Image display apparatus
An image display device and a technology for displaying brightness, which are applied to identification devices, image communication, static indicators, etc., can solve the problems of reduced brightness difference discrimination ability and indistinguishable grayscale, and achieve the effect of avoiding flattening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings. The present invention is applicable to another embodiment in which part or all of the construction of Embodiment 1 is replaced by its alternative construction, and only when the gray scale is closer to its maximum value, is assigned to the difference of the gray scale, the brightness of the The amount of change in the common logarithm becomes larger.
[0044] In this Embodiment 1, a video display device having only a display function, such as a computer monitor, will be described as an image display device. However, television receivers and electronic viewfinders mounted on cameras and video cameras, which are video display devices including video and audio receiving units, are also called video display devices. The video display device can be used for image display devices such as CRTs, liquid crystal displays, plasma displays, and organic EL displays.
[0045] Reg...
example 1
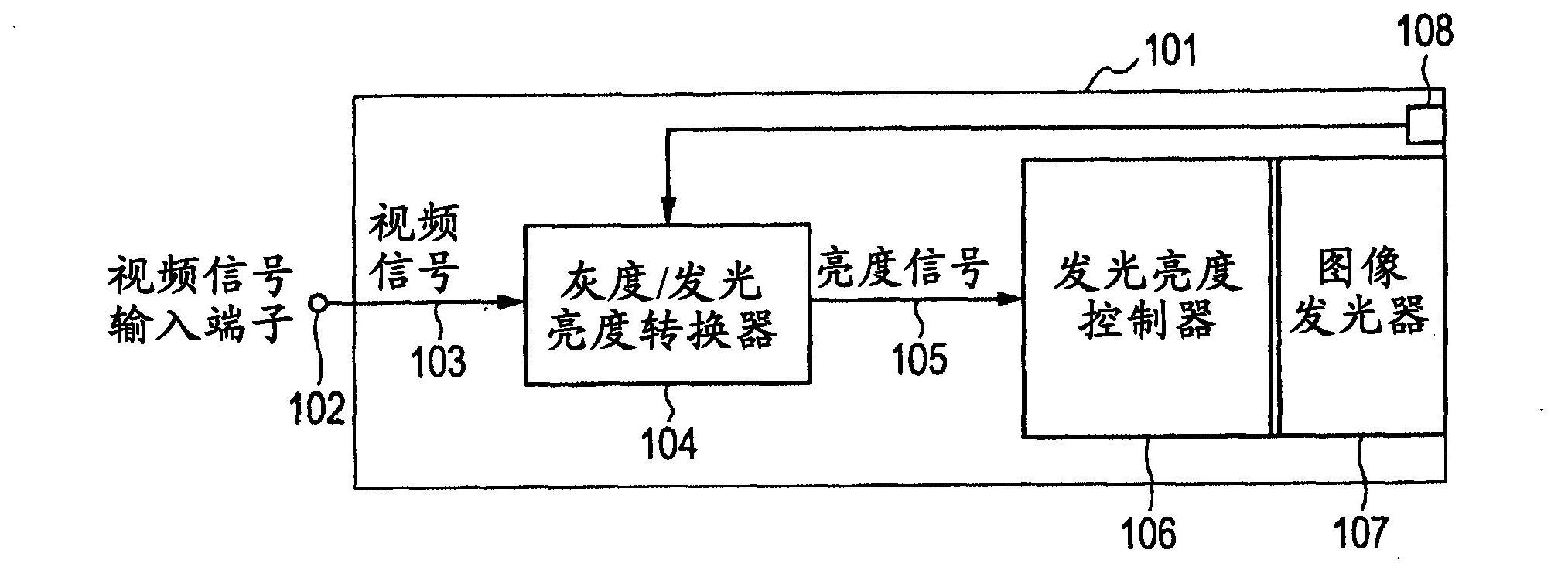
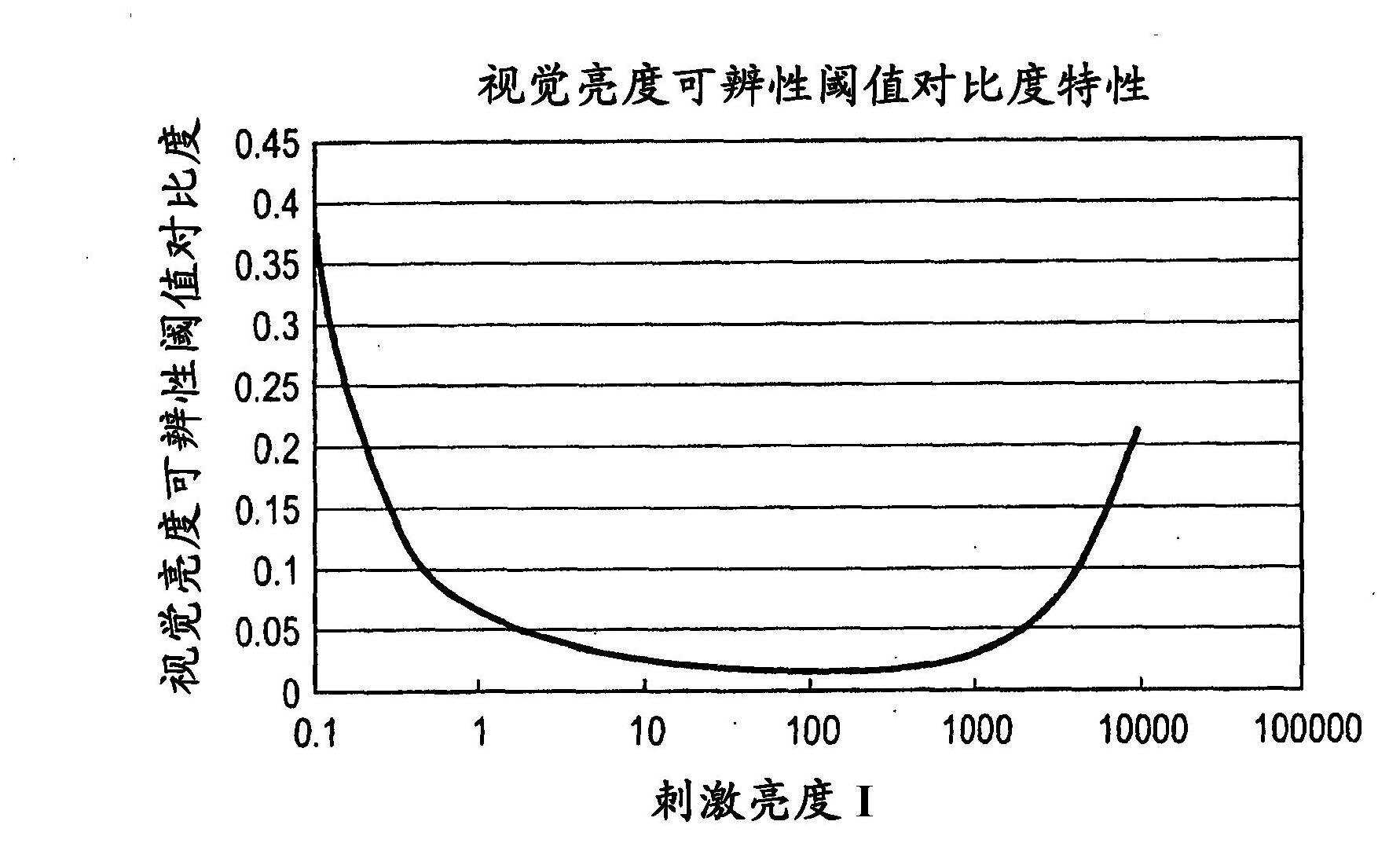
[0077] figure 1 is a diagram of the configuration of an exemplary video display device. figure 2 is a plot of luminance discriminability threshold contrast characteristics versus incident light luminance. image 3 is a graph of the light intensity characteristics of visual stimuli relative to the JND metric. Figure 4 is a plot