Self-adaptive gridding method and self-adaptive gridding system of geometric curved surfaces of three-dimensional plant organs
A plant organ and self-adaptive technology, applied in the field of 3D modeling, can solve the problems of low calculation efficiency, lack of pertinence, and large memory requirements of the algorithm, and achieve strong universality, reduce the number of facets, and wide application wide effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0054] The specific implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
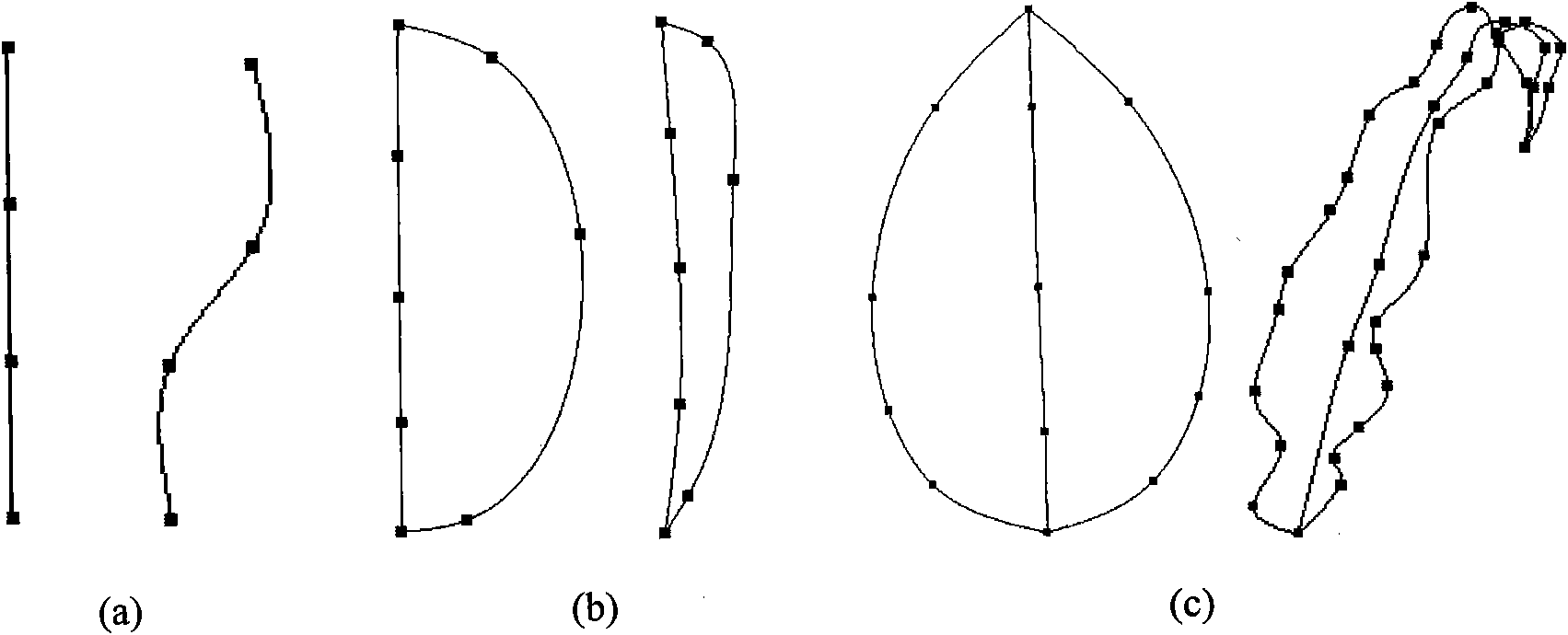
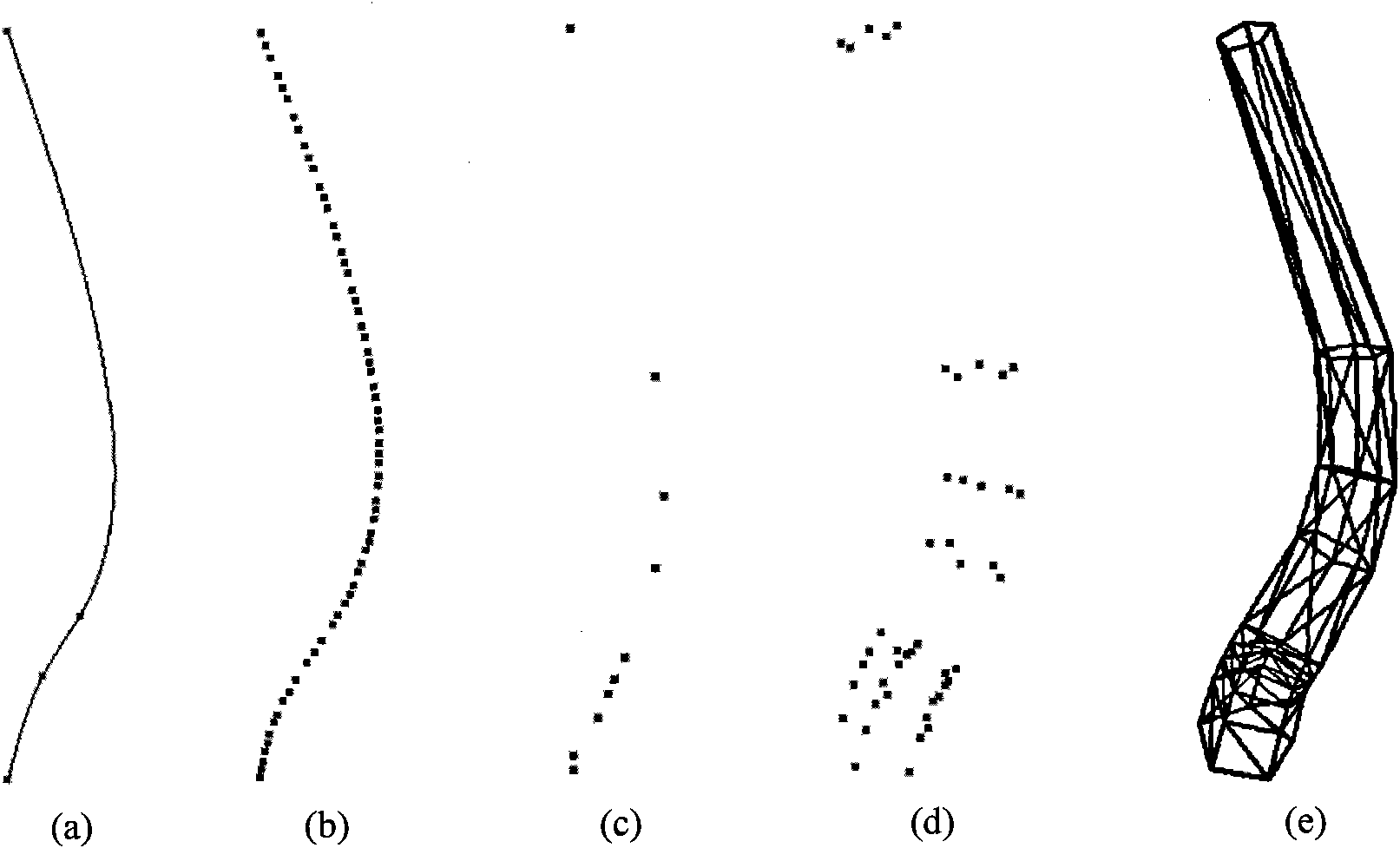
[0055] exist figure 2 and image 3 middle, figure 2 (a) is the shaft skeleton and its deformation, (b) is the half profile-shaft skeleton and its deformation, (c) is the full profile-shaft skeleton and its deformation; image 3 (a) is the skeleton model, (b) is the pre-segmentation point, (c) is the point retained after adaptive detection, (d) is the surface point set, and (e) is the grid model.
