Method and apparatus for camera calibration, and vehicle
A technology of a calibration device and a camera, which is applied in the field of vehicles and can solve the problems of time-consuming calibration of the environment and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example 》
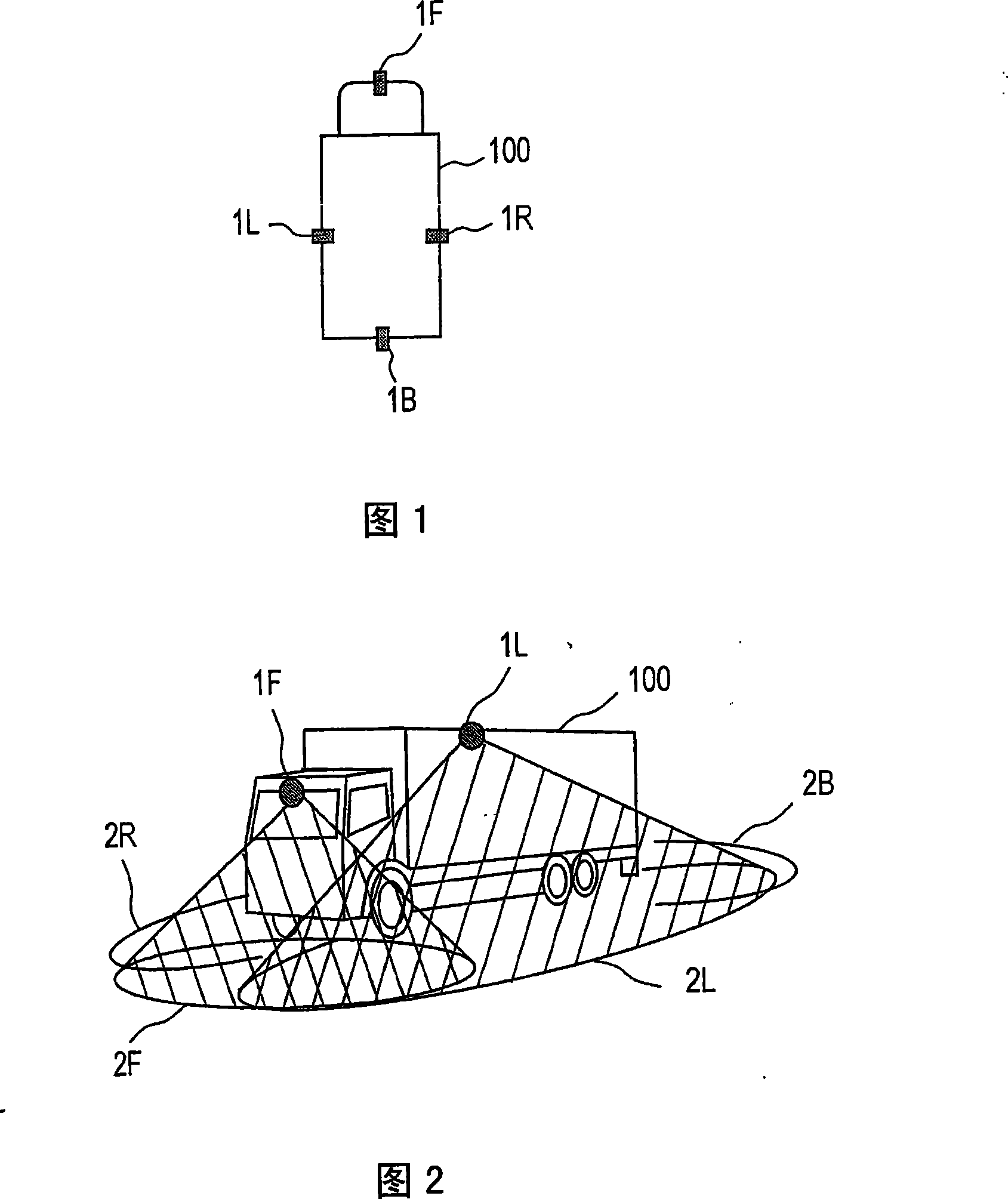
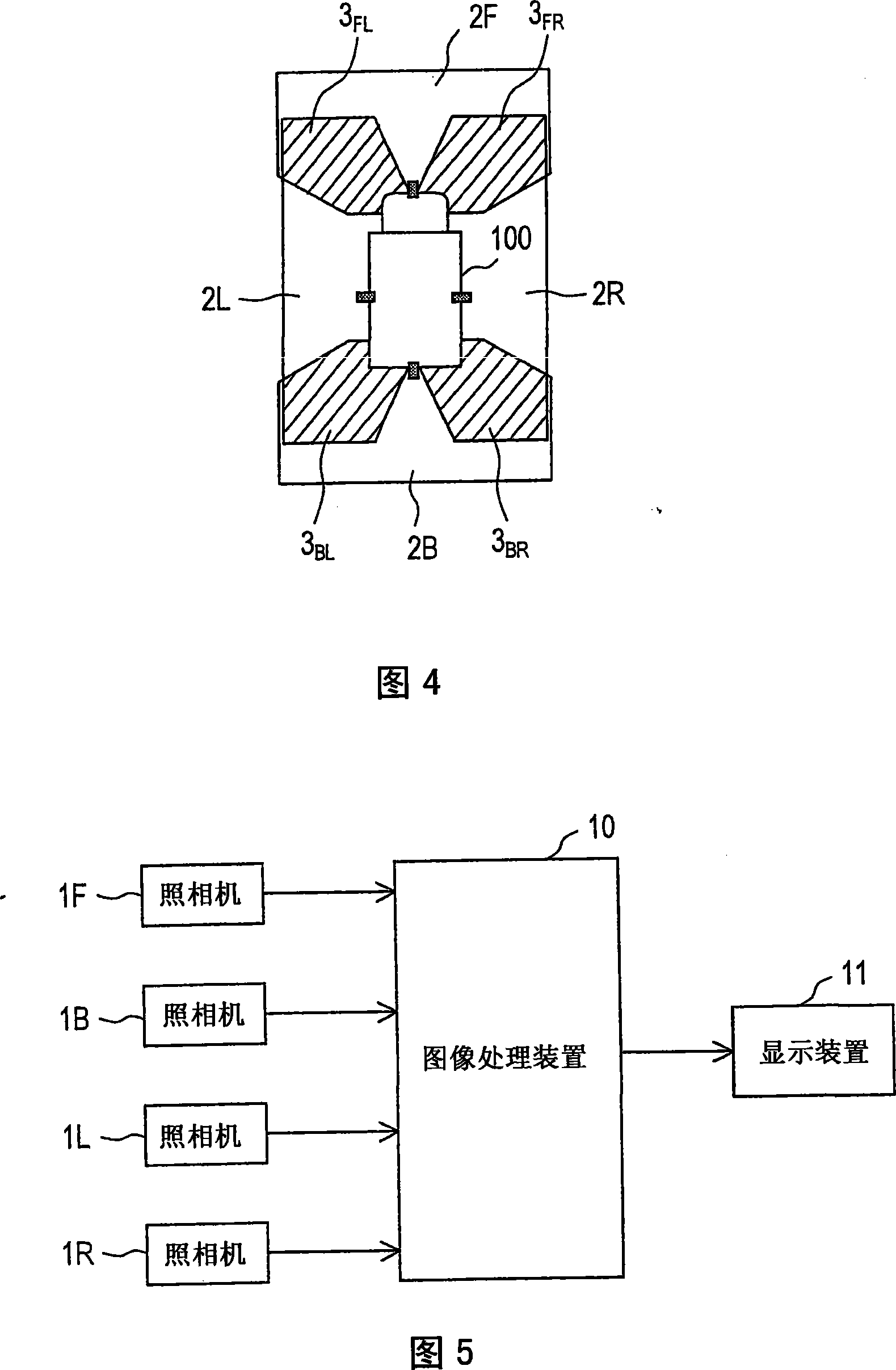
[0092] The first embodiment will be described. FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing the procedure of correction processing according to the first embodiment. The correction processing according to the first embodiment is constituted by each processing of steps S11 to S14, step S11 is executed by each camera and the image processing device 10, and steps S12 to S14 are executed by the image processing device 10.
