Empirical-mode-decomposition-based edge detecting method
An empirical mode decomposition and edge detection technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as uncertain values, unable to cover images, overbrightness, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
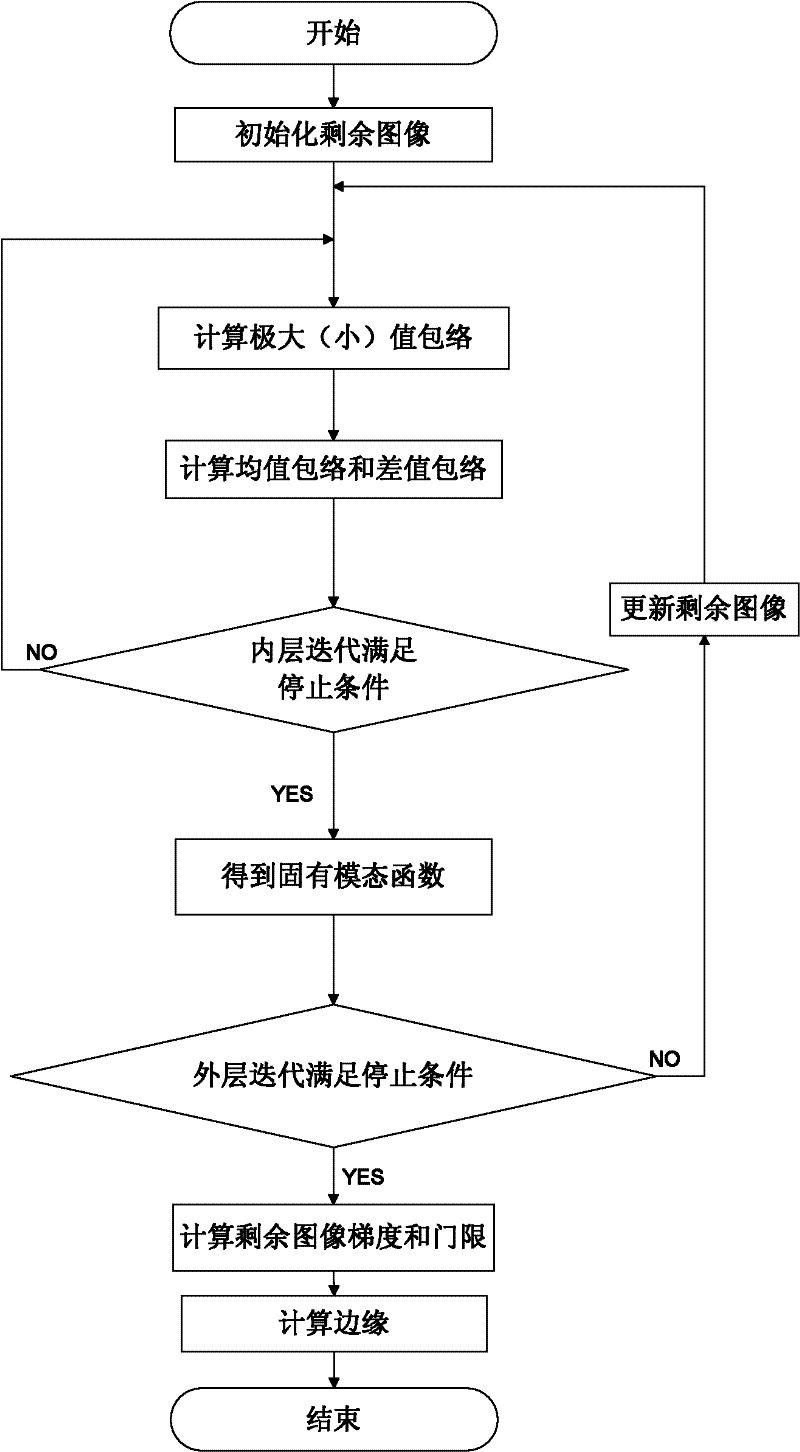
[0037] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of the present invention include as follows:
[0038] Step 1. Set the number of intrinsic mode functions n=0, and initialize the remaining image r n (x, y) is the original image f(x, y), and the remaining image refers to the image obtained by subtracting the sum of intrinsic mode functions from the original image in the empirical mode decomposition.
