Method for assist-breeding low erucic acid, low sulfuric glucoside cabbage type rape self-incompatible line with microspore cultivation and SSR making
A technology for culturing Brassica napus and microspores, which is applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, applications, angiosperms/flowering plants, etc., can solve the problems of long breeding cycle and low efficiency, save manpower and avoid self-crossing decline. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
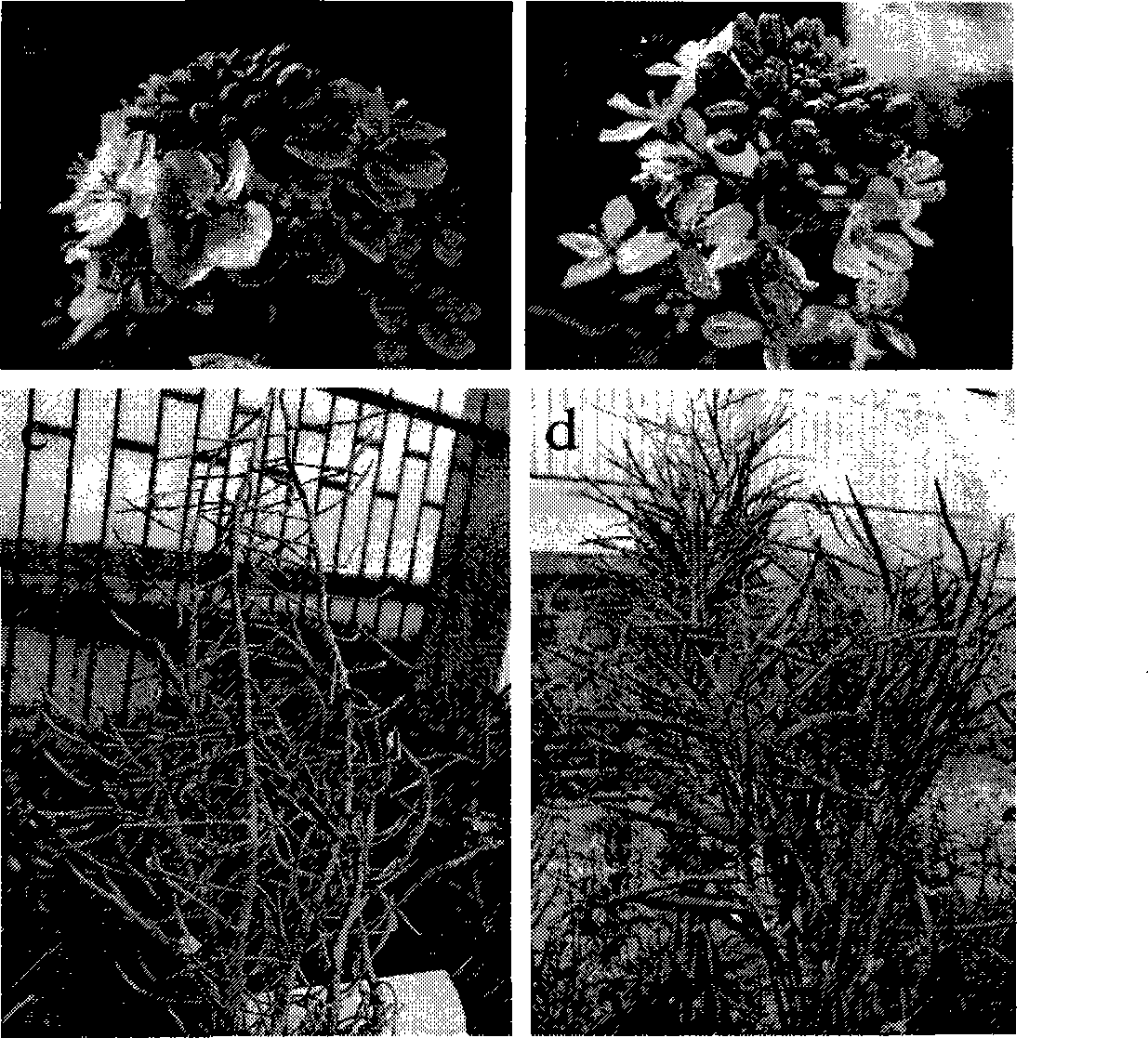
[0020] 1. Brassica napus hybrid F 1 the acquisition
[0021] Brassica napus self-incompatibility line S-1300 (Ma Chaozhi et al., Breeding of Brassica napus double-low self-incompatibility line, Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 1998, 17(3): 211-213) as the female This, and the male parent, Brassica napus variety 04P63wai-52 (this strain was preserved in the Chinese Type Culture Collection Center (English abbreviation: CCTCC) in Wuhan University, Wuhan City, Hubei Province on September 20, 2007, and the preservation number is F 1 seed.
[0022] 2. Brassica napus hybrid F 1 microspore culture
[0023] Will F 1 The seeds were planted under natural conditions (the field strain number was 05-9-1515), and F 1 plants. For the microspore culture method, refer to the method reported by Yu Fengqun et al. Specifically: when F 1 When the plant blooms the third flower, select three individual plants and number them 05-9-1515-1, 05-9-1515-2 and 05-9-1515-3 respectively. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com