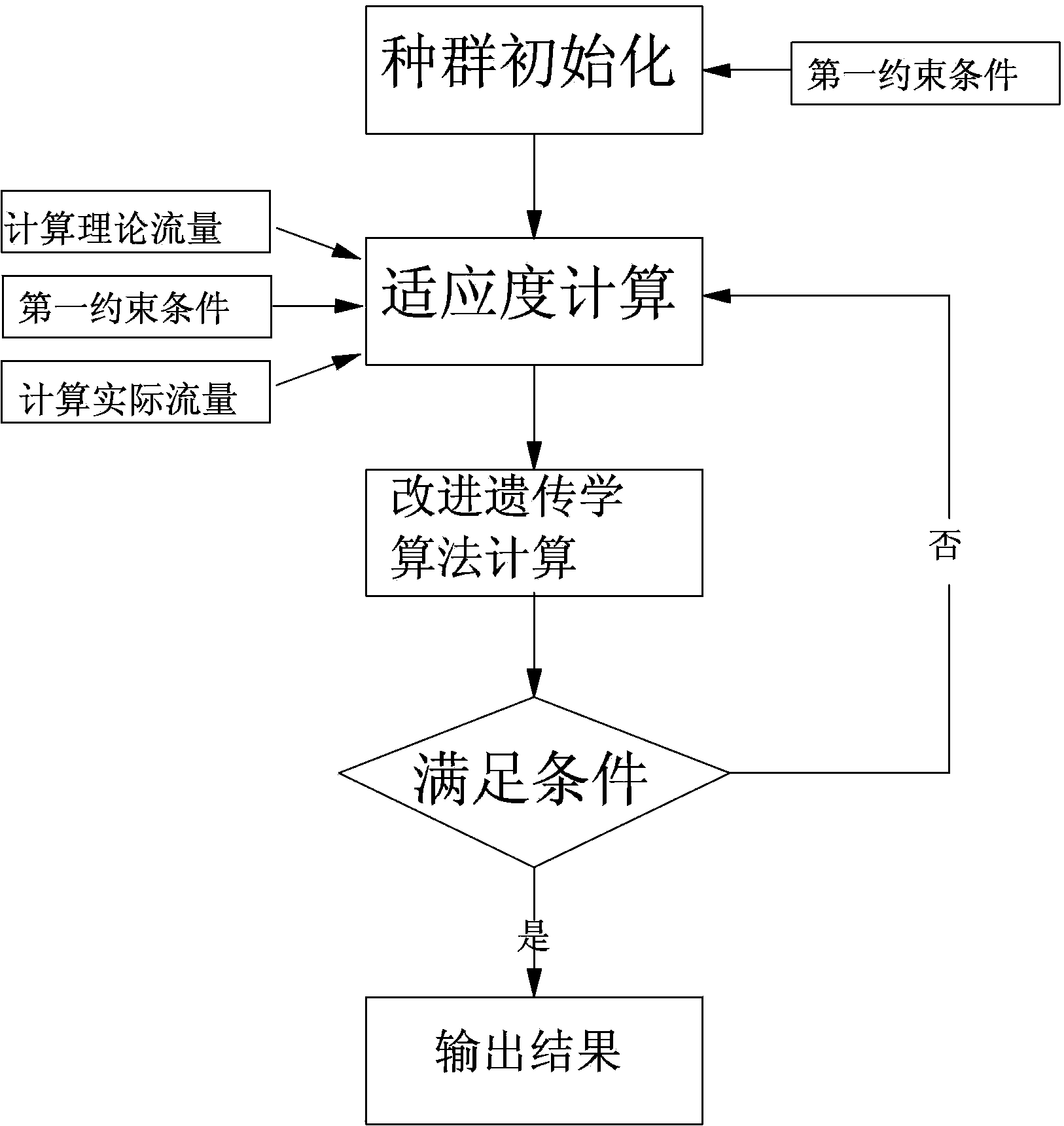
[0043] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the optimization method of this embodiment is to realize based on following model:
[0044] Y=(xgz 1 -Ge 1 ) 2 +(xgz 2 -Ge 2 ) 2 +......+(xgz l -Ge l ) 2 ,
[0045] l is the number of load points, and based on the improved genetic algorithm, the combination of the optimal number of nozzles at a given load point is obtained: the specific process is as follows,
[0046] Step 1. Initial population setting: set constraints:
[0047] First constraint: X 1 +X 2 +......+X n =X z , X z =const 2-2
[0048] The second constraint: X min ≤X i ≤X max , i=1, 2, ..., n; X min = const, X max = const 2-3
[0049] Xi represents the number of nozzles corresponding to the i-th valve, const represents a constant, and is coded by a floating point number, and the coding interval is [X min , X max ]
[0050] The initial population can be represented by a (n-1)×m matrix:
[0051] ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0082] Specific implementation mode two: the calculation method of the adjustment step change working condition described in step two of this embodiment mode is:
[0083] Step 21. Calculate the theoretical flow rate of each valve in the regulating stage: G i =G e · ξ k , where G k is the theoretical flow at the load point, G e is the rated flow of the steam turbine, ξ k is the percentage of steam turbine operating power to rated power at the load point, k=1, 2,...l, k is the number of work load points;
[0084] Step 22. Calculate the actual flow rate G from the number of nozzles of each valve and the corresponding valve opening kj :
[0085] G kj = 0.648 A nk p 0 k ρ 0 ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0091] 1. The user specifies the common working load point of the steam turbine unit, the sliding pressure operation curve, the total number of valve nozzles of the regulating stage, the value range of the number of nozzles in a single nozzle group, and the characteristic curve of the regulating stage calculated by the variable operating conditions of the regulating stage.