of brightness discriminability threshold properties versus stimulus light brightness. Figure 5 is a graph of the emission luminance characteristics with respect to the input signal level. Image 6 It is a quadrant diagram of signal transition from video signal input to light emission.
[0078] Such as figure 1 As shown, in a video display device 101 , a video signal transmitted from a video source (not shown) is captured as a video signal 103 in the video display device 101 through a video signal input terminal 102 . The signal format of video signal 103 may vary depending on the type of video source. In this example, the signal is normalized ...
example 2
[0134] Figure 7 is a graph of brightness discriminability threshold contrast characteristics with respect to incident light brightness in Example 2. Figure 8 is a graph of the brightness characteristics of visual stimuli relative to the JND index in Example 2. Figure 9 is a graph of the emission luminance characteristics with respect to the input signal level in Example 2.
[0135] Example 2 is constructed and controlled in the same manner as Example 1, except that the characteristic of the grayscale-display brightness conversion LUT implemented in the grayscale / luminescence brightness converter 104 of the video display device 101 is different from that of Example 1 . Therefore, the characteristics of the gradation-display luminance conversion LUT different from Example 1 will be described below, and other redundant descriptions will be omitted.
[0136] Figure 7 is a graph representing the luminance discriminability threshold contrast characteristic with respect to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com