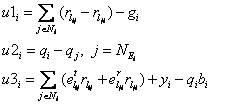Wireless sensor network distributed routing method on basis of Lagrange-Newton method
A wireless sensor, distributed technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, data exchange network and other directions, can solve problems such as slow convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
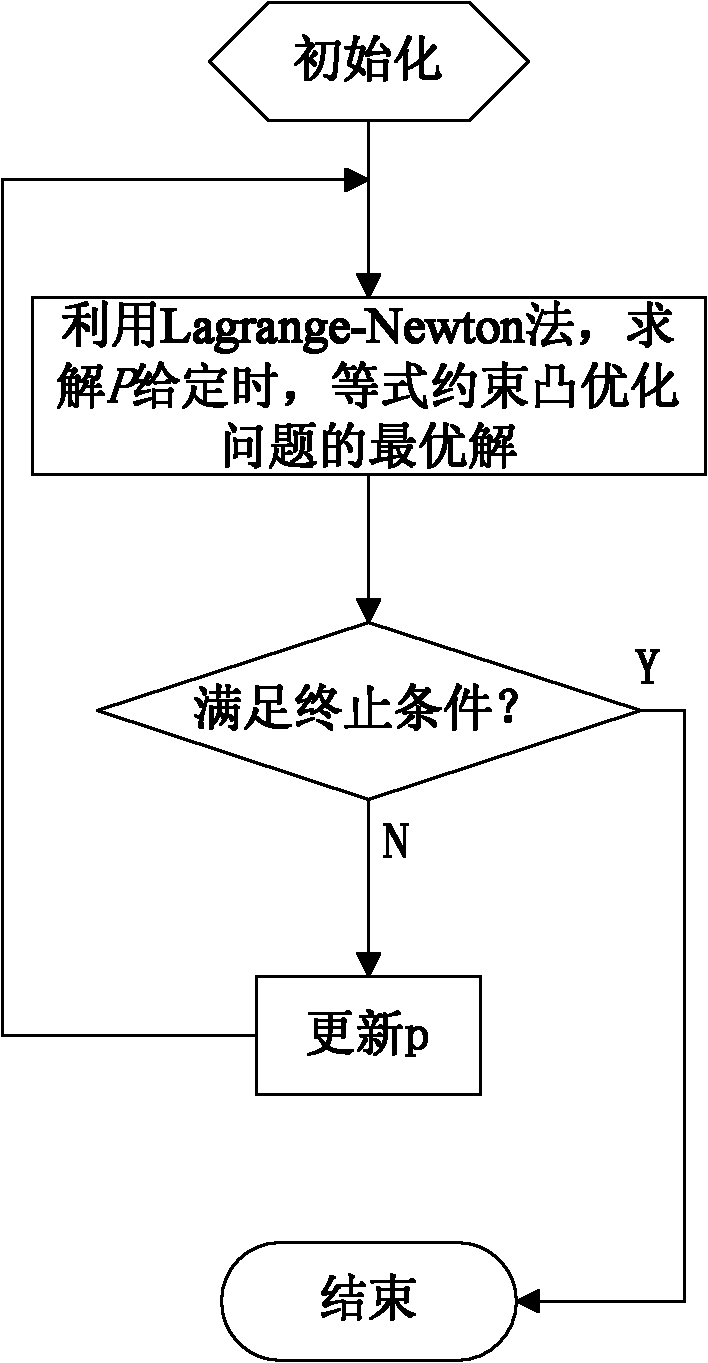
[0085] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0086] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 A distributed routing method for wireless sensor networks based on the Lagrange-Newton method. Typical sensor node energy consumption is mainly generated by wireless data transmission and reception. Therefore, only energy consumption related to wireless communication is considered in the present invention, that is, nodes send / receive k-bit information The energy to be consumed is:
[0087] E. Tx (k,d)=E Tx-elec (k)+E Tx-amp (k, d) = kE elec +kε fs d α (1)
[0088] E. Rx (k)=E Rx-elec (k) = kE elec (2)
[0089] In the formula, d is the distance between the sending node and the receiving node, and α∈[2,4] is the path loss coefficient. E. elec Indicates the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com