Method for remotely sensing and quantitatively monitoring steppe vegetation coverage space-time dynamic change
A technology of vegetation coverage and spatiotemporal dynamics, applied in the direction of complex mathematical operations, can solve problems such as the lack of monitoring of grassland vegetation coverage spatiotemporal dynamic change indicators, the inability to comprehensively, deeply and quantitatively support the research on the dynamic change characteristics of grassland vegetation, and the lack of systematicness, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0051] In order to make the purpose, content, and advantages of the present invention clearer, the specific implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
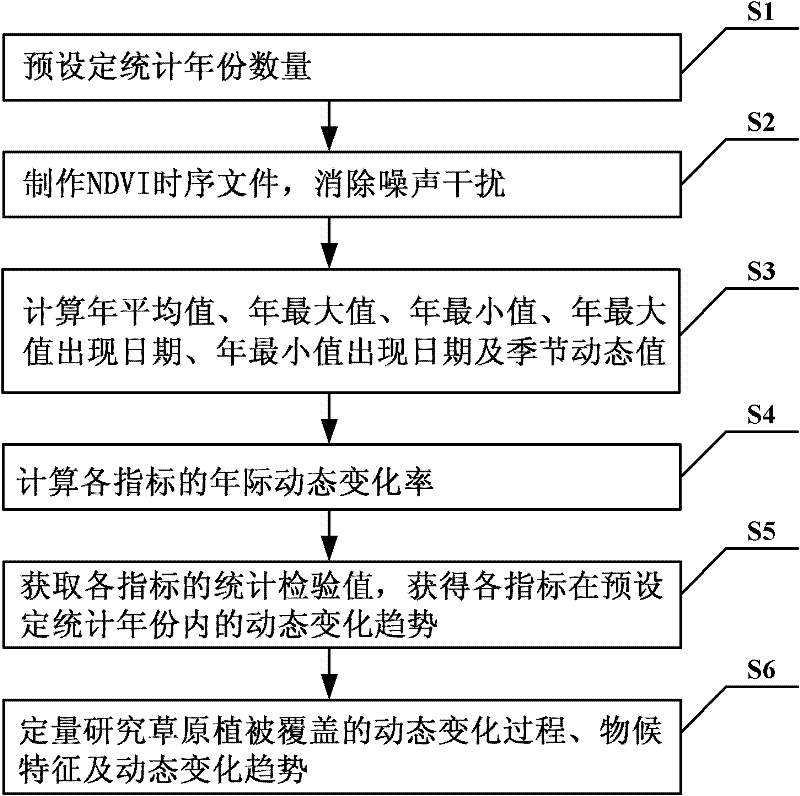
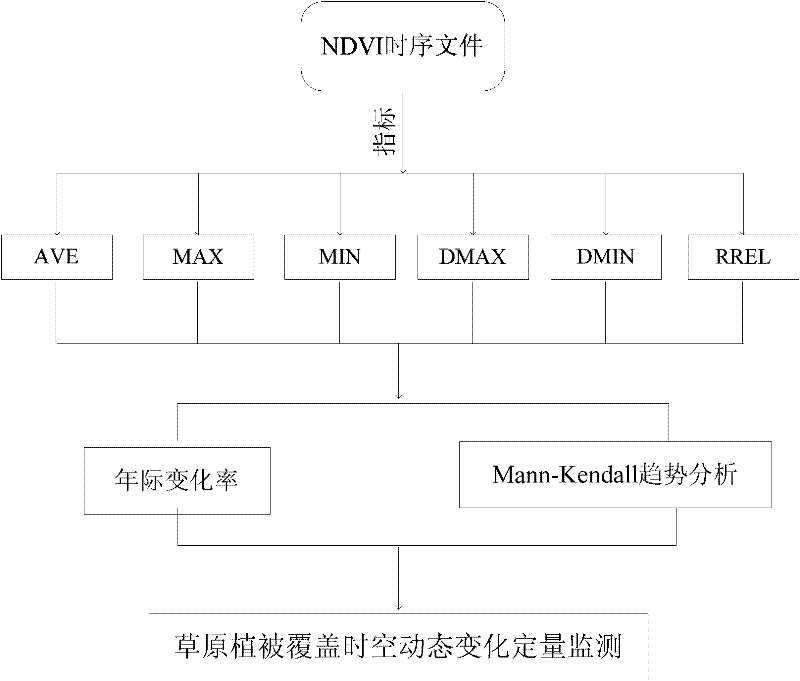
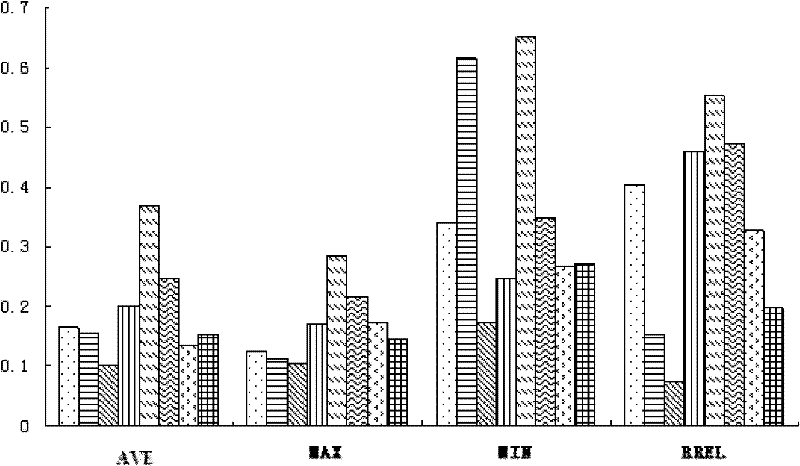
[0052] The remote sensing quantitative monitoring method of the spatial-temporal dynamic change of the grassland vegetation cover involved in the specific embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 1 and figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0053] Step S1: Preset the starting year of the statistical year as the time range for quantitatively monitoring the temporal and spatial dynamic changes of grassland vegetation coverage;
[0054] Step S2: Use the SPOT_VGT vegetation NDVI data or other NVDI data of grassland vegetation coverage to make annual NDVI time series files in the preset statistical year, and then eliminate the noise interference of NDVI time series files; specifically: use remote sensin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com