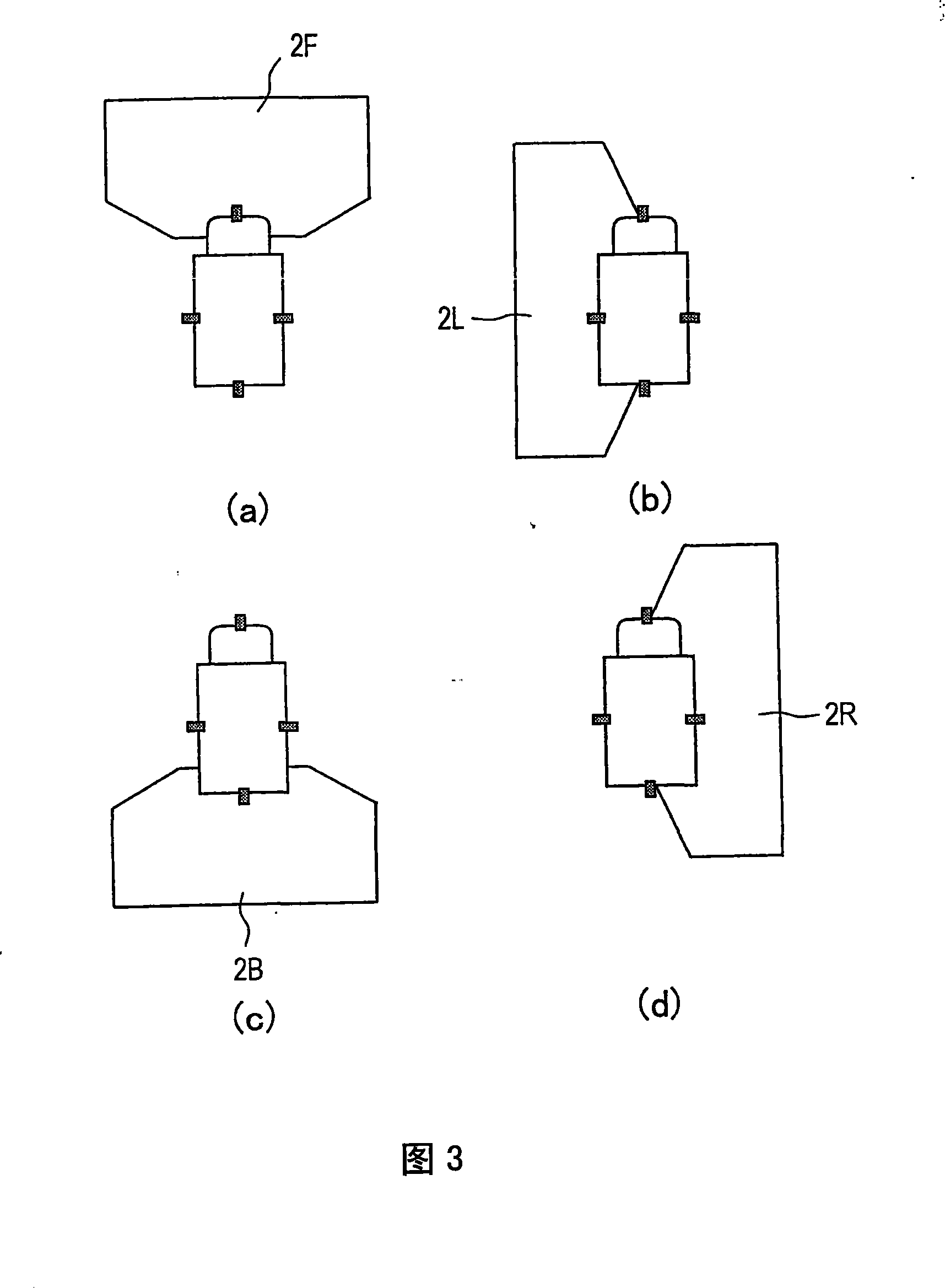
[0093] First, in step S11 , each camera is made to take an image while each calibration pattern is arranged in each common imaged area as described above (see FIG. 6 ), and the image processing device 10 obtains an imaged image from each camera. Hereinafter, the photographed image obtained here will be specifically referred to as a photographed image for calibration. FIG. 11 shows examples of the acquired calibration photographic images. In FIG. 11 , marks 301 , 302 , 303 , and 304 respectively indicate images captured by cameras 1F, 1R, 1L, and 1B for calibration.
[009...
no. 2 example 》
[0122] Next, a second embodiment will be described. FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing the procedure of correction processing according to the second embodiment. The correction processing according to the second embodiment is constituted by each processing of steps S11 to S13 and the processing of step S24. Each processing of steps S11 to S13 is the same as those in the first embodiment (FIG. 10).
[0123] In step S13, each bird's-eye view image obtained in step S12 should be aligned and synthesized through rigid body transformation in such a manner that the coordinates of the corresponding correction patterns are consistent, but as described in the first embodiment (refer to 15, etc.), due to error reasons, usually, the projection points of the feature points on the composite image (full-circumference bird's-eye view image) are not completely consistent between the two cameras. In the first embodiment, the inconsistency of the projection points is reduced by step S14, but in th...
no. 3 example 》
[0138] Next, as an illustration for the homography matrix H 1 ’~H 4 ’, the third embodiment will be described. The third embodiment corresponds to a modified example of the second embodiment. The flowchart showing the procedure of the correction processing according to the third embodiment is the same as the flowchart ( FIG. 16 ) according to the second embodiment, and the correction processing according to the third embodiment is composed of steps S11 to S13 and S24. However, in the third embodiment, the homography matrix H in step S24 1 ’~H 4 The optimization method of ' is different from the second embodiment. Therefore, below, this optimization method, which is a point different from the second embodiment, will be described.
[0139] In the present embodiments including the third example, the shape of the correction pattern is made a square. A square is invariant to rotation with one degree of freedom and parallel movement with two degrees of freedom. Therefore, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com