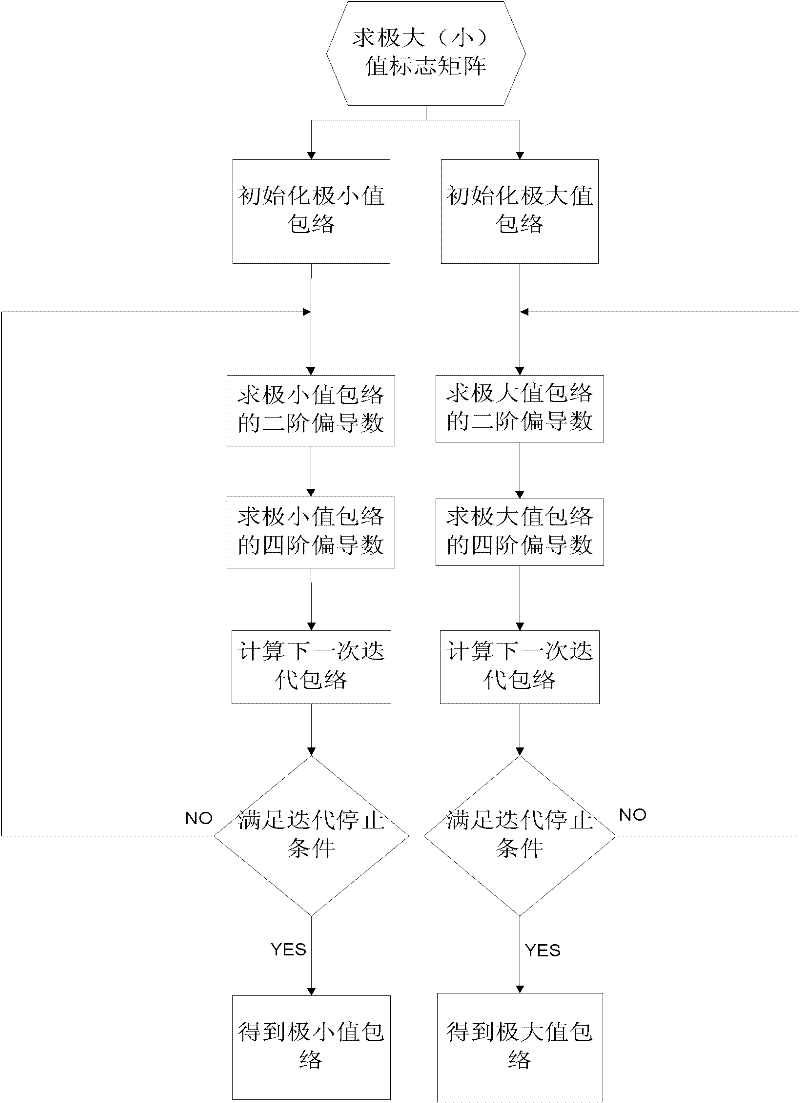
[0039] Step 2. Compute the remaining image r n Envelope of maximum value and minimum value of (x, y).
[0040] refer to figure 2 , the specific implementation of this step is as follows:
[0041] 2.1) Find the remaining image r n (x, y)'s maximum value flag matrix and minimum value flag matrix.
[0042] (2.1.1) Initialization and residual image r n (x, y) the same size maximum value flag matrix IMax (x, y) and minimum value flag matrix IMin (x, y), matrix values are all set to 0, x=1,... h, y= 1,...w, x and y are the abscissa and ordinate of the image, h and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com