Method for testing putrefaction capacity of putrefactive bacteria of fish
A determination method and technology for spoilage bacteria, which can be used in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve problems such as weak spoilage ability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
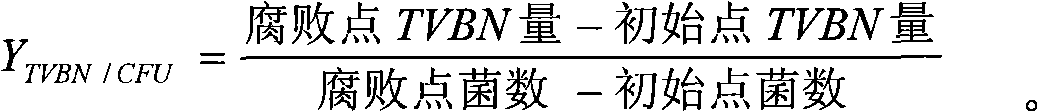
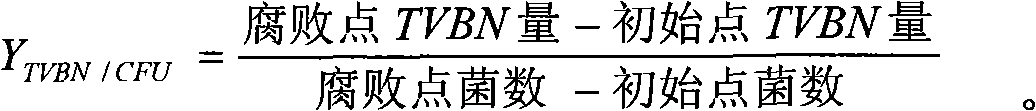
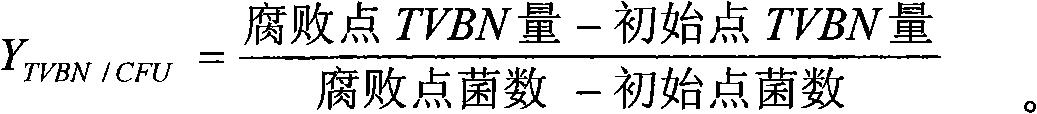
[0007] The determination of the spoilage ability of fish spoilage bacteria is carried out according to the following steps:
[0008] 1. Preparation of pure bacterial liquid of spoilage bacteria
[0009] Select the spoilage bacteria strain to be determined, streak on the nutrient agar medium, and culture at 25°C for 24-48h. Take a ring of bacterial lawn and inoculate it in 300mL nutrient broth (in a 500mL conical flask), and culture it aerobically at 25°C for 12-18h, so that the concentration of the bacterial solution reaches 10 8 About cfu / g, centrifuge the bacterial solution, discard the supernatant, and dilute the bacterial solution with 0.1% peptone saline until the number of spoilage bacteria is 10 6 The pure bacterial liquid of about cfu / g is used for inoculation.
[0010] 2. Preparation of Sterile Fish Blocks
[0011] Select fish that are suitable for the growth of spoilage bacteria to be determined, and choose fresh fish that are killed immediately or stored in ice f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com