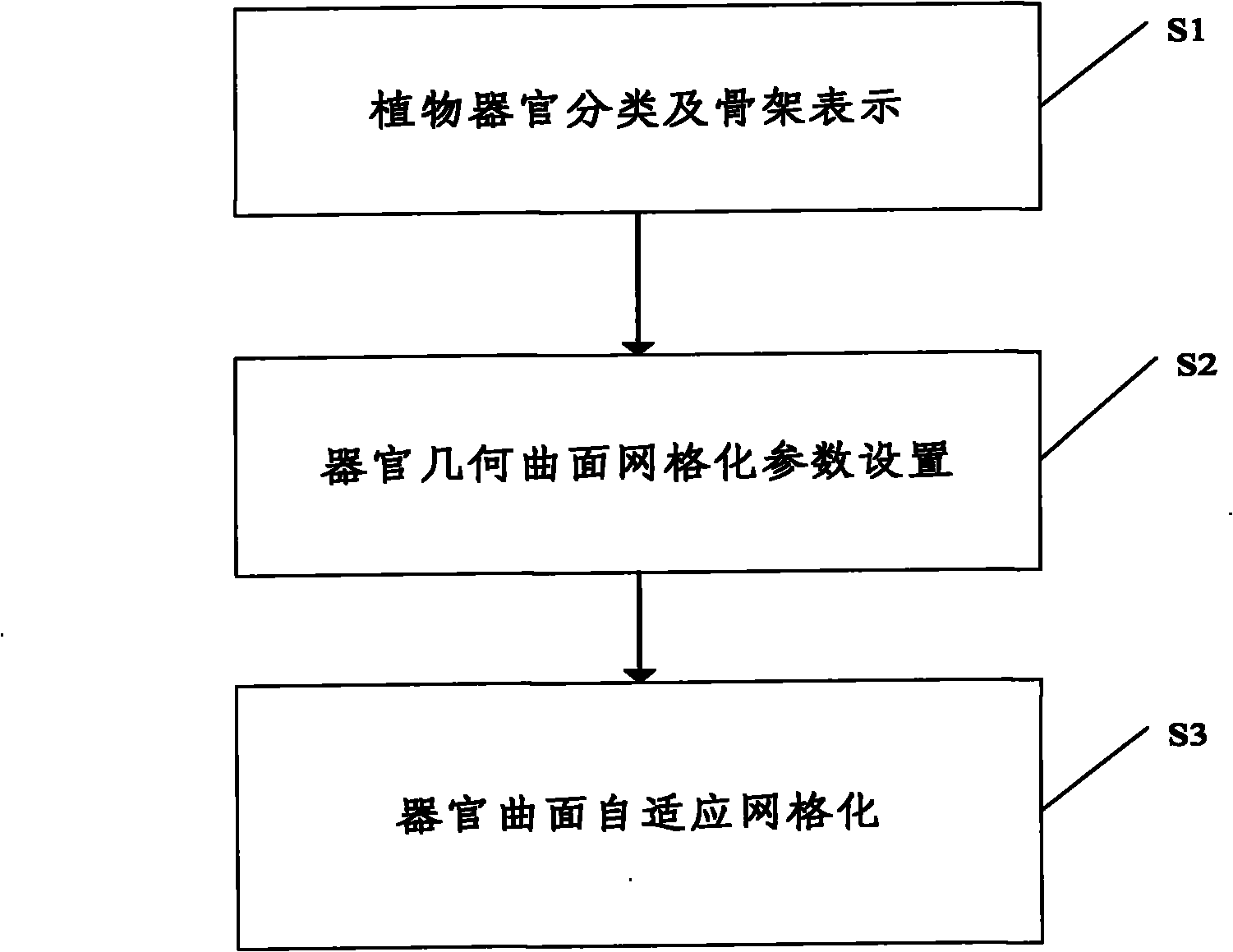
[0056] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 6 As shown, according to the three-dimensional plant organ geometric surface adaptive meshing method of this embodiment, it includes the following steps:
[0057] S1, classify plant organs according to their appearance characteristics, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com