Multi-tag identification method of RFID reader
An identification method and reader technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification, can solve the problems of incorrectly identifying tags and wasting time, and achieve the effects of high recognition rate, improved reading speed, and increased number of reads
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
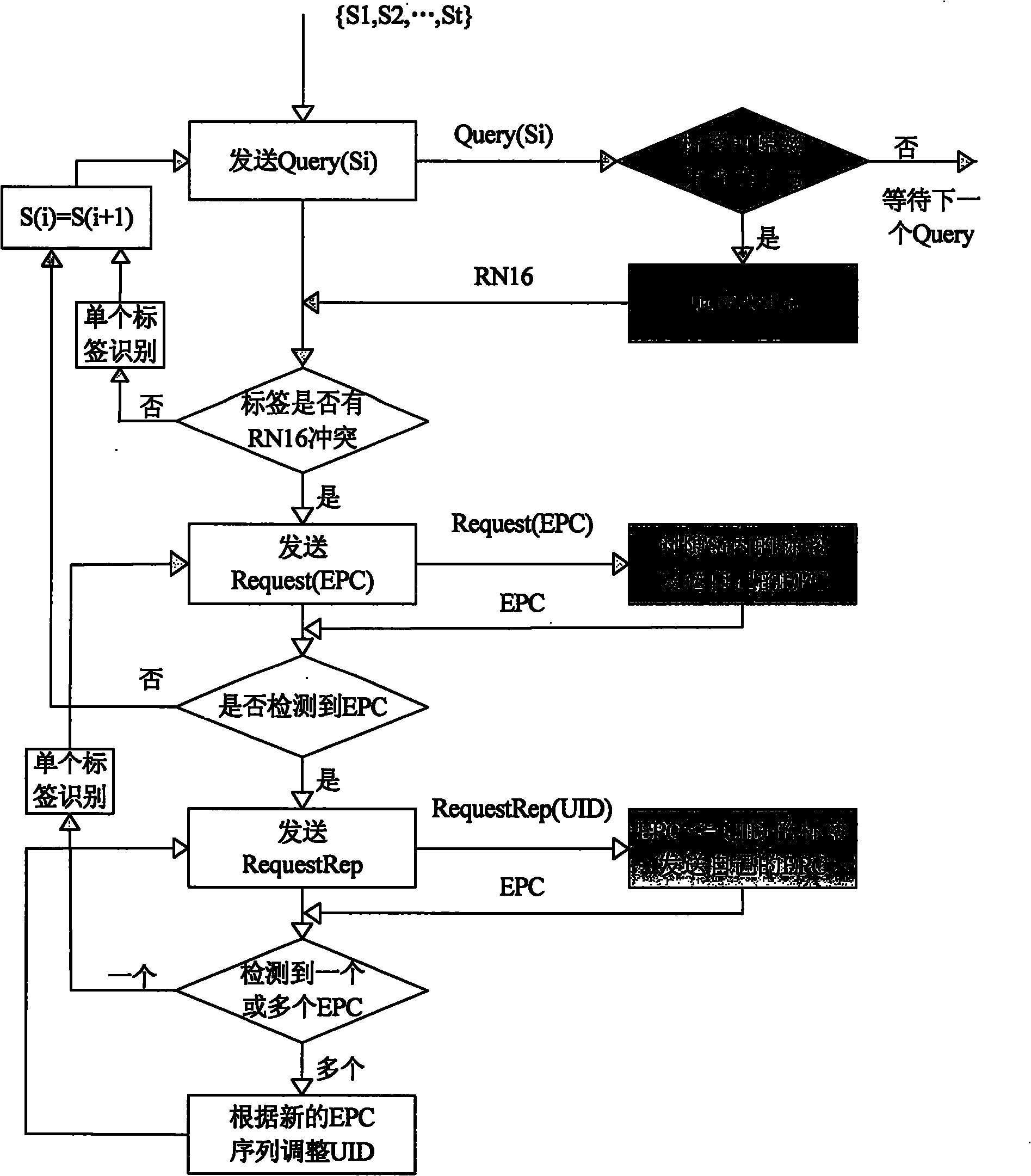
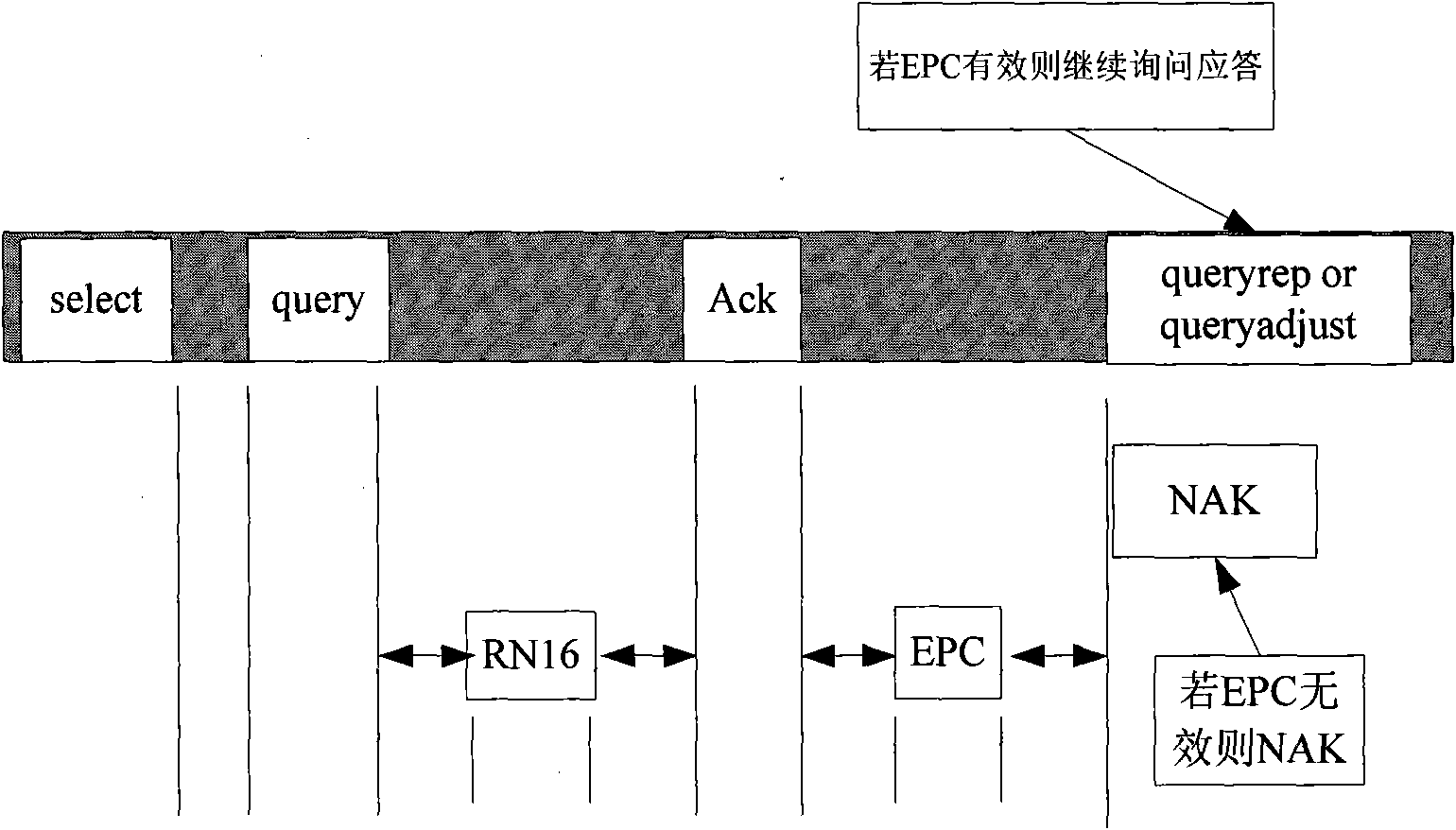
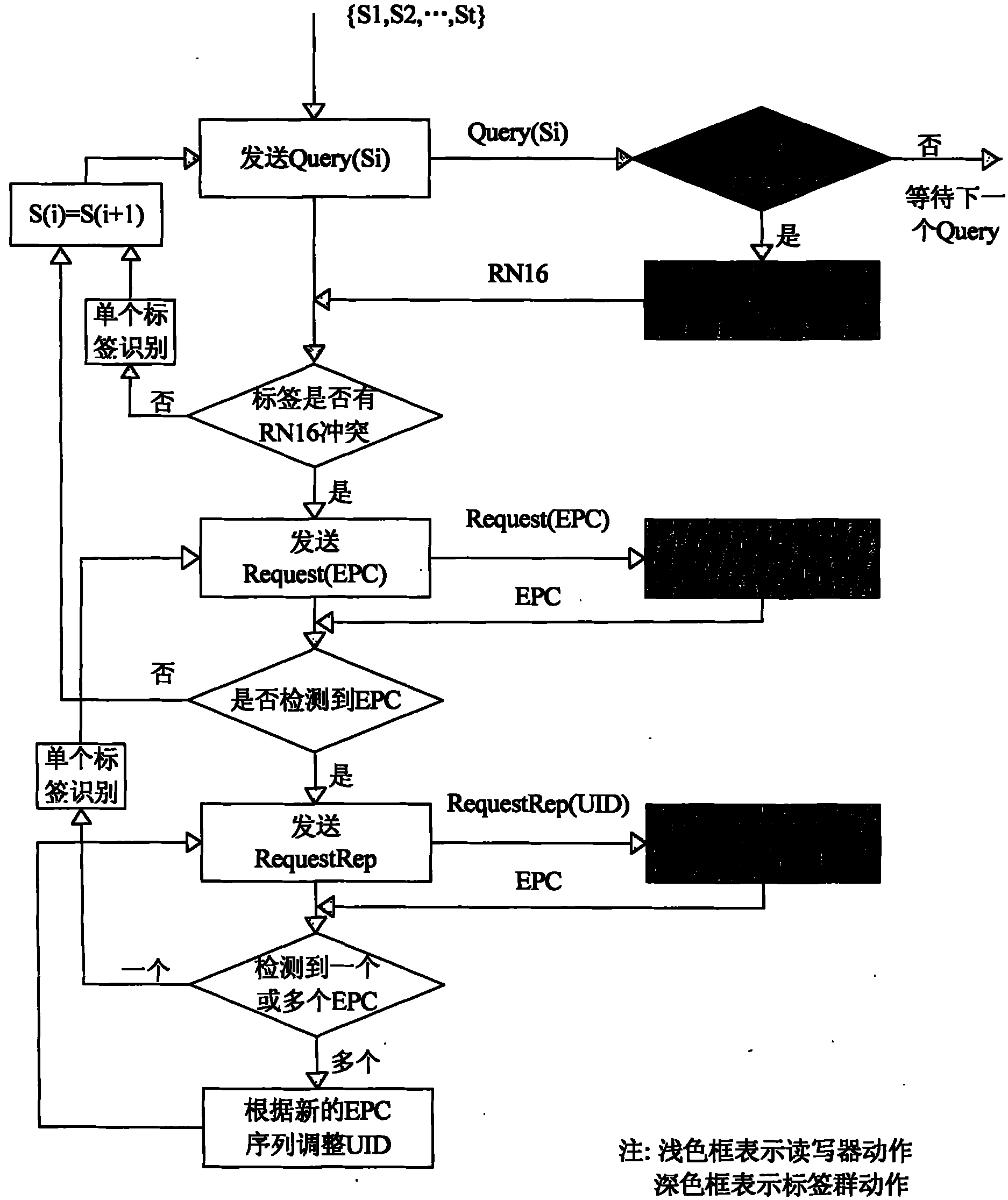
[0022] figure 2 It is a flowchart of the main steps of the identification method of the present invention. Block diagrams with a white background represent the actions of the reader; blocks with a gray background represent the actions of the tag. The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment:
[0023] A multi-tag identification method of an RFID reader is applied in an RFID system including an RFID reader and a plurality of tags. In this embodiment, we assume that there are 5 tags in the radio frequency area (RF Field) of the reader, and Set Q=7, then the time slot number is 0~(2 7 -1), that is, 0 to 127, including the following steps:
[0024] Step 1: The reader sends the detection command Detect(7) to the tag group. After the tag receives the detection command, it randomly starts from time slot 0 to time slot (2) Q In the time slot sequence of -1) (the value of Q is 7 in this embodiment), select on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com