Method and device for determining scheduling strategy
A scheduling strategy and determination method technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of judging, unable to complete UE status, etc., and achieve the effect of balancing differences and reducing interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
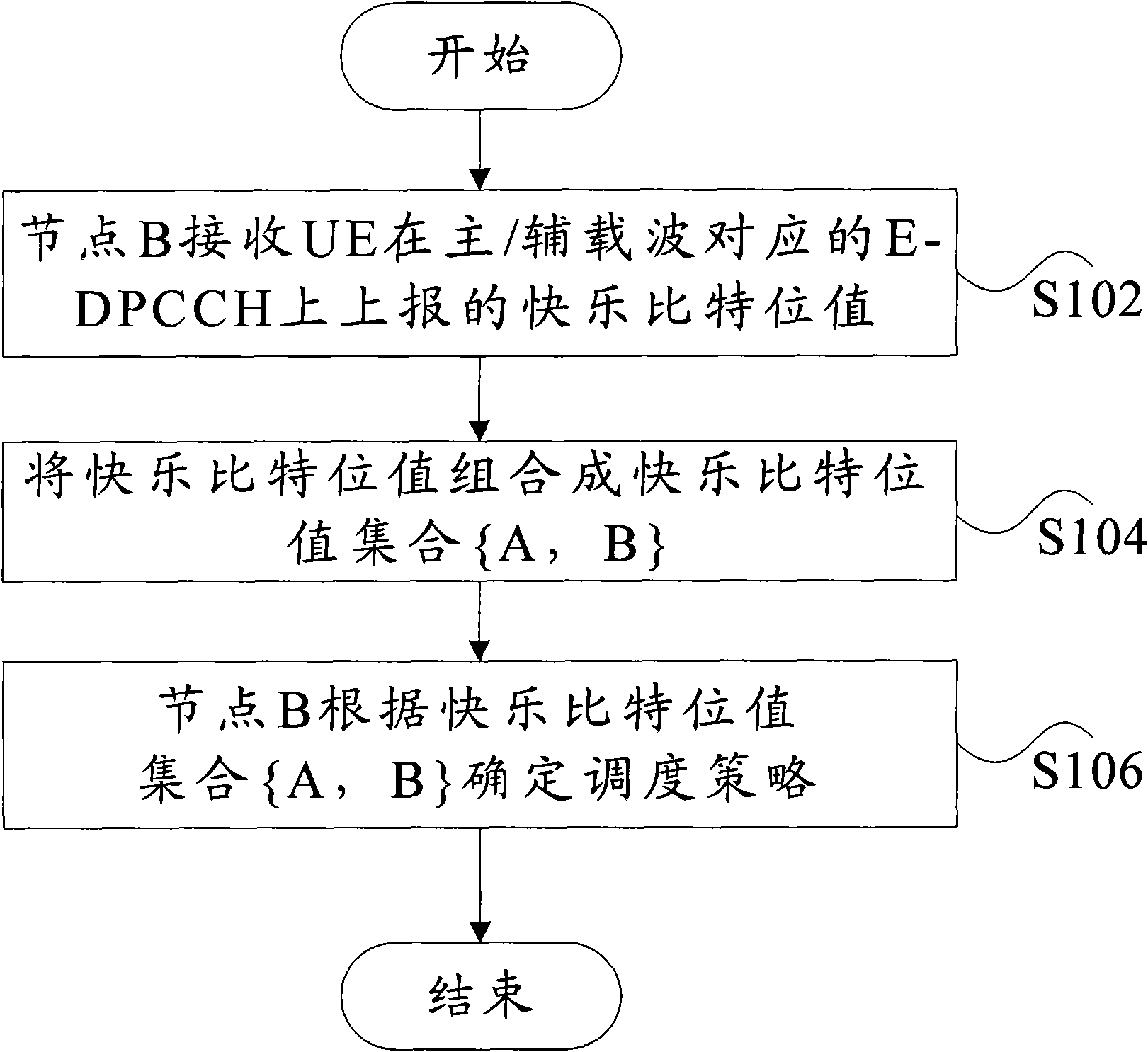
[0051] This embodiment provides a Node B scheduling decision-making solution with simple logical meaning and convenient implementation, including the following steps 110 to 120:
[0052] Step 110: For each E-DCH data transmission, Node B will receive from the same UE, extract Happy bits from the E-DPCCH corresponding to the primary / secondary carrier, and combine the Happy bit value set {HB1, HB2}.