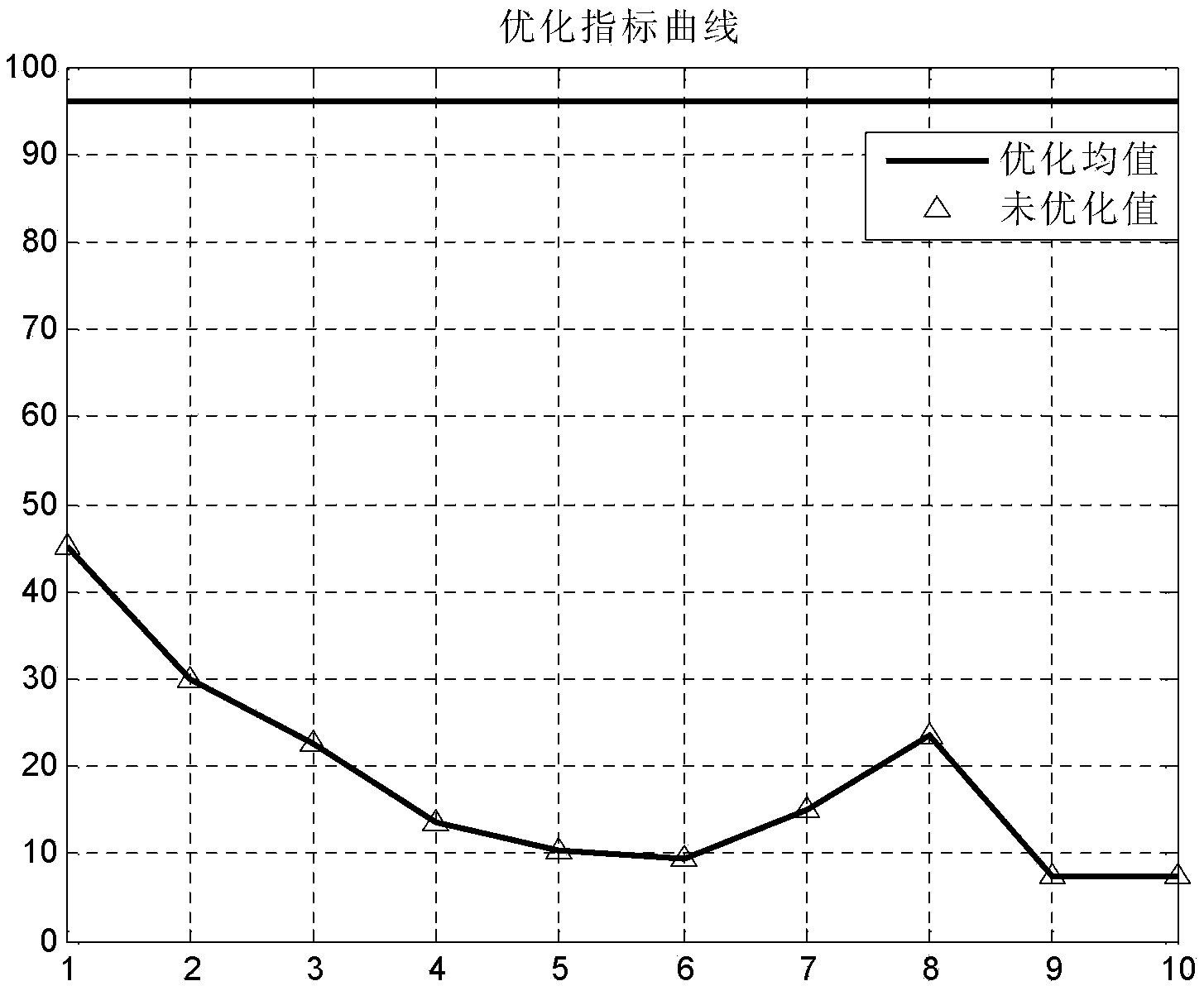
[0092] 2. Optimizing the number of nozzles: If for all the load points given by the user, the corresponding control valve opening (full opening) combination can be found under the condition of the optimally designed nozzle group, then the optimization goal has been achieved. In the analysis and calculation, the degree of deviation between the calculated flow rate when the valve is fully open or fully closed and the theoretical flow rate of a given load is used as the measurement basis. During the process, the operating time of different commonly used load points is fully considered, and the operating frequen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com