DNA microarray-based identification and localization of balanced translocation breakpoints
A DNA sequence and microarray technology, applied in the field of identification and location of balanced translocation breakpoints based on DNA microarrays, can solve the problems of routine analysis of inappropriate clinical samples, time-consuming and labor-intensive, limited throughput, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0122] 4. Preparation of Probes for Detecting Balanced Translocations
[0123] For detection of translocation, any method can be used as long as the method can linearly amplify DNA containing a potential translocation site. An example of a linear amplification method that can be used to practice the present invention includes PCR amplification using a single primer. See Liu, C.L., S.L. Schreiber et al., BMC Genomics, 4: Art. No. 19, 2003 / 5 / 9.
[0124] A typical set of conditions for linear amplification includes a 50 μl volume reaction containing 1 μg of genomic DNA, 200 mM dNTPs and 150 nM linear amplification primers. Amplification can be done using the PCR enzyme system (Advantage 2PCR Enzyme System) of Cloning Technology Co., Ltd. (Clontech) as follows: Denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes, followed by 12 cycles (95°C / 15 seconds, 60°C / 15 seconds and 68°C / 6 minutes).
[0125] Probes can be labeled during linear amplification or after amplification is complete. In the spec...
Embodiment 1
[0148] Example 1: J H Identification of relevant translocation breakpoints
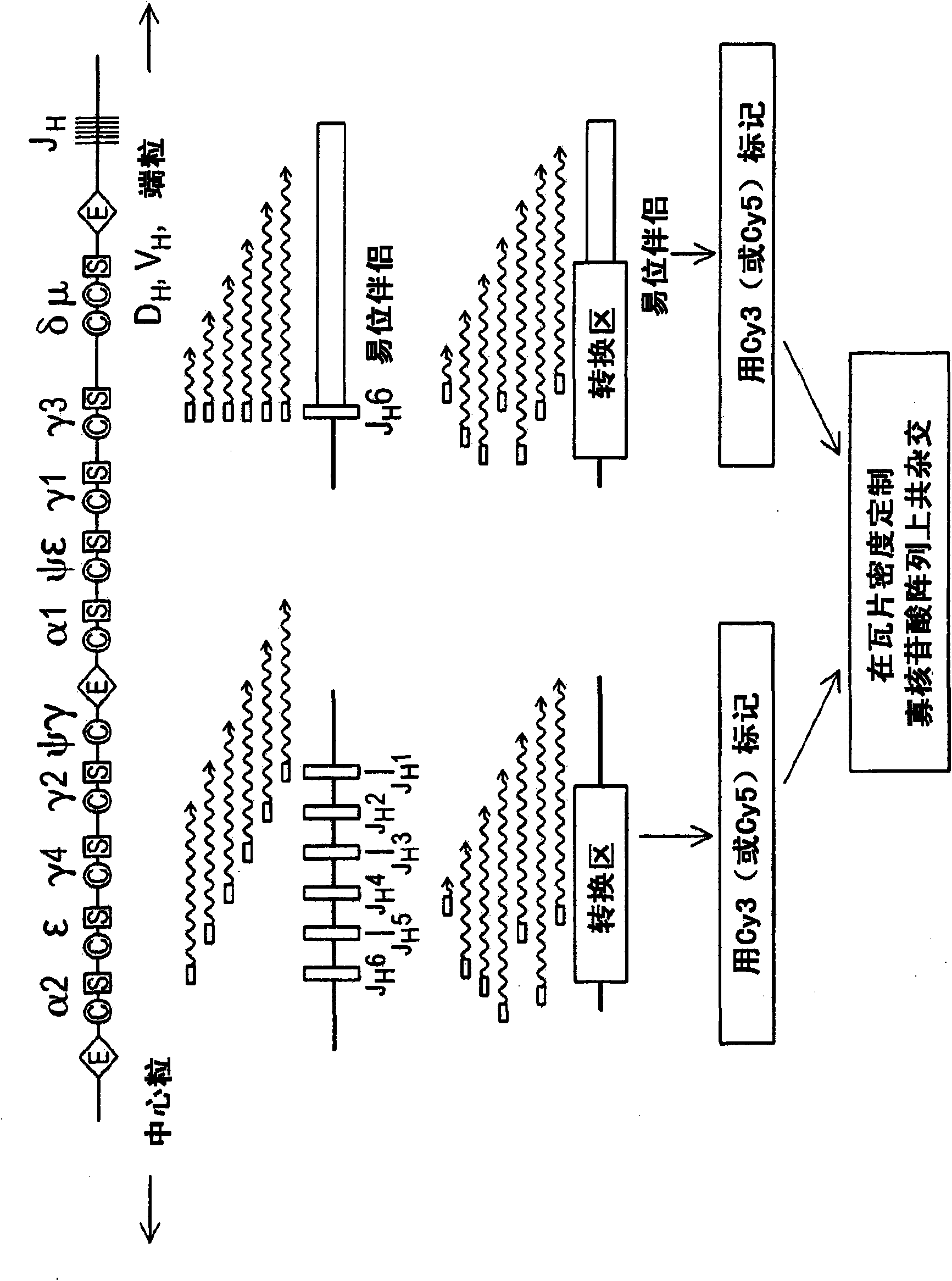
[0149] Array CGH is designed to be useful for detecting genomic imbalances but not balanced genomic rearrangements. We therefore explored a way for synthetic genome imbalances to represent balanced translocation sites on standard CGH arrays. Using balanced immunoglobulin translocations in lymphoma cell lines as a model, we developed an enzyme-catalyzed linear amplification reaction that allows balanced translocations to also be detected by array-based CGH. Genomic DNA is modified during the amplification step, followed by fluorescein labeling and microarray hybridization. Such as figure 1 Shown, J H - Associated translocation breakpoints available using J H Consensus primers enzymatically amplify (van Dongen, 2003), resulting in linear amplification across breakpoint junctions into translocation partner loci. Able to amplify J using a single primer H - Associated translocations, whether or not ...
Embodiment 2
[0152] Example 2: Identification of IgH Switching (SH)-Associated Translocation Breakpoints
[0153] Linear amplification primers were then designed to identify H ) region translocation. Person S H The region contains multiple tandem repeats of the characteristic repeat unit: the S μ , S α and S ε In the E region, the repeating unit is a degenerated pentameric sequence G(A / G)GCT, in which the S γ The length of the region is 80-90, and the structure is more complex (Max, 1982; Mills, 1990; Mills, 1995). S H The relevant translocation breakpoints are respectively within these repeat regions. To facilitate the detection of these scattered breakpoints, linear amplification primers were designed to recognize these repeat units and μ / S α / S ε District (S 5 Primer) or S γ Repeat region (S γ primers) to initiate synthesis at multiple positions. Use J H S at 5 Primer-performed tCGH was used to identify S in the Burkitt lymphoma cell line Raji μ - MYC translocation (Dy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com