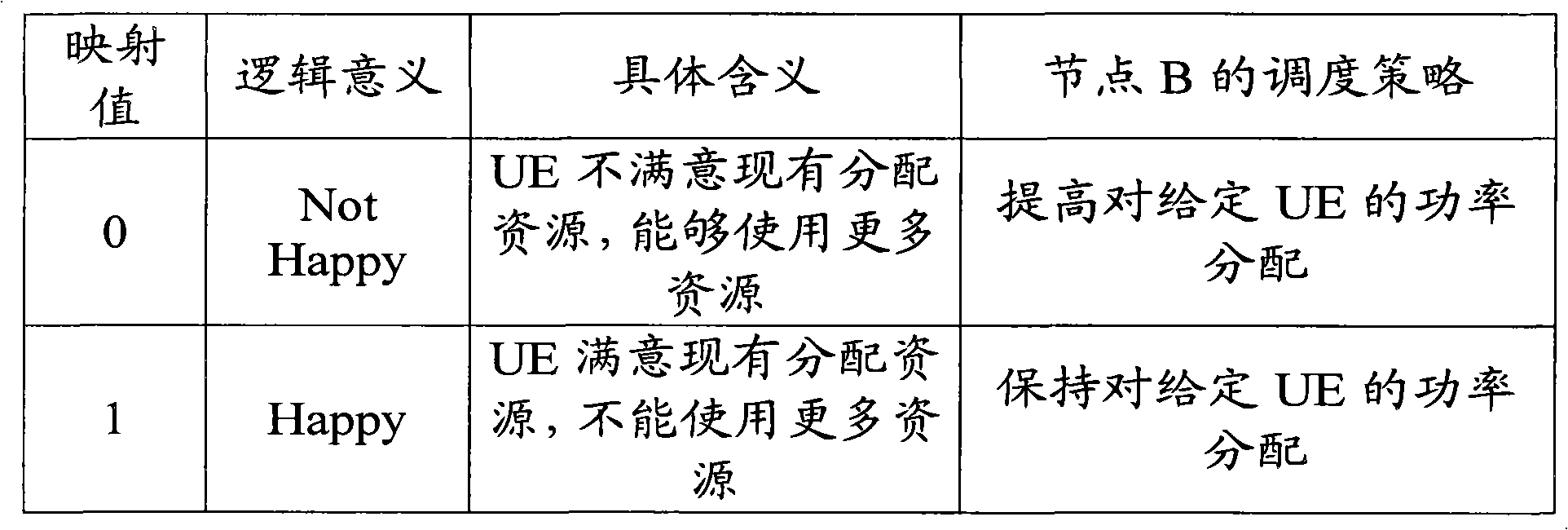
[0053] Step 120: If the received happy bit value set is {0, 0}, it is considered that the power of both the primary and secondary carriers is increased; if the received happy bit value set is {0, 1}, it is considered that the allocated power is not increased ; If the received happy bit value set is {1, 0}, it is considered that the allocated power will not be increased; if the received happy bit value set is {1, 1}, it is considered that neither the main carrier nor the auxiliary carrier needs to increase the power (Specifically as shown in Table 1 below).
[0054] Table 1 Schedul...
Embodiment 2
[0058] This embodiment provides a Node B scheduling decision-making solution with simple logical meaning and convenient implementation, including the following steps 210 to 220:
[0059] Step 210: For each E-DCH data transmission, Node B will receive data from the same UE, extract Happy bits from the E-DPCCH corresponding to the primary / secondary carrier, and combine the Happy bit value set {HB1, HB2}.
[0060] Step 220: If the set of happy bit values received is {0, 0}, it is considered that the power of both the primary and secondary carriers is increased; if the set of happy bit values received is {0, 1}, the allocated power is increased, and the main carrier / Secondary carrier equal priority; if the received Happy bit value set is {1, 0}, then increase the allocated power, the main / secondary carrier equal priority; if the received Happy bit value set is {1, 1}, then It is considered that neither the main carrier nor the auxiliary carrier needs to increase power (specif...
Embodiment 3
[0064] This embodiment provides a Node B scheduling decision-making scheme that comprehensively considers the power difference between primary and secondary carriers, including the following steps 310 to 320:
[0065] Step 310: For each E-DCH data transmission, the Node B will receive the happy bits from the E-DPCCH corresponding to the primary / secondary carrier respectively from the same UE, and combine the happy bit value set {HB1, HB2}.
[0066] Step 320: If the received happy bit value set is {0, 0}, it is considered that the power of both the primary and secondary carriers is increased; if the received happy bit value set is {0, 1}, it is considered that the allocated power can be increased , the current power of the auxiliary carrier is low; if the received happy bit value set is {1, 0}, it is considered that the allocated power can be increased, and the current power of the main carrier is low; if the received happy bit value set is {1, 0}, 1}, it is considered that nei...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com