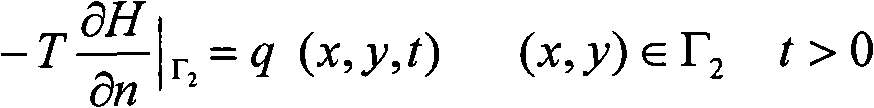Method for judging piping seepage damage of foundation pit containing confined water of soft soil layer
A foundation pit surge and pressurized water technology, applied in excavation, foundation structure engineering, foundation structure test, etc., can solve the problem of soil without bending resistance, quicksand, quicksoil or similar "boiling" water spray Sand, unreasonable and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
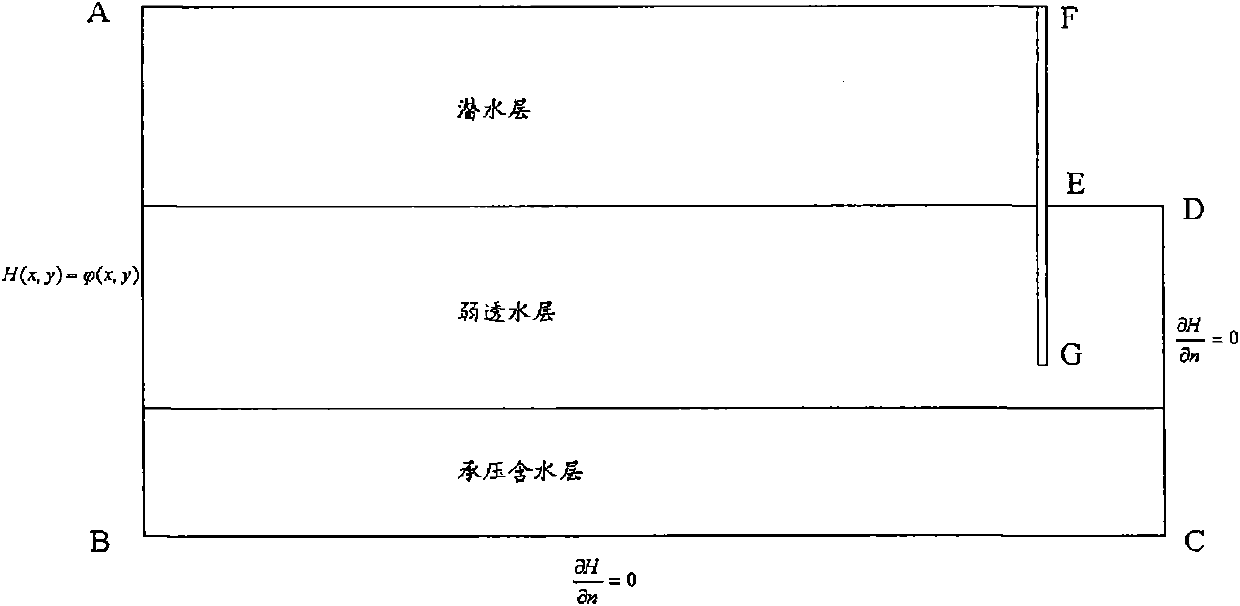
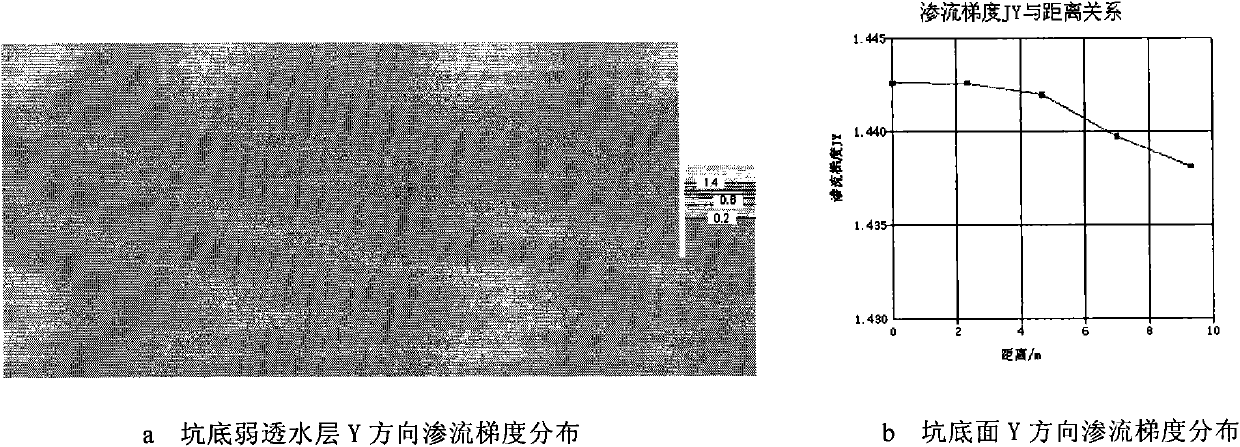
[0029] like figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, a method for judging inrush seepage damage of foundation pits containing confined water in soft soil strata includes the following steps:
[0030] 1) Analyze the force status of the unit body on the seepage surface at the bottom of the foundation pit, and obtain the seepage force γ on the unit body w J, buoyant gravity γ′V, friction between soil particles and the cohesion C of the unit unit body; where, γ w and J are the gravity of the water and the slope of seepage at the bottom of the pit, respectively; γ' is the buoyant bulk density; is the internal friction angle of the soil, and ξ is the lateral pressure coefficient;
[0031] 2) According to the penetration damage equation Obtain the critical seepage gradient of foundation pit inrush damage
[0032] 3) Establish a two-dimensional seepage finite element calculation model of the foundation pit according to the symmetry of the foundation pit structure, support structure f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com